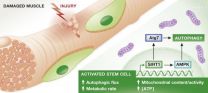
(Press-News.org) HEIDELBERG, 14 October 2014 – Researchers from Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered a link between a protective mechanism used by cells and the activation of muscle stem cells. Cells use autophagy to recycle cellular "building blocks" and generate energy during times of nutrient deprivation. The scientists report in The EMBO Journal that when this protective mechanism is operational it also seems to assist in the activation of stem cells.
"Our study reveals that when stem cells emerge from a quiescent state there is a rapid and dramatic change in their metabolic activity," says Thomas Rando Professor at Stanford University School of Medicine and the lead author of the study. "The induction of autophagy seems to be a critical component of these metabolic shifts and allows stem cells to cope with the stressful demands for nutrients and the building blocks for the synthesis of large molecules like proteins and DNA that arise due to the rapid growth of the cell."
Autophagy involves the engulfment of cellular organelles into specialized vacuoles surrounded by a double membrane. The contents of these vacuoles are delivered to the lysosome, another organelle within the cell, where they are degraded to useful small molecules and help to generate energy and biomass for the synthesis of macromolecules and new organelles.
When stem cells are activated, cells experience large changes in their metabolism since they require increased biosynthesis of proteins and other large molecules. The scientists discovered that autophagy is turned on when muscle stem cells are activated. They also showed that when autophagy was inhibited the activation of the stem cells was delayed.
The researchers were also able to demonstrate that a known nutrient sensor, SIRT1, regulates autophagy in the muscle stem cells. When they interfered with this protein using genetic methods or treatment with chemical inhibitors they were able to delay the activation of muscle stem cells. "This study identifies increased autophagy as a crucial checkpoint in the activation of muscle stem cells," says Professor Amy Wagers, a Professor the Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology at Harvard University and Harvard Stem Cell Institute who is not an author of the study.INFORMATION:
Induction of autophagy supports the bioenergetic demands of quiescent muscle stem cell activation
doi: 10.15252/embj.201488278
Anne H. Tang and Thomas A. Rando
The paper and further information on The EMBO Journal is available at emboj.embopress.org
Media Contacts
Barry Whyte
Head | Public Relations and Communications
barry.whyte@embo.org
Thomas Schwarz-Romond
Senior Editor, The EMBO Journal
Tel: +49 6221 8891 407
schwarzr@embo.org
About EMBO
EMBO is an organization of more than 1700 leading researchers that promotes excellence in the life sciences. The major goals of the organization are to support talented researchers at all stages of their careers, stimulate the exchange of scientific information, and help build a European research environment where scientists can achieve their best work.
EMBO helps young scientists to advance their research, promote their international reputations and ensure their mobility. Courses, workshops, conferences and scientific journals disseminate the latest research and offer training in techniques to maintain high standards of excellence in research practice. EMBO helps to shape science and research policy by seeking input and feedback from our community and by following closely the trends in science in Europe. For more information: http://www.embo.org
Autophagy helps fast track stem cell activation
2014-10-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Testing parents' patience, while treating kids' problem behavior
2014-10-14
Humans have a focus on the short term. We are more interested in a potential benefit if we can get it now.
The ability to delay gratification has been studied in children with the "marshmallow test": a child can have one treat now, or two if he or she can wait a few minutes without gobbling the first treat.
Psychologists and economists have shown that similar trends can be observed and measured in many spheres of life. They call the tendency for the perceived value of a delayed benefit to diminish "delay discounting."
Now researchers at Marcus Autism Center are studying ...
NASA satellite spots Hudhud's remnants
2014-10-14
Cyclone Hudhud made landfall in east-central India on Oct. 12 and caused a lot of damage and several fatalities as it moved inland and weakened to a remnant low pressure area. NASA saw those remnants on Oct. 14.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Indochina, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided picture proof that the remnants of Typhoon Hudhud were still over India, Nepal, and China. Aqua passed over the region on Oct. 14 at 08:05 UTC (4:05 a.m. EDT).
