(Press-News.org) BOSTON – Email has become one of the most widespread forms of communication, with its streamlined interactions benefiting both businesses and individuals. With the advent of secure patient web portals and the faith that online access has the potential to improve care, the medical industry is slowly catching up.
And while it may take time before it's known what impact email exchanges might have on patients and their care, a new study from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) offers some early insights into the effects on doctors, suggesting that reimbursement models and physician workflow may need to adjust to accommodate message management.
The results were published online in October in Health Affairs.
"BIDMC was one of the first hospitals in the country to create a patient web portal providing a secure platform for patients to view parts of their medical record and send emails to their clinicians," says lead author, Bradley Crotty, MD, Division of Clinical Informatics. "The portal became available in 2000, so we were able to take a 10-year look at the data and examine the email traffic resulting from this new use of technology."
From 2000-2010, nearly 50,000 patients enrolled in BIDMC's patient portal, representing about 23 percent of all patients cared for in the system.
"During the study period we saw a nearly threefold increase in email traffic between patients and doctors," says Crotty. But, he says the driver of the increase appeared not to be individual patients sending more messages, but rather more patients signing on to the portal.
"We saw that over time as patients moved through an early adopter phase and settled in to the idea of communicating this way, the overall number of messages per patient didn't continue to rise, but plateaued over time. However, as more patients enrolled in the portal, physicians' inboxes increased."
The bottom line is that overall, patients didn't message more over time. Still, Crotty found that some doctors exchanged more email than others. Primary care doctors, for example, represented only 40 percent of doctors in the system, but received 85 percent of the email traffic.
"Surveys have shown that patients desire the ability to communicate with their doctors using email, and on face value it seems to be a good idea," says Crotty. "There's a lot of efficiency in being able to send an email and get a response. That type of exchange has the potential to be more respectful of patient's time and possibly the doctor's time too."
Additionally, phase two of the federal program, known as "meaningful use," which is administered by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, includes efforts to improve usage of the patient portals. To receive incentives in phase two of meaningful use, medical providers must meet a threshold of exchanging at least one secure email with five percent of patients within a 90-day window.
"There's been some question about whether that's a high threshold," said Crotty. "But in looking at the data, it appears to be reasonable. At BIDMC, 8.4 percent of the health system's patients sent at least one message to their physician in 2010."
Meaningful use literature cites research demonstrating, among other things, that secure messaging can help improve patient adherence to treatment plans, which, in turn, can reduce hospital readmission rates.
"There's good reason to believe that technology can help improve care," says Bruce Landon, MD, Professor in the BIDMC Division of General Medicine and Primary Care and the Department of Health Care Policy at Harvard Medical School. "Secure messaging can help maintain the doctor/patient relationship outside of the office, aid in patients getting clarity about medical concerns and possibly even play a role in lowering healthcare costs."
But, Crotty, Landon and colleagues ask, in a fee-for-service model of care, how do doctors get reimbursed for email time? And as the healthcare industry moves toward managed care models, where email exchanges will likely become an increasingly more important tool, how can doctors better incorporate email exchanges into the flow of their already busy work days?
"We're convinced that technology has an important place in healthcare delivery and that email between clinicians and patients will remain an essential element even as care models move forward," says Crotty. "But it may require some policy changes and will most certainly involve adjusting the doctor's day, building in time going forward to meet patient demand for email communication."
INFORMATION:
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is a patient care, teaching and research affiliate of Harvard Medical School, and currently ranks third in National Institutes of Health funding among independent hospitals nationwide.
BIDMC is in the community with Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital-Milton, Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital-Needham, Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital-Plymouth, Anna Jaques Hospital, Cambridge Health Alliance, Lawrence General Hospital, Signature Healthcare, Beth Israel Deaconess HealthCare, Community Care Alliance, and Atrius Health. BIDMC is also clinically affiliated with the Joslin Diabetes Center and Hebrew Senior Life and is a research partner of Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center. BIDMC is the official hospital of the Boston Red Sox. For more information, visit http://www.bidmc.org.
Super Typhoon Vongfong continued on its trek north through the Philippine Sea while slightly weakening on Oct. 10. NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites provided forecasters with cloud extent, rainfall rates and distribution and more.
