(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Oct. 6, 2014— Melanoma is the fifth most common cancer type in the United States, and it's also the deadliest form of skin cancer, causing more than 75 percent of skin-cancer deaths. If caught early enough though, it is almost always curable. Now a camera, capable of taking snapshots of the entire human body and rendering high-resolution images of a patient's skin may help doctors spot cancer early and save lives.
Developed by a team of researchers at Duke University in North Carolina, USA, the "gigapixel whole-body photographic camera" is essentially three dozen cameras in one, allowing the researchers to image the entire body down to a freckle. The research will be presented at The Optical Society's (OSA) 98th Annual Meeting, Frontiers in Optics, being held Oct. 19-23 in Tucson, Arizona, USA.
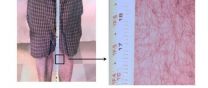
"The camera is designed to find lesions potentially indicating skin cancers on patients at an earlier stage than current skin examination techniques," said Daniel Marks, one of the co-authors on the paper. "Normally a dermatologist examines either a small region of the skin at high resolution or a large region at low resolution, but a gigapixel image doesn't require a compromise between the two."
Although whole-body photography has already been used to identify melanomas and exclude non-dangerous "stable" lesions, the approach is typically limited by the resolution of the cameras used. A commercial camera with a wide-angle lens can easily capture an image of a person's entire body, but it lacks the resolution needed for a dermatologist to zoom in on one tiny spot. So dermatologists typically examine suspicious lesions with digital dermatoscopy, a technique to evaluate the colors and microstructures of suspicious skins not visible to the naked eyes. The need for two types of images drives up costs and limits possibilities for telemedicine.
The gigapixel camera developed by the Duke University team solves this problem by essentially combining 34 microcameras into one. With a structure similar to a telescope and its eyepieces, the camera combines a precise but simple objective lens that produces an imperfect image with known irregularities. The 34 microcameras are arranged in a "dome" to correct these aberrations and form a continuous image of the scene. The exposure time and focus for each microcamera can be adjusted independently, and a computer can do a preliminary examination of the images to determine if any areas require future attention by the specialists.
Marks pointed out that although the resolution of the gigapixel camera is not as high as the best dermatoscope, it is significantly better than normal photography, allows for a larger imaging area than a dermatoscope and could be used for telemedicine, which could make the routine screening available to a larger number of people, even in remote locations.
The gigapixel imaging technology is based on the multiscale camera design, which is part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency program "Advanced Wide Field-of-View Architectures for Image Reconstruction and Exploitation."
Though the camera will still have to prove effective in clinical trials before becoming routinely available to patients, the researchers have gathered enough preliminary data on a healthy volunteer to demonstrate that it has adequate resolution and the field of view needed for skin disease screening. The next step, they say, is to test how well it works in the clinic.
INFORMATION:
Presentation FTu2F.5 "Gigapixel Whole-Body Microphotography," takes place Tuesday, Oct. 21 at 11:30 a.m. MST at the Tucson Ballroom, Salon A at the JW Marriott Tucson Starr Pass Resort.
PRESS REGISTRATION: A press room for credentialed press and analysts will be located in the Marriott, Sunday through Thursday, Oct. 19-23. Those interested in obtaining a press badge for FiO should contact OSA's Lyndsay Meyer at 202.416.1435 or lmeyer@osa.org.
About FiO/LS
Frontiers in Optics (FiO) 2014 is The Optical Society's (OSA) 98th Annual Meeting and is being held together with Laser Science, the 30th annual meeting of the American Physical Society (APS) Division of Laser Science (DLS). The two meetings unite the OSA and APS communities for five days of quality, cutting-edge presentations, fascinating invited speakers and a variety of special events spanning a broad range of topics in optics and photonics—the science of light—across the disciplines of physics, biology and chemistry. An exhibit floor featuring leading optics companies will further enhance the meeting. More information at http://www.FrontiersinOptics.org.
Contact:
Lyndsay Meyer
The Optical Society
+1.202.416.1435
lmeyer@osa.org
Many US patients with liver cancer—even those with early stage disease that can often be cured—do not receive treatment for their disease, according to an analysis of studies published between 1989 and 2013.
