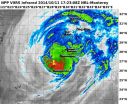
(Press-News.org) The once-powerful Category 5 Typhoon Vongfong has fortunately weakened to a barely Category 1 typhoon as it approaches the big islands of Japan. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite and NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Vongfong on Oct. 11 and noticed the heaviest precipitation was north of the center.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Vongfong on Oct. 11 at 17:23 UTC (1:23 p.m. EDT) and captured an infrared image of the storm from the VIIRS instrument. The VIIRS instrument showed that the strongest thunderstorms that stretched highest in the atmosphere were in the northern quadrant of the storm. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Vongfong on Oct. 11 at 04:15 UTC (12:15 a.m. EDT) and the MODIS instrument captured a visible picture of the storm that showed the eye had become cloud-filled.
On Oct. 11 at 2100 UTC (5 p.m. EDT), Typhoon Vongfong's maximum sustained winds had dropped to 65 knots (75 mph/120 kph), making it a minimal Category 1 typhoon on the Saffir-Simpson scale. It was centered near 7.4 north and 128.0 east, about 32 nautical miles (36.8 miles/59.2 kph) north-northeast of Kadena Air Base, Okinawa, Japan. Vongfong was moving to the north-northeast at 9 knots (10.3 mph//16.6 kph).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted on Oct. 11 at 5 pm EDT, that radar showed the overall structure of the system has started to deteriorate and become elongated. The strongest winds were located on the northern side of the storm. For current warnings and watches from the Japan Meteorological Agency, visit: http://www.jma.go.jp/en/warn/.
Over the next two days, Vongfong is forecast to speed up and become embedded in the mid-latitude westerly winds, which will cause it to spread out and look more like a frontal system as it changes into an extra-tropical storm.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast calls for the center of Typhoon Vongfong (as a tropical storm) to track over the island of Kyushu, then Shikoku, then the big island of Honshu, on which the capital, Tokyo, is located. Vongfong's center is expected to the west of Tokyo, moving northeast, and exiting back into the northwestern Pacific Ocean south of the city of Misawa.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees a weaker Typhoon Vongfong near Amami Oshima
2014-10-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees Cyclone Hudhud approaching India's coast
2014-10-14
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Hudhud as it was nearing east-central India's coastline on Oct. 11.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua captured infrared data on the storm on Oct. 11 at 07:23 UTC (3:23 a.m. EDT) that showed cloud top temperatures had dropped, indicating stronger uplift and stronger thunderstorms. That's an indication that the storm has strengthened in the last day.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated infrared satellite imagery shows the eye feature has become cloud filled while the overall structure ...
Satellite sees cold front headed to absorb Bermuda's Tropical Storm Fay
2014-10-14
VIDEO:
This animation of imagery from NOAA GOES-East satellite from Oct. 10-12 shows the movement of Tropical Storm Fay in the Atlantic an approaching cold front over the eastern US....
Click here for more information.
Tropical Storm Fay is affecting Bermuda on Sunday, Oct. 12, but a cold front over the eastern U.S. is expected to absorb the storm over the next day or two. Both were seen in an image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite.
On Saturday, Oct. 11, Tropical Depression 7 ...
NASA sees newborn Tropical Storm Gonzalo form and threaten Caribbean islands
2014-10-14
Tropical Storm Gonzalo formed quickly on Oct. 12 just east of the Leeward Islands, triggering tropical storm warnings for many islands. NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured an image of the newborn storm on Sunday, Oct. 12, and Tropical Storm Fay northeast of Bermuda.
The GOES East satellite is a geostationary satellite managed by NOAA. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland the NASA/NOAA GOES Project creates images and animations and today's visible image, taken at 2:45 p.m. EDT showed a smaller Gonzalvo east of the Leeward Islands while Fay was ...
One gene links susceptibility to rare infections with predisposition to autoimmune disease
2014-10-14
The mutations were familiar, but the patients' conditions seemed baffling at first. A team lead by Rockefeller University researchers had linked variations in an immune gene to rare bacterial infections. Shortly afterward, Chinese scientists told them of three children in that country with mutated versions of the same gene. However, the Chinese children had no history of the severe bacterial infections. Instead, they had seizures and unusual calcium deposits deep in their brains.
This discrepancy led to the discovery of an immune protein with paradoxical roles: It both ...
Antibiotic resistance: Bacterial defense policies
2014-10-14
High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy has now revealed in unprecedented detail the structural changes in the bacterial ribosome which results in resistance to the antibiotic erythromycin.
Multiresistant bacterial pathogens that are insensitive to virtually all available antibiotics are one of the major public-health challenges of our time. The question of how resistance to various antibiotics develops is the focus of research being carried out by Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich biochemist Daniel Wilson and his colleagues. As they report in the journal ...
Scientists identify potential cause for 40 percent of pre-term births
2014-10-14
Scientists from Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) and UCL (University College London) have identified what they believe could be a cause of pre-term premature rupture of the fetal membrane (PPROM), which accounts for 40 per cent of pre-term births, and is the main reason for infant death world-wide.
The researchers, whose work was funded by the charity Wellbeing of Women, used bioengineering techniques to test the effect of repetitive stretch on tissues of the amniotic membrane which surrounds and protects the baby prior to birth.
They found that stretching of the ...
Balancing renewable energy costs
2014-10-14
New York | Heidelberg, 13 October 2014 Increasing reliance on renewable energies is the way to achieve greater CO2 emission sustainability and energy independence. As such energies are yet only available intermittently and energy cannot be stored easily, most countries aim to combine several energy sources. In a new study in EPJ Plus, French scientists have come up with an open source simulation method to calculate the actual cost of relying on a combination of electricity sources. Bernard Bonin from the Atomic Energy Research Centre CEA Saclay, France, and colleagues demonstrate ...
Ultra-fast charging batteries that can be 70 percent recharged in just 2 minutes
2014-10-14
Scientists from Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) have developed a new battery that can be recharged up to 70 per cent in only 2 minutes. The battery will also have a longer lifespan of over 20 years.
Expected to be the next big thing in battery technology, this breakthrough has a wide-ranging impact on many industries, especially for electric vehicles which are currently inhibited by long recharge times of over 4 hours and the limited lifespan of batteries.
This next generation of lithium-ion batteries will enable electric vehicles to charge 20 times ...
Older women more likely to have multiple health conditions
2014-10-14
In the context of an aging population, the number of cases of people with multimorbidity, or multiple health conditions, is increasing, creating significant healthcare challenges. Now, the first comprehensive systematic review in this field has found higher levels of multimorbidity in women. Equally as importantly, it has revealed the poor quality of evidence on this increasingly critical area of healthcare.
The review's main author, Professor Jose M Valderas, NIHR Clinician Scientist of the University of Exeter Medical School, is calling for better quality research to ...
Bio-inspired 'nano-cocoons' offer targeted drug delivery against cancer cells
2014-10-14
Biomedical engineering researchers have developed a drug delivery system consisting of nanoscale "cocoons" made of DNA that target cancer cells and trick the cells into absorbing the cocoon before unleashing anticancer drugs. The work was done by researchers at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
"This drug delivery system is DNA-based, which means it is biocompatible and less toxic to patients than systems that use synthetic materials," says Dr. Zhen Gu, senior author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor in ...