(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. — An oral biologic medication has successfully treated chronic, precancerous inflammation in the intestine, according to results of an animal study authored by an MD/PhD student in the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences.
The study is featured on the cover of the current issue of Cancer Research; it was published online ahead of print in September. The journal's editors characterized the study's findings as "striking."
Inflammatory cells in the colon, or polyps, are very common after the age of 50. The average 60-year-old has an estimated 25 percent chance of having polyps. Most polyps are benign, but some will develop into colon cancer. For that reason, the standard treatment for polyps is to remove them.
"Our most important finding is that disease-promoting inflammatory cells in the mouse intestine can be targeted by oral formulations of purified cellular proteins, rendering the inflammatory cells less able to cause disease," says first author Allen Chung, an MD/PhD student in the UB medical school's Medical Scientist Training Program.
According to the paper, this is one of the first times an oral biologic has been used successfully to change the natural history of a genetic disease; in this case, a mutation that puts individuals at very high risk for colon cancer.
Oral biologics are drugs based on biological molecules derived from natural substances from humans, animals or microorganisms. Oral biologics have an obvious advantage over other biologics, which must be injected or otherwise administered.
But even though it was administered orally, the drug used in the study did not deliver its pharmaceutical payload until it reached the intestinal surface.
"We found that high pharmacologic levels of the bioactive drug of interest can be achieved at the intestinal surface without systemic circulation of the drug," Chung explains, so the drug can be administered without the threat of potential toxicities associated with exposure to kidney, liver and brain tissue.
Using animal models of precancerous polyps in the bowel, Chung and his team determined that certain types of immune cells within a chronically inflamed intestine can become rewired, causing them — paradoxically — to contribute to disease development rather than protect against it.
The researchers went on to reprogram these immune cells, making them lose their pathogenic potential.
They did it by delivering immuno-modulatory compounds — specifically, the bioactive protein interleukin-10 — into the inflamed intestine, which reduced both the speed and severity of polyp formation. Interleukin-10 was administered as a whole recombinant protein encapsulated within polymer micro-particles, a process originally developed by some of Chung's collaborators at Brown University.
This, in turn, significantly benefited the mice, relieving symptoms including anemia, enlarged spleen and weight loss, and lengthening their lifespan.
"Site-specific oral therapy for intestinal disorders is a promising avenue of research," says Chung, whose findings formed the basis for his doctoral thesis at UB.
Chung became interested in exploring the relationship between inflammation and polyp formation as a PhD candidate in UB's Department of Microbiology and Immunology. He began investigating how immunologic activity in the intestine may contribute to the development of precancerous polyps — or polyposis — within the bowel.
"It has long been known that inflammation within the colon increases the risk of developing colon cancer," says Chung. Rates of colon cancer are much higher in individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, than in the overall population, he notes.
"There are also genetic mutations that predispose individuals to develop colon cancer in early adulthood — and these individuals have been found to develop intestinal inflammation even before the appearance of their neoplastic disease," he says.
Chung and his co-author and doctoral mentor Nejat Egilmez, PhD, formerly of UB and now at the University of Louisville, have applied for patent protection on the research.
"We are now involved in studies which hope to determine whether some of the immunologic phenomenon we observed in our mouse models are representative of intestinal disease in human patients who harbor genetic mutations which predispose them to develop colon cancer," says Chung.
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors are from UB's Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Life Sciences; Roswell Park Cancer Institute; the Wadsworth Center (New York State Department of Health); Brown University; Northwestern University; and the University of Florida.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Oral drug reduces formation of precancerous polyps in the colon, UB researchers find
Journal editors call findings of animal study 'striking'
2014-10-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA satellite sees wind shear affecting Tropical Storm Vongfong
2014-10-14
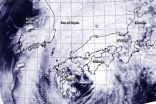
Tropical Storm Vongfong continues to weaken as it tracks across the big islands of Japan, and NASA satellite data showed that westerly wind shear is taking its toll on the storm's structure.
On Oct. 12 at 0500 UTC (1 a.m. EDT), the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Vongfong approaching Japan. Despite weakening to a tropical storm, Vongfong still appeared to have an eye as its northeastern quadrant blanketed the large island of Kyushu, Japan. By 11 a.m. EDT, Maximum sustained winds had dropped to 55 knots (63 mph/102 kph). ...
Tropical Storm Gonzalo triggered many warnings in Eastern Caribbean
2014-10-14
The Eastern Caribbean islands were getting the brunt of Tropical Storm Gonzalo as the storm slowly moved through on Oct. 13. NASA's Terra satellite and NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided data on the storm. Gonzalo is the sixth named storm in the Atlantic Ocean Hurricane Season.