Infrared satellite imagery and multispectral satellite imagery indicated ...
EMA open to discuss use of complementary methodologies for rare cancers
2014-10-14
On 3 October 2014, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) hosted a meeting with representatives of Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) to discuss RCE's recent publication of a consensus paper on the methodology of clinical trials in rare cancers (1).
Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) is a multi stakeholder initiative promoted by ESMO (representing healthcare professionals, patients and industry) dedicated to putting rare cancers on the European political agenda. In their consensus document, RCE argue that a higher degree of uncertainty should be accepted for regulatory as well as clinically ...
New information about how neurons act could lead to brain disorder advancements
2014-10-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Neurons are electrically charged cells, located in the nervous system, that interpret and transmit information using electrical and chemical signals. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that individual neurons can react differently to electrical signals at the molecular level and in different ways—even among neurons of the same type. This variability may be important in discovering underlying problems associated with brain disorders and neural diseases such as epilepsy.
"Genetic mutations found in neurological disorders ...
Orphanage care linked to thinner brain tissue in regions related to ADHD
2014-10-14
Under the rule of dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, thousands of Romanian children were placed in overcrowded orphanages with bleak conditions and minimal human contact. Even after the 1989 revolution, the legacy of institutionalization continued. Only recently has research and public concern over early childhood environments caused changes in policies.
University of Washington research on children who began life in these institutions shows that early childhood neglect is associated with changes in brain structure. A paper published this month in Biological Psychiatry shows ...
Corruption of the health care delivery system
2014-10-14
LEBANON, NH – The foundation of evidence-based research has eroded and the trend must be reversed so patients and clinicians can make wise shared decisions about their health, say Dartmouth researchers in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Drs. Glyn Elwyn and Elliott Fisher of The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice are authors of the report in which they highlight five major problems set against a backdrop of "obvious corruption." There is a dearth of transparent research and a low quality of evidence synthesis. ...
Personalised treatment for stress-related diabetes
2014-10-14
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden are testing a treatment for type 2 diabetes which targets the disease mechanism itself - and not just the symptoms. For the first time, knowledge about the individual patient's genetic risk profile is being used. The treatment completely restores the capacity to secrete insulin, which is impaired by the risk gene.
"The concept of treatment personalised to the individual's risk profile has great potential. Our results show that it is possible to block the effects of a common risk gene for type 2 diabetes", says Anders Rosengren, ...
Are there enough fish to go around?
2014-10-14
Scientists from the University of York have released a report highlighting the gap between declining wild fish supplies and healthy eating advice recommending more seafood.
While the health benefits of eating fish have become better appreciated in recent years, many wild fish stocks continue to be overfished.
In a study published in Marine Pollution Bulletin, Dr Ruth Thurstan, now a Research Fellow at the University of Queensland, and Professor Callum Roberts, Professor of Marine Conservation at the University of York, used historical fisheries data and population ...
Immune cells in the liver drive fatty liver disease and liver cancer
2014-10-14
The results of their research have been published as the cover story of the renowned medical journal Cancer Cell.
Fatty liver disease – alongside fatty liver due to massive alcohol consumption – is mainly caused by excessive consumption of fat and sugar combined with a lack of exercise or a sedentary life style. This is referred to as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). If NAFLD becomes chronic – e.g. through the constant uptake of high lipids and high sugar combined with lack of excercise a chronic inflammatory response is triggered in the liver ...
Parkinson: How toxic proteins stress nerve cells
2014-10-14
This news release is available in German. FRANKFURT Parkinson's Disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder. In Germany alone, almost half a million people are affected. The focus of the disease is the progressive degeneration of dopamine-producing nerve cells in a certain region of the midbrain, the substantia nigra. Misfolded proteins are the cause. Until recently, it was unclear why damage is confined to specific nerve cells. A team or researchers led by Frankfurt neurophysiologists has now defined how this selective disease process begins using ...