(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – A little known secret in data mining is that simply feeding raw data into a data analysis algorithm is unlikely to produce meaningful results, say the authors of a new Cornell University study.
From recognizing speech to identifying unusual stars, new discoveries often begin with comparison of data streams to find connections and spot outliers. But most data comparison algorithms today have one major weakness – somewhere, they rely on a human expert to specify what aspects of the data are relevant for comparison, and what aspects aren't. But experts aren't keeping pace with the growing amounts and complexities of big data.
Cornell computing researchers have come up with a new principle they call "data smashing" for estimating the similarities between streams of arbitrary data without human intervention, and without access to the data sources. Hod Lipson, associate professor of mechanical engineering and computing and information science, and Ishanu Chattopadhyay, a former postdoctoral associate with Lipson and now at the University of Chicago, have described their method in Royal Society Interface, Oct. 1.
Data smashing is based on a new way to compare data streams. The process involves two steps. First, the data streams are algorithmically "smashed" to "annihilate" the information in each other. Then, the process measures what information remained after the collision. The more information remained, the less likely the streams originated in the same source.
Data smashing principles may open the door to understanding increasingly complex observations, especially when experts do not know what to look for, according to the researchers.
The authors demonstrated the application of their principle to data from real-world problems, including the disambiguation of electroencephalograph patterns from epileptic seizure patients; detection of anomalous cardiac activity from heart recordings; and classification of astronomical objects from raw photometry.
In all cases and without access to original domain knowledge, the researchers demonstrated performance on par with the accuracy of specialized algorithms and heuristics devised by experts.
INFORMATION:
The work in the paper, "Data smashing: Uncovering lurking order in data," was supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and the U.S. Army Research Office.
Study: http://rsif.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/11/101/20140826.full
'Data smashing' could unshackle automated discovery
2014-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unstoppable magnetoresistance
2014-10-09
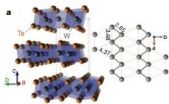
Mazhar Ali, a fifth-year graduate student in the laboratory of Bob Cava, the Russell Wellman Moore Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, has spent his academic career discovering new superconductors, materials coveted for their ability to let electrons flow without resistance. While testing his latest candidate, the semimetal tungsten ditelluride (WTe2), he noticed a peculiar result.
Ali applied a magnetic field to a sample of WTe2, one way to kill superconductivity if present, and saw that its resistance doubled. Intrigued, Ali worked with Jun Xiong, a student ...
College athletes in contact sports more likely to carry MRSA, study finds
2014-10-09
PHILADELPHIA – Even if they don't show signs of infection, college athletes who play football, soccer and other contact sports are more likely to carry the superbug methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), suggests a study on MRSA and athletes, which is being presented at IDWeek 2014™. This puts them at higher risk for infection and increases the likelihood of spreading the bug, which can cause serious and even fatal infections. The study is the first to observe college athletes who are not part of a larger MRSA outbreak.
Contact sport athletes were more ...
When judging art, men and women stand apart
2014-10-09
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- The sexes show stark differences in how they evaluate art, finds a new study co-authored by a Michigan State University marketing scholar.
Men seem to focus more on the artist's background and authenticity, while women pay more attention to the art itself.
The study, which appears in the journal Psychology & Marketing, is the first to investigate how important an artist's "brand" is to average consumers when they appraise art. Turns out, that personal brand is very important, a finding that has implications for the $64 billion art market and ...
'Superglue' for the atmosphere
2014-10-09
This news release is available in German.
It has been known for several years that sulfuric acid contributes to the formation of tiny aerosol particles, which play an important role in the formation of clouds. The new study by Kürten et al. shows that dimethylamine can tremendously enhance new particle formation. The formation of neutral (i.e. uncharged) nucleating clusters of sulfuric acid and dimethylamine was observed for the first time.
Previously, it was only possible to detect neutral clusters containing up to two sulfuric acid molecules. However, ...
New advances in additive manufacturing using laser solid forming to produce metallic parts
2014-10-09
New Rochelle, NY, October 9, 2014—Laser Solid Forming (LSF) is an innovative method for direct fabrication of metallic components in additive manufacturing. Renowned researchers Weidong Huang and Lin Xin, from China's Northwestern Polytechnical University, Shaanxi, describe their progress and applications with LSF technology and the excellent mechanical properties of the metallic parts produced in a Review article in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the 3D Printing ...
All that glitters is... slimy? Gold nanoparticles measure the stickiness of snot
2014-10-09
WASHINGTON, Oct. 9, 2014—Some people might consider mucus an icky bodily secretion best left wrapped in a tissue, but to a group of researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, snot is an endlessly fascinating subject. The team has developed a way to use gold nanoparticles and light to measure the stickiness of the slimy substance that lines our airways. The new method could help doctors better monitor and treat lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The research team will present their work at The ...
Drinking decaf coffee maybe good for the liver
2014-10-09
Researchers from the National Cancer Institute report that decaffeinated coffee drinking may benefit liver health. Results of the study published in Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, show that higher coffee consumption, regardless of caffeine content, was linked to lower levels of abnormal liver enzymes. This suggests that chemical compounds in coffee other than caffeine may help protect the liver.
Coffee consumption is highly prevalent with more than half of all Americans over 18 drinking on average three cups each day ...
Cellular 'power grid' failure triggers abnormal heart rhythms after a heart attack
2014-10-09
VIDEO:
The 'heart attack in a dish' experiment reveals that the mitochondria--or cellular powerhouses--of heart muscle cells flicker and oscillate following heart attack and disrupt the heart's entire electrical system...
Click here for more information.
Heart attack survivors often experience dangerous heart rhythm disturbances during treatment designed to restore blood flow to the injured heart muscle, a common and confounding complication of an otherwise lifesaving intervention. ...
The mathematics behind the Ebola epidemic
2014-10-09
This news release is available in German. The Ebola epidemic in West Africa appears to be spiralling out of control. More than ever, local and global health authorities want to know how the epidemic will develop and, above all, how to prevent it from spreading further. Certain parameters help them to determine this, such as the reproductive number, which is the average number of infections caused by a single infected individual. The incubation and infectious periods are also highly relevant; i.e. the time from infection to the onset of symptoms and the time from onset ...
New increase in antimicrobial use in animals in Denmark
2014-10-09
Antimicrobial usage in animals in Denmark continued to increase in 2013 – mainly due to an increased use in pigs. However, antimicrobial use in pigs is still 12% lower than in 2009. In general, livestock received very little of the critically important antimicrobials, which are used to treat humans. These findings appear in the annual DANMAP report from Statens Serum Institut and the National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark. DANMAP is the Danish integrated antimicrobial resistance monitoring and research programme.
In 2013, the total use of antimicrobials ...