Vongfong was a super typhoon with wind maximum sustained winds of 145 knots (167 mph) when the TRMM satellite flew over on October 8, 2014 at 2328 UTC 7:28 p.m. EDT). TRMM's Microwave Imager showed that Vongfong was producing rainfall over a large area and heavy rainfall in the eye wall (the powerful thunderstorms around the open eye) and in multiple ...
DURHAM, N.C. –- No single "one-size-fits-all" model can explain how biodiversity hotspots come to be, finds a study of more than 700 species of reptiles and amphibians on the African island of Madagascar.
By analyzing the geographic distribution of Madagascar's lizards, snakes, frogs and tortoises, an international team of researchers has found that each group responded differently to environmental fluctuations on the island over time.
The results are important because they suggest that climate change and land use in Madagascar will have varying effects on different ...
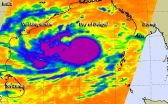
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Hudhud on Oct. 10 as it reached hurricane-force.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite read temperatures of thunderstorm cloudtops that make up Tropical Cyclone Hudhud when it passed overhead on Oct. 9 at 19:53 UTC (3:53 p.m. EDT). The data showed the coldest cloud top temperatures were in thunderstorms circling a developing eye. Cloud top temperatures were as cold as -63F/-53C, which have the potential for dropping heavy rainfall.
Hudhud's maximum sustained winds ...
Small cues that display a user's transaction history may help a website feel almost as interactive as chatting with an online customer service agent, paving the way for more cost-effective websites, according to researchers.
"One of the challenges with online interactivity is trying to imbue the site with a sense of contingency -- the back-and-forth feel of a real conversation," said S. Shyam Sundar, Distinguished Professor of Communications and co-director of the Media Effects Research Laboratory. "What we found is that providing some information about a user's interaction ...
A new study led by a Canadian marine zoologist reviews the world list of specialist driftwood talitrids, which so far comprises a total of 7 representatives, including two newly described species. These tiny animals with peculiar habits all live in and feed on decomposing marine driftwood. Dispersed across distant oceanic islands they use floating driftwood to hitch a ride to their destination. The study was published in the open access journal Zoosystematics and Evolution.
Tourists are familiar with talitrids as sandhoppers, found in burrows on sand beaches, or shorehoppers, ...
New clinical research from UC San Francisco shows that 341 HIV-infected men who reported using stimulants such as methamphetamine or cocaine derived life-saving benefits from being on antiretroviral therapy that were comparable to those of HIV-infected men who do not use stimulants.
That said, those who reported using stimulants at more than half of at least two study visits did have modestly increased chances of progressing to AIDS or dying after starting antiretroviral therapy compared to non-users. The data was collected between 1996 and 2012.
"Patients with HIV ...
PHILADELPHIA –The pneumococcal vaccine recommended for young children not only prevents illness and death, but also has dramatically reduced severe antibiotic-resistant infections, suggests nationwide research being presented at IDWeek 2014™. Pneumococcal infection – which can cause everything from ear infections to pneumonia and meningitis – is the most common vaccine-preventable bacterial cause of death.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), first available in 2010 (replacing 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, PCV7), reduced the ...
PHILADELPHIA – Old-school face-to-face social networking is a more effective way to identify people with HIV than the traditional referral method, suggests research being presented at IDWeek 2014™. The study shows that social networking strategies (SNS) – enlisting people in high-risk groups to recruit their peers to get tested – is more efficient and targeted than traditional testing and referral programs, resulting in 2-1/2 times more positive test results.
As many as 20 percent of HIV-positive people are unaware of being infected with the virus, ...
The experiments were carried out on endofullerenes, molecules of C60 into which smaller molecules of Hydrogen (H2) had been inserted. The results, published in Physical Review Letters, represent the first known example of a quantum selection rule found in a molecule.
Similar techniques were also used by the same team to uncover an exciting new symmetry-breaking interaction of water molecules with C60 cages, published last month in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics.
The use of fullerenes such as C60 to trap smaller molecules, using cutting-edge molecular surgery techniques, ...
This news release is available in German.
The distance between the Earth and the Sun has no influence on the decay rate of radioactive chlorine. You could ask: "And why should it anyway?", because it is well known that the decay of radionuclides is as reliable as a Swiss clock. Recently, US-American scientists, however, attracted attention when they postulated that the decay rate depends on the flow of solar neutrinos and, thus, also on the distance from the Earth to the Sun. Their assumption was based, among other things, on older measurement data of the Physikalisch-Technische ...