(Press-News.org) Responding to the large number of people with serious mental illnesses in the criminal justice system will require more than mental health services, according to a new report.
In many ways, the criminal justice system is the largest provider of mental health services in the country. Estimates vary, but previous research has found that about 14 percent of persons in the criminal justice system have a serious mental illness, and that number is as high as 31 percent for female inmates.
Researchers are defining serious mental illnesses to include such things as schizophrenia, bipolar spectrum disorders and major depressive disorders.
"It has been assumed that untreated symptoms of mental illness caused criminal justice involvement, but now we're seeing that there is little evidence to support that claim," said Matthew Epperson, assistant professor at the University of Chicago School of Social Service Administration. Specialized interventions for people with mental illness in the criminal justice system have been developed over the past 20 years, such as mental health courts and jail diversion programs, Epperson said.
"But we need a new generation of interventions for people with serious mental health issues who are involved in the criminal justice system, whether it be interactions with police, jails, probation programs and courts," he said. "Research shows that people with serious mental illnesses, in general, display many of the same risk factors for criminal involvement as persons without these conditions."
Epperson and his colleagues are the authors of a paper in the September–October 2014 theme issue on "New Directions in Corrections and Mental Health," published by the International Journal of Law and Psychiatry.
More potent interventions are needed, the study's authors report. "First, effective and accessible mental health treatment will be an active component of any intervention for this population," said Epperson. He adds that it is vital to develop a better understanding of the many factors, in addition to mental illness, that place persons with serious mental illness at risk for criminal involvement. There is also a need to define which risk factors are modifiable as targets for the next generation of interventions.
In addition to mental illness, the researchers identified factors that contribute to a person becoming involved in the criminal justice system, including a tendency for criminal thinking, antisocial attitudes, substance abuse and addictions, and trauma exposure.
The study additionally reports that people with serious mental illnesses are frequently unemployed and homeless. They might also be receiving assistance to live in areas of poverty with few services, including mental health treatment centers.
Reacting in unhealthy ways to stress, including acting out frustration through violence, self-medication through drugs, alcohol, sex, gambling, or other reckless behavior, can result in encounters with the justice system, explained Epperson. He added that persons with severe mental illnesses often do not have good coping skills or social support systems.
"We need to move our collective thinking away from the uncomplicated notion that mental illness is the sole cause of criminal behavior and criminal justice involvement," Epperson said. The study's authors suggest an intervention program targeting multiple issues, including medication adherence, developing alternatives to criminal thinking patterns, providing supports for more stable and healthy living situations and personal relationships, decreasing substance abuse, helping to build skills to reduce stress and addressing trauma exposure and its negative effects.
Epperson said a social work perspective is extremely beneficial to these efforts, as it will be necessary to influence both the person and their environment.
Epperson is applying the lessons from this study to his classes at SSA in an effort to educate a new generation of social workers who can be at the forefront of developing more effective interventions for this population.
"The ultimate goal of these next generation interventions is to alleviate the overrepresentation of people with serious mental illnesses in the criminal justice system, and that will require significant changes to existing interventions, alongside completely new and innovative approaches," Epperson concluded.
INFORMATION:
WORCESTER, MA – A team of scientists led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Medical School (UMMS) and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine (UMMSM) have identified what is likely a key genetic pathway underlying bipolar (manic depressive) disorder, a breakthrough that could lead to better drugs for treating bipolar affective disorder, as well as depression and other related mood disorders.
The new findings, published online this week in Nature Molecular Psychiatry, show that a rare genetic dwarfism called Ellis van-Creveld (EvC) syndrome ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. – As more and more high schools around the country drop home economics classes due to budget cuts or changes in educational priorities, many high school students are left without basic skills, such as preparing meals and sewing. Now, researchers have found that a significant gap exists in the amount of "common" clothes repair skills possessed by members of the baby boomer generation and millennials. Pamela Norum, a professor in the Department of Textile and Apparel Management in the MU College of Human Environmental Sciences, found that many more of ...
NASA's MAVEN spacecraft has provided scientists their first look at a storm of energetic solar particles at Mars and produced unprecedented ultraviolet images of the tenuous oxygen, hydrogen and carbon coronas surrounding the Red Planet, said University of Colorado Boulder Professor Bruce Jakosky, the mission's principal investigator.
In addition, the new observations allowed scientists to make a comprehensive map of highly variable ozone in the Martian atmosphere underlying the coronas, he said. The spacecraft entered Mars' orbit Sept. 21 and is in the process of lowering ...
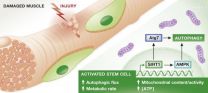
HEIDELBERG, 14 October 2014 – Researchers from Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered a link between a protective mechanism used by cells and the activation of muscle stem cells. Cells use autophagy to recycle cellular "building blocks" and generate energy during times of nutrient deprivation. The scientists report in The EMBO Journal that when this protective mechanism is operational it also seems to assist in the activation of stem cells.
"Our study reveals that when stem cells emerge from a quiescent state there is a rapid and dramatic change in ...
Humans have a focus on the short term. We are more interested in a potential benefit if we can get it now.
The ability to delay gratification has been studied in children with the "marshmallow test": a child can have one treat now, or two if he or she can wait a few minutes without gobbling the first treat.
Psychologists and economists have shown that similar trends can be observed and measured in many spheres of life. They call the tendency for the perceived value of a delayed benefit to diminish "delay discounting."
Now researchers at Marcus Autism Center are studying ...
Cyclone Hudhud made landfall in east-central India on Oct. 12 and caused a lot of damage and several fatalities as it moved inland and weakened to a remnant low pressure area. NASA saw those remnants on Oct. 14.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Indochina, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided picture proof that the remnants of Typhoon Hudhud were still over India, Nepal, and China. Aqua passed over the region on Oct. 14 at 08:05 UTC (4:05 a.m. EDT).
Infrared satellite imagery and multispectral satellite imagery indicated ...
On 3 October 2014, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) hosted a meeting with representatives of Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) to discuss RCE's recent publication of a consensus paper on the methodology of clinical trials in rare cancers (1).
Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) is a multi stakeholder initiative promoted by ESMO (representing healthcare professionals, patients and industry) dedicated to putting rare cancers on the European political agenda. In their consensus document, RCE argue that a higher degree of uncertainty should be accepted for regulatory as well as clinically ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Neurons are electrically charged cells, located in the nervous system, that interpret and transmit information using electrical and chemical signals. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that individual neurons can react differently to electrical signals at the molecular level and in different ways—even among neurons of the same type. This variability may be important in discovering underlying problems associated with brain disorders and neural diseases such as epilepsy.
"Genetic mutations found in neurological disorders ...
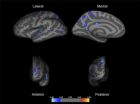
Under the rule of dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, thousands of Romanian children were placed in overcrowded orphanages with bleak conditions and minimal human contact. Even after the 1989 revolution, the legacy of institutionalization continued. Only recently has research and public concern over early childhood environments caused changes in policies.
University of Washington research on children who began life in these institutions shows that early childhood neglect is associated with changes in brain structure. A paper published this month in Biological Psychiatry shows ...
LEBANON, NH – The foundation of evidence-based research has eroded and the trend must be reversed so patients and clinicians can make wise shared decisions about their health, say Dartmouth researchers in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Drs. Glyn Elwyn and Elliott Fisher of The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice are authors of the report in which they highlight five major problems set against a backdrop of "obvious corruption." There is a dearth of transparent research and a low quality of evidence synthesis. ...