(Press-News.org) A Greek and international team of divers and archaeologists has retrieved stunning new finds from an ancient Greek ship that sank more than 2,000 years ago off the remote island of Antikythera. The rescued antiquities include tableware, ship components, and a giant bronze spear that would have belonged to a life-sized warrior statue.
The Antikythera wreck was first discovered in 1900 by sponge divers who were blown off course by a storm. They subsequently recovered a spectacular haul of ancient treasure including bronze and marble statues, jewellery, furniture, luxury glassware, and the surprisingly complex Antikythera Mechanism. But they were forced to end their mission at the 55-meter-deep site after one diver died of the bends and two were paralyzed. Ever since, archaeologists have wondered if more treasure remains buried beneath the sea bed.
Now a team of international archaeologists including Brendan Foley of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Theotokis Theodoulou of the Hellenic Ephorate of Underwater Antiquities have returned to the treacherous site using state-of-the-art technology. During their first excavation season, from September 15 to October 7, 2014, the researchers have created a high-resolution, 3D map of the site using stereo cameras mounted on an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV). Divers then recovered a series of finds which prove that much of the ship's cargo is indeed still preserved beneath the sediment.
Components of the ship, including multiple lead anchors over a metre long and a bronze rigging ring with fragments of wood still attached, prove that much of the ship survives. The finds are also scattered over a much larger area than the sponge divers realized, covering 300 meters of the seafloor. This together with the huge size of the anchors and recovered hull planks proves that the Antikythera ship was much larger than previously thought, perhaps up to 50 meters long.
"The evidence shows this is the largest ancient shipwreck ever discovered," says Foley. "It's the Titanic of the ancient world."
The archaeologists also recovered a beautiful intact table jug, part of an ornate bed leg, and most impressive of all, a 2-meter-long bronze spear buried just beneath the surface of the sand. Too large and heavy to have been used as a weapon, it must have belonged to a giant statue, perhaps a warrior or the goddess Athena, says Foley. In 1901, four giant marble horses were discovered on the wreck by the sponge divers, so these could have formed part of a complex of statues involving a warrior in a chariot that was pulled by the four horses.
The shipwreck dates from 70 to 60 BC and is thought to have been carrying a luxury cargo of Greek treasures from the coast of Asia Minor west to Rome. Antikythera stands in the middle of this major shipping route and the ship probably sank when a violent storm smashed it against the island's sheer cliffs.
The wreck is too deep to dive safely using regular scuba equipment, so the divers had to use rebreather technology, in which carbon dioxide is scrubbed from the exhaled air while oxygen is introduced and recirculated. This allowed them to dive on the site for up to three hours at a time.
The archaeologists plan to return next year to excavate the site further and recover more of the ship's precious cargo. The finds, particularly the bronze spear, are "very promising," says Theodolou. "We have a lot of work to do at this site to uncover its secrets."
INFORMATION:
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Mass., dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930 on a recommendation from the National Academy of Sciences, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate a basic understanding of the ocean's role in the changing global environment. For more information, please visit http://www.whoi.edu.
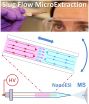
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new technique makes it possible to quickly detect the presence of drugs or to monitor certain medical conditions using only a single drop of blood or urine, representing a potential tool for clinicians and law enforcement.
The technique works by extracting minute quantities of target molecules contained in specimens of blood, urine or other biological fluids, and then testing the sample with a mass spectrometer.
Testing carried out with the technology takes minutes, whereas conventional laboratory methods take hours or days to yield results ...
SAN FRANCISCO -- The information that interprets the genetic code in a new embryo differs depending on whether it comes from the father or mother, researchers at San Francisco State University have found.
The research, detailed in an article published today in the journal PLOS Genetics, sheds light on the multilayered process of how a sperm and egg pass along information needed for successful reproduction. Though one layer is the DNA code that is transferred, the new study identifies information not encoded by DNA, a so-called "epigenetic" layer of information that helps ...
Most women are infected with HIV through vaginal intercourse, and without effective vaccines or microbicides, women who cannot negotiate condom use by their partners remain vulnerable. How exactly the virus establishes infection in the female reproductive tract (FRT) remains poorly understood. A study published on October 9th in PLOS Pathogens reports surprising results from a study of HIV transmission in the FRT of rhesus macaques.
Most studies of HIV transmission after vaginal exposure to date have been done in rhesus macaques and focused on the cervix, the lower part ...
VIDEO:
This video explains research done to understand the motion used by sidewinder snakes to climb sandy slopes and to apply that motion to a snake-like robot. Researchers from Georgia Tech,...
Click here for more information.
The amazing ability of sidewinder snakes to quickly climb sandy slopes was once something biologists only vaguely understood and roboticists only dreamed of replicating. By studying the snakes in a unique bed of inclined sand and using a snake-like robot ...
CANCER RESEARCH UK scientists have discovered that lung cancers can lie dormant for over 20 years before suddenly turning into an aggressive form of the disease, according to a study published in Science* today (Thursday).
The team studied lung cancers from seven patients – including smokers, ex-smokers and never smokers. They found that after the first genetic mistakes that cause the cancer, it can exist undetected for many years until new, additional, faults trigger rapid growth of the disease.
During this expansion there is a surge of different genetic faults ...
When young mice with the rodent equivalent of a rare autism spectrum disorder (ASD), called Rett syndrome, were fed a diet supplemented with the synthetic oil triheptanoin, they lived longer than mice on regular diets. Importantly, their physical and behavioral symptoms were also less severe after being on the diet, according to results of new research from The Johns Hopkins University.
Researchers involved in the study think that triheptanoin improved the functioning of mitochondria, energy factories common to all cells. Since mitochondrial defects are seen in other ...
During their approximately 100-day lifespan in the bloodstream, red blood cells lose membrane surface area, volume, and hemoglobin content. A study publishing this week in PLOS Computational Biology finds that of these three changes, only the observed surface-area loss can be explained by RBCs shedding small hemoglobin-containing vesicles budding off their cells' membrane.
Red blood cell concentration, mean volume, and hemoglobin content are routinely measured in the complete blood count, a fundamental clinical test essential to the screening, diagnosis, and management ...
As birth rates decline in countries that include parts of Europe and East Asia, threatening the economic slowdown associated with aging populations, a global study from the University of California, Berkeley, and the East-West Center in Hawaii suggests that in much of the world, it actually pays to have fewer children. The results challenge previous assumptions about population growth.
Researchers in 40 countries correlated birth rates with economic data and concluded that a moderately low birth rate – a little below two children per woman – can actually ...
A team of scientists including a University of Colorado Boulder professor used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to make the most detailed global map yet of the glow from a giant, oddball planet orbiting another star, an object twice as massive as Jupiter and hot enough to melt steel.
The Hubble observations show that the planet, called WASP-43b, is no place to call home. It's a world of extremes, where winds howl at the speed of sound from a 3,000-degree-Fahrenheit dayside to a pitch-black nightside when temperatures plunge to a relatively cool 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit, ...
Using X-rays and neutron beams, a team of researchers from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, University of Utah and Oak Ridge National Laboratory have teased out new information about Protein Kinase A (PKA), a ubiquitous master switch that helps regulate fundamental cellular functions like energy consumption and interactions with hormones, neurotransmitters and drugs.
"Mutations in PKA can lead to a variety of different human diseases, including cancers, metabolic and cardiovascular diseases and diseases involving the brain and nervous system," ...