(Press-News.org) Curiosity helps us learn about a topic, and being in a curious state also helps the brain memorize unrelated information, according to researchers at the UC Davis Center for Neuroscience. Work published Oct. 2 in the journal Neuron provides insight into how piquing our curiosity changes our brains, and could help scientists find ways to enhance overall learning and memory in both healthy individuals and those with neurological conditions.
"Our findings potentially have far-reaching implications for the public because they reveal insights into how a form of intrinsic motivation — curiosity — affects memory. These findings suggest ways to enhance learning in the classroom and other settings," says first author Matthias Gruber, a postdoctoral researcher at the center.
Participants in the study first rated their curiosity about the answers to a series of trivia questions. Later, they had their brains scanned via functional magnetic resonance imaging while they learned the answers to these questions. First, they were presented with a selected trivia question and while they waited for the answer to pop up on the screen, they were shown a picture of a neutral, unrelated face.
Afterwards, participants performed a surprise recognition memory test for the presented faces, followed by a memory test for the answers to the trivia questions.
As might be expected, people were better at learning the trivia information when they were highly curious about it. More surprisingly, they also showed better learning of the unrelated faces that were shown while their curiosity was aroused. Information learned during a curious state was better retained over a 24-hour delay.
"Curiosity may put the brain in a state that allows it to learn and retain any kind of information, like a vortex that sucks in what you are motivated to learn, and also everything around it," Gruber said.
Secondly, the investigators found that when curiosity is stimulated, there is increased activity in the brain circuit related to reward.
"We showed that intrinsic motivation actually recruits some of the same brain areas that are heavily involved in tangible, extrinsic motivation," Gruber said. This reward circuit relies on dopamine, a chemical that relays messages between neurons.
The team also discovered that when learning was motivated by curiosity, there was increased activity in the hippocampus, a brain region that is important for forming new memories, as well as increased interactions between the hippocampus and the dopamine reward circuit.
"So curiosity recruits the reward system, and interactions between the reward system and the hippocampus seem to put the brain in a state in which you are more likely to learn and retain information, even if that information is not of particular interest or importance," said Charan Ranganath, senior author, and Professor at the UC Davis Center for Neuroscience and Department of Psychology.
Brain circuits that rely on dopamine tend to decline in function with aging, or sooner in people with neurological or psychiatric disorders. Understanding the relationship between motivation and memory could stimulate new efforts to improve memory in the healthy elderly and new approaches for treating patients with memory disorders. And in the classroom or workplace, learning could be enhanced if teachers or managers can engage students' and workers' curiosity about something they are naturally motivated to learn.
INFORMATION:
Coauthors on the study were Gruber, Ranganath and research scientist Bernard Gelman. The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Simon J. Guggenheim Foundation, and the Leverhulme Trust.
White Americans may view diversity and multiculturalism more negatively as the U.S. moves toward becoming a minority-majority nation, UCLA psychologists report.
As part of their study, the researchers divided 98 white Americans from all regions of the country — half male, half female, with an average age of 37 — randomly into two groups. One group was told that whites will no longer be the majority in the U.S. by 2050; in fact, this is likely to be true as soon as 2043, according to some projections. The second group was told that whites would retain their majority status ...
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA -- New applications of structures and materials that replicate complex yet efficient arrangements that have evolved in nature over millennia are featured in a special section on biomimetic and bioinspired materials for applications in biophotonics in the October issue of the Journal of Biomedical Optics. The journal is published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, in the SPIE Digital Library. Several of the peer-reviewed articles are accessible via open access.
"Biomimetic and bioinspired materials present an emerging ...
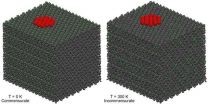
VIDEO:
The video compares the two sliding states of the C60 flake attached to the tip of the microscope: a) commensurate state at low temperature where the C60 do not rotate...
Click here for more information.
About 3500 years ago, man invented the wheel to make life easier. Then, thanks to Leonardo Da Vinci's genius, the wheel was made smaller to obtain ball bearings. And today? "Today we are trying to get even smaller: scientists are thinking about nano-bearings", comments ...
PULLMAN, Wash.—A Washington State University undergraduate has helped develop a new method for detecting water on Mars. Her findings appear in Nature Communications, one of the most influential general science journals.
Kellie Wall, 21, of Port Orchard, Wash., looked for evidence that water influenced crystal formation in basalt, the dark volcanic rock that covers most of eastern Washington and Oregon. She then compared this with volcanic rock observations made by the rover Curiosity on Mars' Gale Crater.
"This is really cool because it could potentially be useful for ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio—Is it a solar cell? Or a rechargeable battery?
Actually, the patent-pending device invented at The Ohio State University is both: the world's first solar battery.
In the October 3, 2014 issue of the journal Nature Communications, the researchers report that they've succeeded in combining a battery and a solar cell into one hybrid device.
Key to the innovation is a mesh solar panel, which allows air to enter the battery, and a special process for transferring electrons between the solar panel and the battery electrode. Inside the device, light and oxygen ...
Too many stroke patients in Canada are not getting the rehabilitation they need to return to a healthy, active life, according to a new study which will be presented at the Canadian Stroke Congress in Vancouver tomorrow. The research findings strongly suggest that such decisions are being made based on what services are available in the health system rather than what patients really need.
It found that overall just 16 per cent of patients with stroke were discharged to inpatient rehabilitation but that the rates varied widely by province (1% to 26%) and hospital (0% to ...
They base their findings on 1221 Danish men between the ages of 18 and 28, all of whom underwent a medical examination to assess their fitness for military service, which is compulsory in Denmark, between 2008 and 2012.
As part of their assessment, the military recruits were asked how much alcohol they drank in the week before their medical exam (recent drinking); whether this was typical (habitual); and how often they binge drank, defined as more than 5 units in one sitting, and had been drunk in the preceding month.
They were also invited to provide a semen sample ...
There is some evidence to suggest that alcohol impairs the workings of the immune system, both in terms of the initial protective inflammatory response to infection and the development of subsequent immunity.
And habitual drinking is known to increase susceptibility to bacterial pneumonia, septicaemia, tuberculosis and viral hepatitis. The researchers therefore wanted to find out if there was any association between drinking patterns and susceptibility to HPV infection.
They included 1313 men who were already taking part in the US arm of the HPV in Men (HIM) study, ...
Previous research has suggested that gout might be associated with diabetes, but the findings were restricted to one study of men at high risk of heart disease and stroke. The researchers wanted to know if the link existed in the general population, and also applied to women.
They searched the Health Improvement Network (THIN), an electronic database of the anonymised health records of almost 7.5 million patients registered with 477 general practices across the UK.
They included adults who were at least 20 years old, and whose details had been entered into the database ...
Ovarian tissue and egg freezing to preserve fertility should no longer be reserved for cancer patients, and healthy women should also be offered these options to safeguard their future chances of conceiving a child, say world renowned fertility experts writing in a new Series on fertility preservation, published in The Lancet [Paper 3].
Over the past 10 years, researchers have restored the fertility of female cancer patients who would otherwise have been left infertile after treatment, having been offered oocyte cryopreservation. The technique enables women to freeze ...