On Oct. 12 at 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT), NASA's Terra satellite flew over Tropical Storm Gonzalo while it moved over the Lesser Antilles. The MODIS instrument captured a visible image of the storm that showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation and in a thick ...
Satellites confirm Fay weakened to a Tropical Storm
2014-10-14
The fifth named Atlantic storm didn't maintain hurricane status long. Fay became a hurricane late on Oct. 12 and by early on Oct. 13, had weakened back to a tropical storm.
A visible image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on Oct. 13 at 1145 UTC (7:45 a.m. EDT) showed Tropical Storm Fay northeast of Bermuda and Tropical Storm Gonzalo over the Lesser Antilles. Fay appeared circular, but didn't have the signature shape of a tropical storm like Gonzalo, with bands of thunderstorms spiraling into the center. The image was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard ...
ORNL researchers make first observation of atoms moving inside bulk material
2014-10-14
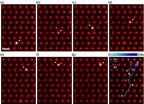
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Oct. 13, 2014 -- Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have obtained the first direct observations of atomic diffusion inside a bulk material. The research, which could be used to give unprecedented insight into the lifespan and properties of new materials, is published in the journal Physical Review Letters (06 October 2014, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.155501).
"This is the first time that anyone has directly imaged single dopant atoms moving around inside a material," said Rohan Mishra of Vanderbilt University who ...
Charged graphene gives DNA a stage to perform molecular gymnastics
2014-10-14
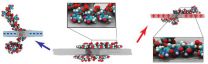
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When Illinois researchers set out to investigate a method to control how DNA moves through a tiny sequencing device, they did not know they were about to witness a display of molecular gymnastics.
Fast, accurate and affordable DNA sequencing is the first step toward personalized medicine. Threading a DNA molecule through a tiny hole, called a nanopore, in a sheet of graphene allows researchers to read the DNA sequence; however, they have limited control over how fast the DNA moves through the pore. In a new study published in the journal Nature ...
Scientists sniff out unexpected role for stem cells in the brain
2014-10-14
For decades, scientists thought that neurons in the brain were born only during the early development period and could not be replenished. More recently, however, they discovered cells with the ability to divide and turn into new neurons in specific brain regions. The function of these neuroprogenitor cells remains an intense area of research. Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) report that newly formed brain cells in the mouse olfactory system — the area that processes smells — play a critical role in maintaining proper connections. The results ...
Light-activated drug could reduce side effects of diabetes medication
2014-10-14
Scientists have created a drug for type 2 diabetes that is switched on by blue light, which they hope will improve treatment of the disease.
Diabetes drugs that promote the release of insulin from the pancreas can in some cases cause side effects due to their actions on other organs such as the brain and heart. Some can also stimulate too much insulin release, causing blood sugar levels to drop too low.
To help create better drugs, researchers at Imperial College London and LMU Munich adapted an existing type of drug called a sulfonylurea so that it changes shape when ...
New forecasting method: Predicting extreme floods in the Andes mountains
2014-10-14
This might allow for improved disaster preparedness. As the complex systems technique builds upon a mathematical comparison that can be utilised for any time series data, the approach could be applied to extreme events in all sorts of complex systems.
"Current weather forecast models cannot capture the intensity of the most extreme rainfall events, yet these events are of course the most dangerous, and can have severe impacts for the local population, for example major floods or even landslides," says lead author Niklas Boers of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact ...
Teenage baseball pitchers at risk for permanent shoulder injury
2014-10-14
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Young baseball pitchers who throw more than 100 pitches per week are at risk for a newly identified overuse injury that can impede normal shoulder development and lead to additional problems, including rotator cuff tears, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
The injury, termed acromial apophysiolysis by the researchers, is characterized by incomplete fusion and tenderness at the acromion. The acromion, which forms the bone at the top or roof of the shoulder, typically develops from four individual bones into one bone ...
New clues behind the resilience of a leading sexually transmitted pathogen, Chlamydia
2014-10-14
In the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution, authors Domman, et al. have explored factors behind the resilience of the most common sexually transmitted disease in the U.S., chlamydia, with an estimated 1 million infected.
The research team sequenced 4 new strains of close genetic cousins of chlamydial pathogens, and examined these with existing DNA data. They found an extensive and robust shuffling of the genomic deck between chlamydia families has played a major role in the evolution of the pathogen, often serving to outwit and exploit its hosts. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Oral drug reduces formation of precancerous polyps in the colon, UB researchers findJournal editors call findings of animal study 'striking'