(Press-News.org) Quantum computing will allow for the creation of powerful computers, but also much smarter and more creative robots than conventional ones. This was the conclusion arrived at by researchers from Spain and Austria, who have confirmed that quantum tools help robots learn and respond much faster to the stimuli around them.
Quantum mechanics has revolutionised the world of communications and computers by introducing algorithms which are much quicker and more secure in transferring information. Now researchers from the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM) and the University of Innsbruck (Austria) have published a study in the journal 'Physical Review X' which states that these tools can be used to apply to robots, automatons and the other agents that use artificial intelligence (AI).
They demonstrate for the first time that quantum machines can respond the best and act the fastest against the environment surrounding them. More specifically, they adapt to situations where the conventional ones, which are much slower, cannot finish the learning and response processes.
"In the case of very demanding and 'impatient' environments, the outcome is that the quantum robot can adapt itself and survive, while the classic robot is destined to collapse," explains G. Davide Paparo and Miguel A. Martín-Delgado, the two researchers from UCM who have participated in the study.
Their theoretical work has focused on using quantum computing to accelerate ahead with one of the most difficult points to resolve in information technology: machine learning, which is used to create highly accurate models and predictions. It is applied, for example, to know how the climate or an illness will evolve or in the development of Internet search engines.
More creative quantum robots
"Building a model is actually a creative act, but conventional computers are no good at it," says Martín-Delgado. "That is where quantum computing comes into play. The advances it brings are not only quantitative in terms of greater speed, but also qualitative: adapting better to environments where the classic agent does not survive. This means that quantum robots are more creative".
The authors assess the scope of their study as such: "It means a step forward towards the most ambitious objective of artificial intelligence: the creation of a robot that is intelligent and creative, and that is not designed for specific tasks".
This work comes under a new discipline, the so-called 'quantum AI', an area in which the company Google has started to invest millions of dollars via the creation of a specialised laboratory in collaboration with the NASA.
INFORMATION:
References:
Giuseppe Davide Paparo, Vedran Dunjko, Adi Makmal, Miguel Angel Martin-Delgado, and Hans J. Briegel. "Quantum Speedup for Active Learning Agents". Phys. Rev. X 4, 031002, July 2014.
Pressing the accelerator on quantum robotics
2014-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A glimpse into the 3-D brain: How memories form
2014-10-06
The way neurons are interconnected in the brain is very complicated. This holds especially true for the cells of the hippocampus. It is one of the oldest brain regions and its form resembles a see horse (hippocampus in Latin). The hippocampus enables us to navigate space securely and to form personal memories. So far, the anatomic knowledge of the networks inside the hippocampus and its connection to the rest of the brain has left scientists guessing which information arrived where and when.
Signals spread through the brain
Accordingly, Dr Martin Pyka and his colleagues ...
No need for water, enzymes are doing it for themselves
2014-10-06
New research by scientists at the University of Bristol has challenged one of the key axioms in biology - that enzymes need water to function. The breakthrough could eventually lead to the development of new industrial catalysts for processing biodiesel.
Enzymes are large biological molecules that catalyse thousands of different chemical reactions that are essential for all life, from converting food into energy, to controlling how our cells replicate DNA.
Throughout this diverse range of biological environments in which enzymes perform their various roles, the only ...
Research paves way for new generation of fungicides
2014-10-06
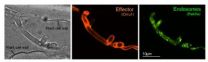
Plants that come under attack from pathogens have an automatic immune response. Fungi get around this plant immunity by injecting proteins into the host plant cells. These 'effector proteins' enable the fungi to escape the plant's immune system and allow the fungal cells to enter the plant unrecognised.
Exeter scientists have now shown that signalling organelles, known as 'early endosomes' act as long distance messengers in the fungi. They travel rapidly along long tube-like cells between the plant-invading fungal cell tip and the fungal cell nucleus. This rapid communication ...
Online games and remote experiments could reduce scientific fraud, cherry-picking
2014-10-06
PITTSBURGH—One way to combat the rising level of errors and fraud in life sciences research is through massive online laboratories, which use videogames to engage large numbers of non-professional investigators and prevent scientists from manually testing their own hypotheses, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Stanford University say.
Though unconventional, CMU's Adrien Treuille and Stanford's Rhiju Das argue that this online, game-like approach actually is more scientifically rigorous than the standard practice of scientists proposing an explanation for ...
Treatments for HIV-visceral leishmaniasis co-infected patients
2014-10-06
This news release is available in Spanish. [Gondar, Ethiopia and Geneva, Switzerland – October 6, 2014] - The international research & development (R&D) consortium, AfriCoLeish, formed by six research organizations from East Africa and Europe, has launched a Phase III clinical study to address the extreme difficulty in treating visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in patients who also are HIV-positive. The study will assess the efficacy and the safety of two treatments: a combination treatment of AmBisome® and miltefosine, and AmBisome® alone. This is the first randomized clinical ...
A vicious cycle in osteoarthritis: Sleep disturbance-pain-depression-disability
2014-10-06
New research confirms that sleep disturbances are linked to pain and depression, but not disability, among patients with osteoarthritis (OA). Study results published in Arthritis Care & Research, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), found that poor sleep increases depression and disability, but does not worsen pain over time.
Arthritis is one of the top three health concerns that cause disability in the U.S., with OA being the most common form of arthritis. Medical evidence reports that nearly 30 million Americans are affected by OA, which has increased ...
A new way to extract bone-making cells from fat tissue
2014-10-06
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Within our fat lives a variety of cells with the potential to become bone, cartilage, or more fat if properly prompted. This makes adipose tissue, in theory, a readily available reservoir for regenerative therapies such as bone healing if doctors can get enough of those cells and compel them to produce bone.
In a new study in the journal Stem Cell Research & Therapy, scientists at Brown University demonstrate a new method for extracting a wide variety of potential bone-producing cells from human fat. They developed a fluorescent tag ...
Innovative stroke patient management system cuts hospital bed usage by more than 25 percent
2014-10-06
An innovative patient management system at the acute stroke unit of Kelowna (BC) General Hospital has reduced the number of stroke patient bed days by more than 25 per cent, according to a study of the system presented at the annual Canadian Stroke Congress in Vancouver.
In total, it is estimated the new system is saving the 380-bed hospital more than 1,000 bed days per year. This represents annual savings of up to $800,000, all achieved without the need for any new investment in devices, treatments or personnel.
"It's a win-win situation," says Dr. John B. Falconer, ...
Code stroke on the ward
2014-10-06
At the first sign of a stroke, time is of the essence. For every minute of delay in treatment, people typically lose almost two million brain cells. Yet a new study presented at the Canadian Stroke Congress reveals that those delays – in getting the right tests and the right drugs – can be longer when people experience a stroke in a hospital.
Investigators from the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine, the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) and the University Health Network looked at data from acute care facilities in Ontario over nine years. They ...
Teen hormones and cellphones
2014-10-06
Researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston say that sexting may be the new "normal" part of adolescent sexual development and is not strictly limited to at-risk teens. The findings, published in the journal Pediatrics, are from the first study on the relationship between teenage sexting, or sending sexually explicit images to another electronically, and future sexual activity.
The study results indicate that sexting may precede sexual intercourse in some cases and further cements the idea that sexting behavior is a credible sign of teenage sexual ...