(Press-News.org) According to Nationwide Children's Hospital researchers, 63,000 children under the age of six experienced out-of-hospital medication errors annually between 2002 and 2012. One child is affected every eight minutes, usually by a well-meaning parent or caregiver unintentionally committing a medication error.
The most common medication mistakes in children under the age of six occur in the children's home, or another residence and school. The most common medicines involved are painkillers and fever-reducers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
"This is more common than people may realize," said Huiyun Xiang, MD, MPH, PhD, director of the Center for Pediatric Trauma Research at Nationwide Children's Hospital, principal investigator at the hospital's Center for Injury Research and Policy. "The numbers we report still underestimate the true magnitude of these incidents since these are just cases reported to national poison centers."
Instances in which these mistakes can occur include caregivers giving one child the same medication twice, misreading dosing instructions or administering the wrong medication.
"We found that younger children are more apt to experience error than older children, with children under age one accounting for 25 percent of incidents," said Xiang, senior author of the study published by Pediatrics online today and also a faculty member at The Ohio State University College of Medicine.
"There are public health strategies being used to decrease the frequency and severity of medication errors among young children," said Henry Spiller, director of the Central Ohio Poison Center and co-author of the study. "Product packaging needs to be redesigned in a way that provides accurate dosing devices and instructions, and better labeling to increase visibility to parents."
INFORMATION:
Data for this first-known comprehensive national study of its kind, conducted by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy and the Central Ohio Poison Center, both at Nationwide Children's Hospital, and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, came from the National Poison Database System, the most comprehensive and accurate database available for investigation of pediatric out-of-hospital medication errors in the U.S.
The Center for Injury Research and Policy (CIRP) of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital works globally to reduce injury-related pediatric death and disabilities. With innovative research at its core, CIRP works to continually improve the scientific understanding of the epidemiology, biomechanics, prevention, acute treatment and rehabilitation of injuries. CIRP serves as a pioneer by translating cutting edge injury research into education, policy, and advances in clinical care. To learn more about CIRP, visit http://www.injurycenter.org.
The Central Ohio Poison Center provides central and southeastern Ohio residents with state-of-the-art poison prevention, assessment and treatment. The center services are available to the public, medical professionals and industry and human service agencies. The Poison Center handles more than 42,000 poison exposure calls annually, and confidential, free emergency poisoning treatment advice is available 24/7. To learn more about the Poison Center, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/poison-center.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a systemic disease that causes inflammation in the spinal joints and was thought to have affected members of the ancient Egyptian royal families. Now a new study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), refutes that claim, finding instead a degenerative spinal condition called diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) in royal Egyptian mummies from the 18th to early 20th Dynasties.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a member of a group of inflammatory conditions called the spondyloarthropathies ...
CHICAGO, OCTOBER 20, 2014 – The U.S. Government has initiated a major effort to prevent and effectively treat Alzheimer's disease by 2025. However, a workgroup of nearly 40 Alzheimer's researchers and scientists says the research milestones in the U.S. Government's National Plan to Address Alzheimer's Disease must be broadened in scope, increased in scale, and adequately funded in order to successfully achieve this goal. A series of proposals by the workgroup to enlarge and strengthen the Plan are published today in Alzheimer's & Dementia: the Journal of the Alzheimer's ...
Scientists have uncovered a surprising way to reduce the brain damage caused by head injuries - stopping the body's immune system from killing brain cells. The study, published in the open access journal Acta Neuropathologica Communications, showed that in experiments on mice, an immune-based treatment reduced the size of brain lesions. The authors suggest that if the findings apply to humans, this could help prevent brain damage from accidents, and protect players of contact sports like American football, rugby and boxing.
To date, there are no effective treatments to ...
Viagra could be used as a safe treatment for heart disease, finds new research published today in the open access journal BMC Medicine. The study reveals that long-term daily treatment of Viagra can provide protection for the heart at different stages of heart disease, with few side effects.
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) is the main ingredient in Viagra and other drugs commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction. The inhibitor blocks the enzyme PDE5, which prevents relaxation of smooth muscle tissue. The presence of PDE5 in the heart has led to previous research ...
The findings suggest that this disturbing trend could be due the emergence of more virulent group B streptococcal strains and call for a renewed evaluation of preventive strategies to reduce neonatal disease.
Passed from mother to child during birth, group B streptococcus is the most common cause of infection in newborns. Guidelines for the prevention of disease have been widely adopted in high-income countries. But despite these efforts, the bacterium remains a leading cause of blood stream infections and meningitis worldwide, typically affecting babies younger than ...
BETHESDA, MD – Breaking down complex conditions such as Type 2 Diabetes and obesity into the specific metabolic proteins and processes that underlie them offers a new approach to studying the genetics of these diseases and how they are interrelated, according to research presented today at the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) 2014 Annual Meeting in San Diego.
By studying specific proteins that contribute to such conditions – and the genes that encode them – scientists can develop new drugs that directly target the metabolic processes that do ...
Improving household electricity access in India over the last 30 years contributed only marginally to the nation's total carbon emissions growth during that time, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Climate Change.
"Energy access is fundamental to development: it brings improvements to all aspects of life, including education, communication, and health," says IIASA researcher Shonali Pachauri, who conducted the study.
While increased energy access is widely agreed to be an important goal for development efforts, such as the UN Sustainable Energy ...
VIDEO:
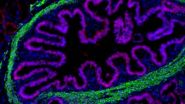
Michael Helmrath, M.D., M.S., surgical director of the Intestinal Rehabilitation Program at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, talks about researchers successfully growing human intestinal tissue in mice. The study describes...
Click here for more information.
CINCINNATI --Researchers have successfully transplanted "organoids" of functioning human intestinal tissue grown from pluripotent stem cells in a lab dish into mice – creating an unprecedented ...
DNA has garnered attention for its potential as a programmable material platform that could spawn entire new and revolutionary nanodevices in computer science, microscopy, biology, and more. Researchers have been working to master the ability to coax DNA molecules to self assemble into the precise shapes and sizes needed in order to fully realize these nanotechnology dreams.
For the last 20 years, scientists have tried to design large DNA crystals with precisely prescribed depth and complex features – a design quest just fulfilled by a team at Harvard's Wyss Institute ...
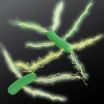
AMHERST, Mass. ¬– The claim by microbiologist Derek Lovley and colleagues at the University of Massachusetts Amherst that the microbe Geobacter produces tiny electrical wires, called microbial nanowires, has been mired in controversy for a decade, but the researchers say a new collaborative study provides stronger evidence than ever to support their claims.
UMass Amherst physicists working with Lovley and colleagues report in the current issue of Nature Nanotechnology that they've used a new imaging technique, electrostatic force microscopy (EFM), to resolve ...