(Press-News.org) Many patients with psychosis develop health risks associated with premature death early in the course of their mental illness, researchers have found.
Patients with schizophrenia are already known to have higher rates of premature death than the general population. The study found that elevated risks of heart disease and metabolic issues such as high blood sugar in people with first episode psychosis are due to an interaction of mental illness, unhealthy lifestyle behaviors and antipsychotic medications that may accelerate these risks.
Patients entered treatment with significant health concerns – including excess weight, smoking, and metabolic issues – despite an average age of only 24 years. The study identifies key opportunities for health care systems to improve the treatment of such patients with first episode psychosis. The research was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Christoph Correll, M.D., of The Zucker Hillside Hospital, Hofstra North Shore-Long Island Jewish School of Medicine, New York, and colleagues, report their findings on Oct. 8, 2014 in JAMA Psychiatry.
The study is among the first of several to report results from the Recovery After an Initial Schizophrenia Episode (RAISE) project, which was developed by NIMH to examine first episode psychosis before and after specialized treatment was offered in community settings.
The researchers studied nearly 400 individuals between the ages of 15 and 40 with first episode psychosis, who presented for treatment at 34 community-based clinics across 21 states.
The frequency of obesity was similar to the same age group in the general population. However, smoking and metabolic syndrome (a combination of conditions including obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal blood fats, such as cholesterol and triglycerides) were much more common. Frequencies of dyslipidemia (an abnormal amount of blood fats, such as cholesterol and triglycerides) and pre-hypertension in this relatively young group of study participants were at least as high as rates typically found in people 15-20 years older.
Notably, treatment with antipsychotic medication, even after brief exposure (participants' average exposure was 47 days), was associated with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, which is a major risk for future cardiovascular illness.
Researchers concluded that people with first episode psychosis need a team-based health care approach that combines psychiatric and general medical care to address the full range of needs. Patients need early interventions for psychiatric illness, lower-risk antipsychotic medications, routine monitoring, and smoking cessation programs to improve health and reduce healthcare expenditures1.
"Our results strongly suggest that clinicians need to pay much more attention to promoting physical health in people with severe mental illness," said lead author Christoph Correll, M.D. "We need to routinely educate patients about healthy lifestyle behaviors, monitor physical health, choose lower risk treatments whenever possible, and manage issues as they arise. Without a combined physical and mental health care approach, we miss major opportunities to improve psychiatric as well as medical health in patients with schizophrenia and other severe conditions."
INFORMATION:
Reference:
1Correll CU, Robinson DG, Schooler NR, Brunette MF, Mueser KT, Rosenheck RA, Marcy P, Addington J, Estroff SE, Robinson J, Penn D, Azrin S, Goldstein A, Severe J, Heinssen R, Kane JM. Cardiometabolic Risk in First Episode Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorder Patients: Baseline Results from the RAISE-ETP Study, JAMA Psychiatry, Oct. 8, 2014
Increased health risks linked to first-episode psychosis
Researchers call for coordinated care to address risks -- NIH-funded
2014-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug-infused nanoparticle is right for sore eyes
2014-10-08
For the millions of sufferers of dry eye syndrome, their only recourse to easing the painful condition is to use drug-laced eye drops three times a day. Now, researchers from the University of Waterloo have developed a topical solution containing nanoparticles that will combat dry eye syndrome with only one application a week.
The eye drops progressively deliver the right amount of drug-infused nanoparticles to the surface of the eyeball over a period of five days before the body absorbs them. One weekly dose replaces 15 or more to treat the pain and irritation of dry ...
Community justice court associated with lower rearrest rates
2014-10-08
The opening of a community court in a high-crime area of San Francisco was associated with a lower chance that offenders would be arrested for another crime within a year, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
San Francisco opened the Community Justice Center in 2009 to serve the city's Tenderloin district and adjacent neighborhoods. RAND researchers examined whether the Community Justice Center reduces the risk of rearrest when compared to more-traditional approaches for addressing arrestees.
San Francisco's Community Justice Center is a multifaceted intervention ...
NASA's GPM satellite's find before Hurricane Simon was caught rapidly intensifying
2014-10-08
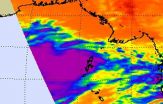
Hurricane Simon appeared to be keeping a secret before it rapidly intensified on Oct. 4, but the Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM satellite was able uncover it.