Less than one fourth of patients undergo curative treatment, and nearly 50% do not receive any treatment. Elderly, non-Caucasians and patients of low socioeconomic status had lower treatment rates than their counterparts.
"We found the low treatment rates among patients with early stage tumors particularly concerning. Many of these patients currently fail to receive ...
Vitamin D deficiency is linked with advanced stages of liver cancer and may be an indicator of a poor prognosis, according to a study of 200 patients with the disease who were followed for an average of 46 weeks.
Blood levels of vitamin D negatively correlated with stages of the disease, and patients with severe vitamin D deficiency had more than a 2-fold increased risk of dying during the study, according to Dr. Oliver Waidmann, senior author of the Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics study.
INFORMATION:
...
A new phase 1 safety trial has demonstrated that idarubicin-loaded beads are well tolerated by patients but are toxic to liver cancer cells. Idarubicin is an anthracycline that is currently used to treat leukemias.
Two months into the 21-patient trial, the tumors of 28% of patients had complete responses to the drug, and the tumors of 24% of patients had a partial response. The findings are published in Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
INFORMATION:
...
Eating lots of white meat (such as poultry) or fish may reduce the risk of developing liver cancer by 31% and 22%, respectively, according to a recent analysis of studies published between 1956 and 2013.
Consuming red meat, processed meat, or total meat was not associated with liver cancer risk. The Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics findings suggest that dietary interventions may be a promising approach for preventing liver cancer.
INFORMATION: ...
While all prescription opioids can be abused, oxycodone may be more potent in its ability to promote changes in the brain relevant to addiction.
A new study in the European Journal of Neuroscience revealed greater increases of dopamine in the brain following the delivery of oxycodone compared with morphine. The release of dopamine, a chemical messenger between neurons, is consistently tied with reward and motivation.
The study's investigators say that it is essential to understand how drugs differentially alter brain chemistry if we hope to understand addiction and ...
Efforts to reduce China's carbon dioxide emissions are being offset by the country's rampant economic growth, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
Research published today in Nature Climate Change reveals how carbon efficiency has improved in nearly all Chinese provinces. But the country's economic boom has simultaneously led to a growth in CO2-emitting activities such as mining, metal smelting and coal-fired electricity generation – negating any gains.
According to the study, China, the world's largest producer of CO2 emissions, increased ...
This issue was supported by the Qatar Foundation and World Innovation Summit for Health (WISH), Hamad Medical Corporation, Imperial College London, and The Commonwealth Fund.
How is accountable care taking shape internationally?
Mark McClellan of the Brookings Institution and coauthors seek to offer a global description of an accountable care system and a mechanism to assess related reforms. They suggest five components for a framework applicable internationally: population, outcomes, metrics and learning, payments and incentives, and coordinated delivery. They also ...
A new and potentially more revealing way of studying how animal evolution is affected by the geography of climate has been designed by researchers at The University of Nottingham and Harvard University.
The research, published in the prestigious journal, The American Naturalist, uses a new approach to investigate how animals across (interspecific) and within (intraspecific) species change in size along temperature gradients, shedding light on a 150-year-old evolutionary puzzle. Bergmann's rule — the tendency for warm-blooded animal body size to increase in colder environments ...
Life on the Antarctic sea floor is under threat from crabs that could invade the area thanks to favorable conditions as a result of global warming, researchers warn.
In a Journal of Biogeography editorial, experts say invasive species degrade marine ecosystems by preying on or outcompeting local species. Early signs of biological invasion are already apparent.
"Biological invasion is a major worry in the Arctic," said lead author Dr. Richard Aronson, "but we should be just as concerned about the Antarctic." Assessing the extent of the problem requires long-term monitoring ...
LIVERMORE, California -- Using satellite observations and a large suite of climate models, Lawrence Livermore scientists have found that long-term ocean warming in the upper 700 meters has likely been underestimated.
"This underestimation is a result of poor sampling prior to the last decade and limitations of the analysis methods that conservatively estimated temperature changes in data-sparse regions," said LLNL oceanographer Paul Durack, lead author of a paper appearing in the October 5th issue of the journal Nature Climate Change.
Ocean heat storage is important ...