Back off: Female chimps stressed out by competing suitors
Aggressive tactics of male chimps could put a damper on female chimps' chances to conceive
2014-10-07
(Press-News.org) Being the center of attention can have its drawbacks. For female chimpanzees, being around too many rowdy males is disadvantageous when foraging for food, an effect that can ultimately interfere with her reproductive ability. These are some of the findings of an 11-year-long study of wild East African chimpanzees in Uganda, led by Melissa Emery Thompson of the University of New Mexico in the US. It is published in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
Female chimpanzees have an exceedingly slow reproductive schedule, and only give birth every five to seven years. When ready to reproduce, females display very large swellings of their genitals and often do so for several months before conceiving. Male chimpanzees compete quite fiercely – and in great numbers – for the attention of the rare female who might bear their offspring. The contested female may have little choice than to tolerate the attentions of these would-be suitors, as mating with many males ensures that their young are not killed by jealous males. However, all this harassment and jealous guarding by males can influence the ability of females to feed. Some females, such as those with young infants, can avoid this chaos, but only if there is high-quality food to be found elsewhere.
Emery Thompson and her team spent more than 11 years observing the daily interactions and diets of 50 members of the Kanyawara community of East African chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) in the Kibale National Park in Uganda. In the process, they collected urine samples from at least 25 females, either by capturing falling urine with a plastic bag or by pipetting urine from plants.
Laboratory tests gauged the levels of C-peptide (a by-product in the synthesis of insulin) and estrogen and progesterone (two ovarian steroids central to the reproductive cycle) in the urine of females. This showed that the more males gathered around a cycling or lactating female during a given month, the lower were her C-peptide levels. In contrast, the number of females she associated with had no effect on these levels. Declining C-peptide levels mean that the female is spending more energy than she consumes, and can result in weight loss. In this study, C-peptide levels also predicted production of ovarian steroids, indicating an effect on reproductive ability.
"This has significant downstream effects on females' reproductive functioning and fertility rates, and demonstrates that the reproductive tactics of male chimps could put a damper on the ability of the female members of their species to conceive," says Emery Thompson.
The findings add to previous work by Emery Thompson's research group that showed how male sexual aggression on females increases the production of stress hormones.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Emery Thompson, M. et al. (2014). Male Chimpanzees Compromise the Foraging Success of Their Mates in Kibale National Park, Uganda. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. DOI 10.1007/s00265-014-1803-y
The full-text article and photos are available to journalists on request.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-07
New Rochelle, NY, October 7, 2014—Low sexual desire is common among both pre- and post-menopausal women. It can cause personal distress, harm relationships, and have a negative impact on body image and self confidence. Yet few women seek medical care for this condition, and the reasons are explored in a timely article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jwh.2014.4743 until November 7, ...
2014-10-07
Winston-Salem, N.C. – Sept. Oct. 7, 2014 – Children who start toilet training before age 2 have a three times higher risk of developing daytime wetting problems later, according to new research at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
"Parents who train their children early to meet preschool deadlines, to save landfills from diapers or because they think toddlers are easier to train should know there can be serious repercussions," says lead author Steve Hodges, M.D., an associate professor of pediatric urology at Wake Forest Baptist.
The study, reported ...
2014-10-07
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Physical therapy after total hip (THR) or total knee replacement (TKR) surgery is standard care for all patients. A new study, appearing in the October 1 issue of the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS), also found that physical therapy before joint replacement surgery, or "prehabilitation," can diminish the need for postoperative care by nearly 30 percent, saving an average of $1,215 per patient in skilled nursing facility, home health agency or other postoperative care.
Approximately 50 million U.S. adults have physician-diagnosed arthritis. ...
2014-10-07
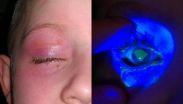
San Francisco, CA, October 7, 2014 – Liquid laundry and dishwasher detergent pods are an emerging source of chemical exposure in children. When squeezed or bitten into, these pods can burst and send detergent into the mouth, nose, and eyes. A new report published in the current issue of the Journal of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) cautions that these products should be kept away from children because the bursting detergent pods can cause significant corneal injury.
Detergent pods may offer a simpler way to do laundry, ...
2014-10-07
Studying rats as model subjects, scientists found that adolescents were at an increased risk of suffering negative health effects from sugar-sweetened beverage consumption.
Adolescent rats that freely consumed large quantities of liquid solutions containing sugar or high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in concentrations comparable to popular sugar-sweetened beverages experienced memory problems and brain inflammation, and became pre-diabetic, according to a new study from USC. Neither adult rats fed the sugary drinks nor adolescent rats who did not consume sugar had the same ...
2014-10-07
Research on zoantharians, a group of animals related to corals and anemones, by researchers James Reimer of the University of the Ryukyus in Okinawa, Japan, Angelo Poliseno of Universita Politecnica delle Marche in Italy, and Bert Hoeksema from Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Netherlands, has demonstrated how little we know about marine diversity in the so-called "center of marine biodiversity" located in the central Indo-Pacific Ocean. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The researchers utilized previously collected specimens from Indonesia, ...
2014-10-07
Philadelphia, PA, October 6, 2014 – Sandwiches make up a substantial part of the American diet and are a significant contributor to daily energy and sodium intake. By closely analyzing data from the federal nationwide dietary intake survey known as "What We Eat in America NHANES 2009-2010," a team of Department of Agriculture (USDA) researchers found that on any given day 49 percent of U.S. adults eat at least one sandwich, and sandwiches account for one-fifth of total daily sodium intake. The study was conducted by USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) investigators ...
2014-10-07
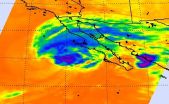
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows what looks like an arm from Tropical Storm Simon's northern quadrant, reaching over Baja California to mainland Mexico. Forecasters at the National Hurricane Center noted that Simon is just an "arm's reach" to the southern U.S. and expect rainfall and rough surf to affect that area of the country.
On Oct. 6 at 0347 UTC (Oct. 5 at 11:47 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Simon. On band of thunderstorms wrapping into ...
2014-10-07
Over the weekend of Oct. 5 and 6, Typhoon Phanfone's center made landfall just south of Tokyo and passed over the city before exiting back into the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite captured a picture of the typhoon as Tokyo braced for its large eye.
On its way to mainland Japan, Phanfone struck Kadena Air Base on the island of Okinawa. According to the website for U.S. Air Force Kadena Air Base, "One Airman is confirmed deceased and two more are missing after they were washed out to sea from the northwest coast of Okinawa at about 3:45 p.m. Oct. 5. An ...
2014-10-07
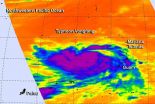
Typhoon Vongfong has exited the Mariana Islands. Now, as the island of Iwo To begins recovery from Typhoon Phanfone, NASA's Aqua satellite is eyeing Typhoon Vongfong over 1,000 miles south of Iwo To. Although Vongfong is expected to turn north toward Iwo To, it is forecast to stay west of the island on its track.
On Oct. 6 at 0347 UTC (Oct. 5 at 11:47 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Vongfong. AIRS data showed strongest thunderstorms within the typhoon circled the center ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Back off: Female chimps stressed out by competing suitors
Aggressive tactics of male chimps could put a damper on female chimps' chances to conceive