On Oct. 4 at 0940 UTC (5:40 a.m. EDT) observations by the Ku-band radar on the GPM satellite suggested that the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Hurricane Simon was hiding a very compact eyewall hours before the National Hurricane Center detected rapid intensification of Simon's surface winds. The GPM satellite was launched in February of this year and is managed by both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration ...
Teens still sending naked selfies
2014-10-08
A new study from the University of Utah confirms that substantial numbers of teens are sexting – sending and receiving explicit sexual images via cellphone. Though the behavior is widely studied, the potentially serious consequences of the practice led the researchers to more accurately measure how frequently teens are choosing to put themselves at risk in this fashion.
The study surveyed 1,130 undergraduate students about their experiences sexting in high school. Nearly 20 percent reported they had sent a nude photo of themselves to another via cellphone and 38 ...
Two NASA satellites get data on category 5 Super Typhoon Vongfong
2014-10-08
Two NASA satellites provided data on clouds, rainfall and the diameter of the eye of Super Typhoon Vongfong as it turned north in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
Typhoon Vongfong formed on October 2, 2014 southeast of Guam. Typhoon Phanfone, that recently pummeled Japan, formed near the same area in the western Pacific Ocean.
Vongfong had wind speeds of about 120 knots (138 mph) when the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew above the intensifying typhoon's eye on October 7, 2014 at 0800 UTC (4 a.m. EDT). TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) showed that ...
Zoos exonerated in baby elephant deaths; Data support new branch of herpesvirus family
2014-10-08
WASHINGTON, DC – October 8, 2014 - Elephants are among the most intelligent non-humans, arguably on par with chimps, but both African and Asian elephants—separate species—are endangered. In 1995, 16-month old Kumari, the first Asian elephant born at the National Zoo in Washington, DC, died of a then-mysterious illness. In 1999, Gary Hayward of Johns Hopkins University and collaborators published their results identifying a novel herpesvirus, EEHV1 as the cause of Kumari's sudden death. They now show that severe cases like this one are caused by viruses ...
Plant scientist discovers basis of evolution in violins
2014-10-08
ST. LOUIS, MO – OCTOBER 8, 2014 – What could the natural diversity and beauty of plant leaves have in common with one of mankind's greatest creative inventions, the violin? Much more than you might imagine.
"There are many parallels between leaves and violins," says Dan Chitwood, Ph.D., assistant member, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center in St. Louis, Missouri. "Both have beautiful shapes that are potentially functional, change over time, or result from mimicry. Shape is information that can tell us a story. Just as evolutionary changes in leaf shape inform ...
Zeroing in on a source of gamma rays
2014-10-08
Gamma rays are the highest-energy form of radioactive waves known in the universe. However, how they're made and where they come from have been a bit of a mystery.
But now a team of researchers, led by Michigan State University astronomer Laura Chomiuk, has made a discovery that may shed some light on the subject.
Using highly detailed radio telescope images, Chomiuk and her team have pinpointed the location where an explosion on the surface of a star, known as a nova, emitted gamma rays.
This, said Chomiuk, is something they did not expect to encounter.
"We not ...
What's your status?
2014-10-08
In western society, where keeping up with the Joneses — or, better yet, surpassing them — is expected and even encouraged, status matters. So important is it that for many people, physical and emotional wellbeing are directly connected to their place in the social hierarchy.
That's hardly news to anthropologists at UC Santa Barbara, but they were taken by surprise when research findings indicated that the same relationship exists among the Tsimane, an egalitarian society of forager-farmers in the Bolivian Amazon. Their work is published online in the journal ...
NASA sees newborn Tropical Storm Hudhud in Northern Indian Ocean
2014-10-08
The Northern Indian Ocean has awakened after a tropical slumber and created Tropical Storm Hudhud on Oct. 8 and NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Hudhud on Oct. 8 at 6:53 UTC (2:53 a.m. EDT and captured infrared data on the storm revealing bands of strong thunderstorms around the center.
Animated infrared satellite imagery showed that the low-level circulation center was consolidating, and there is an improvement in the banding of thunderstorms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] Increased health risks linked to first-episode psychosisResearchers call for coordinated care to address risks -- NIH-funded