(Press-News.org) Studying rats as model subjects, scientists found that adolescents were at an increased risk of suffering negative health effects from sugar-sweetened beverage consumption.
Adolescent rats that freely consumed large quantities of liquid solutions containing sugar or high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in concentrations comparable to popular sugar-sweetened beverages experienced memory problems and brain inflammation, and became pre-diabetic, according to a new study from USC. Neither adult rats fed the sugary drinks nor adolescent rats who did not consume sugar had the same issues.
"The brain is especially vulnerable to dietary influences during critical periods of development, like adolescence," said Scott Kanoski, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.
Kanoski collaborated with USC's Ted Hsu, Vaibhav Konanur, Lilly Taing, Ryan Usui, Brandon Kayser, and Michael Goran. Their study, which tested a total of 76 rats, was published online by the journal Hippocampus on Sept. 23.
About 35 to 40 percent of the rats' caloric intake was from sugar or HFCS. For comparason, added sugars make up about 17 percent of the total caloric intake of teens in the U.S. on average, according to the CDC.
The rats were then tested in mazes that probe their spatial memory ability. Adolescent rats that had consumed the sugary beverages, particularly HFCS, performed worse on the test than any other group – which may be the result of the neuroinflammation detected in the hippocampus, Kanoski said.
The hippocampus is a part of the temporal lobe located deep within the brain that controls memory formation. People with Alzheimer's Disease and other dementias often suffer damage to the hippocampus.
"Consuming a diet high in added sugars not only can lead to weight gain and metabolic disturbances, but can also negatively impact our neural functioning and cognitive ability." Kanoski said. Next, Kanoski and his team plant to see how different monosaccharides (simple sugars) and HFCS affect the brain.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by USC institutional support.
Sugar linked to memory problems in adolescent rats
Sugar consumption led to memory problems and brain inflammation
2014-10-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The unexamined diversity in the 'Coral Triangle'
2014-10-07
Research on zoantharians, a group of animals related to corals and anemones, by researchers James Reimer of the University of the Ryukyus in Okinawa, Japan, Angelo Poliseno of Universita Politecnica delle Marche in Italy, and Bert Hoeksema from Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Netherlands, has demonstrated how little we know about marine diversity in the so-called "center of marine biodiversity" located in the central Indo-Pacific Ocean. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The researchers utilized previously collected specimens from Indonesia, ...
Sandwiches are a major contributor to dietary sodium intake
2014-10-07
Philadelphia, PA, October 6, 2014 – Sandwiches make up a substantial part of the American diet and are a significant contributor to daily energy and sodium intake. By closely analyzing data from the federal nationwide dietary intake survey known as "What We Eat in America NHANES 2009-2010," a team of Department of Agriculture (USDA) researchers found that on any given day 49 percent of U.S. adults eat at least one sandwich, and sandwiches account for one-fifth of total daily sodium intake. The study was conducted by USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) investigators ...
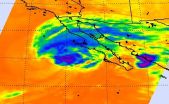
Tropical Storm Simon says, 'US Southwest is an 'arm's reach'
2014-10-07
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows what looks like an arm from Tropical Storm Simon's northern quadrant, reaching over Baja California to mainland Mexico. Forecasters at the National Hurricane Center noted that Simon is just an "arm's reach" to the southern U.S. and expect rainfall and rough surf to affect that area of the country.
On Oct. 6 at 0347 UTC (Oct. 5 at 11:47 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Simon. On band of thunderstorms wrapping into ...
NASA spots Typhoon Phanfone affecting Japan
2014-10-07
Over the weekend of Oct. 5 and 6, Typhoon Phanfone's center made landfall just south of Tokyo and passed over the city before exiting back into the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite captured a picture of the typhoon as Tokyo braced for its large eye.
On its way to mainland Japan, Phanfone struck Kadena Air Base on the island of Okinawa. According to the website for U.S. Air Force Kadena Air Base, "One Airman is confirmed deceased and two more are missing after they were washed out to sea from the northwest coast of Okinawa at about 3:45 p.m. Oct. 5. An ...
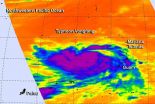
NASA sees Typhoon Vongfong leaving the Mariana Islands
2014-10-07
Typhoon Vongfong has exited the Mariana Islands. Now, as the island of Iwo To begins recovery from Typhoon Phanfone, NASA's Aqua satellite is eyeing Typhoon Vongfong over 1,000 miles south of Iwo To. Although Vongfong is expected to turn north toward Iwo To, it is forecast to stay west of the island on its track.
On Oct. 6 at 0347 UTC (Oct. 5 at 11:47 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Vongfong. AIRS data showed strongest thunderstorms within the typhoon circled the center ...
A warm dark matter search using XMASS: Editors' suggestion of Physical Review Letters
2014-10-07
The XMASS collaboration, led by Yoichiro Suzuki at the Kavli IPMU, has reported its latest results on the search for warm dark matter. Their results rule out the possibility that super-weakly interacting massive bosonic particles (bosonic super-WIMPs) constitute all dark matter in the universe. This result was published in the September 19th issue of the Physical Review Letters as an Editors' Suggestion.
The universe is considered to be filled with dark matter, which cannot be observed by ordinary light. Although much evidence supports the existence of dark matter, it ...
Program to reduce hospital readmissions doesn't have impact
2014-10-07
Researchers at UC San Francisco have found that a nurse-led intervention program designed to reduce readmissions among ethnically and linguistically diverse older patients did not improve 30-day hospital readmission rates. Their findings suggest hospitals evaluate such programs before implementing or continuing.
Their study is in the Oct. 7 issue of Annals of Internal Medicine.
"The lack of effect in this population, which was well connected to primary care, suggests reducing readmissions is challenging," said co-lead author L. Elizabeth Goldman, MD, MCR, associate ...
Asthma risk varies with ethnic ancestry among Latinos, UCSF team finds
2014-10-07
Native American ancestry is associated with a lower asthma risk, but African ancestry is associated with a higher risk, according to the largest-ever study of how genetic variation influences asthma risk in Latinos, in whom both African and Native American ancestry is common. The study, led by UC San Francisco researchers, was published online October 6, 2014 in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Although differences in the environments in which people live often are suspected when asthma risks among populations differ, the new findings illustrate the importance ...
Small molecule 'jams the switch' to prevent inflammatory cell death
2014-10-07
Walter and Eliza Hall Institute scientists have discovered a small molecule that blocks a form of cell death that triggers inflammation, opening the door for potential new treatments for inflammatory disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and psoriasis.
The researchers made the discovery while investigating how a protein called MLKL kills cells in a process known as necroptosis. Their findings were published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Necroptosis is a recently discovered cell death pathway linked to immune disorders. ...
Making the world's most dreaded undergrad course fun (video)
2014-10-07
WASHINGTON, Oct. 7, 2014 — Organic chemistry: It's among the most feared courses undergraduate science students take. Whether you call it "orgo" or "o-chem," it has reduced many hopeful scholars to tears. One professor thinks he has a solution. William Dichtel, Ph.D., of Cornell University shares his thoughts on making organic chemistry classes more interesting and relevant to students in the newest episode of Prized Science from the American Chemical Society. Watch the interview at http://youtu.be/A6j1qAOOeHs.
Subscribe to the ACS channel at http://bit.ly/ACSYoutube ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Sugar linked to memory problems in adolescent ratsSugar consumption led to memory problems and brain inflammation