The quick life and death of Tropical Storm Trudy
2014-10-20
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Trudy formed on Saturday, Oct. 17 and by Oct.19 the storm made landfall in southern Mexico and weakened to a remnant low pressure area.
Tropical Storm Trudy formed near the southwestern coast of Mexico during the morning of Oct. 18 triggering warnings and watches. A Hurricane Watch was posted from east of Acapulco to Laguna De Chacahua Mexico and a Tropical Storm Warning was posted for Tecpan De Galeana to Laguna De Chacahua Mexico.
On Sat. Oct. 18 at 8 a.m. EDT, radar from Mexico indicated that the center of Tropical Storm Trudy was located on the coast near latitude 16.6 north and longitude 98.8 west. Trudy was moving toward the east near 2 mph (4 kph). Maximum sustained winds were near 60 mph (95 kph).
The National Hurricane Center said that since a portion of the circulation was already inland at the time, no significant change in strength was expected as it continued moving inland.
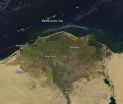
A GOES-West satellite image of Trudy on Oct. 18 at 8 a.m. EDT showed the storm centered along the southwestern coast of Mexico, while clouds from its eastern quadrant stretched over mainland Mexico. The image was created by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Tropical Storm Trudy weakened to a remnant low pressure system after making landfall in southern Mexico on Oct. 18, but the abundance of moisture continued to generate thunderstorms, downpours and large amounts of rainfall.
At 8 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Oct. 19 the remnants of Trudy were located near latitude 17.4 north and longitude 98.2 west. That put the center of the low pressure area about 115 miles (190 km) east-northeast or Acapulco, Mexico. Maximum sustained winds had decreased to near 30 mph (45 kph) and the low pressure area continued to weaken over the day.
By Oct. 20, Trudy's remnant clouds still blanketed the states of Guerrero and Oaxaca in Southern Mexico. At 11:42 a.m. EDT, Oaxaca reported a mostly cloudy sky with a temperature of 69F (21C) and calm winds, indicating that Trudy had faded.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-20
VIDEO:
This video shows the movement of Tropical Storm Ana near the Hawaiian Islands from Oct. 17-20.
Click here for more information.
Tropical Storm Ana made a slow track west of the Hawaiian islands over the last couple of days, and by Oct. 20 was moving westward away from the main Hawaiian islands and heading toward the northwest Hawaiian islands. NASA's Terra satellite caught Ana on a flyby on Oct. 19 that showed the storm's clouds blanketing the chain of islands.
The ...
2014-10-20
This NASA satellite image is of the Egyptian River Delta. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire. The location, widespread nature, and number of fires in this image and confirmation from the Ministry of Environment in Egypt. Fires are witnessed every year in October and November, caused ...
2014-10-20
Looking forward in science often requires looking back, evaluating trends to extrapolate future outcomes. A classic case is Moore's Law, which predicts that the density of components on an integrated circuit will double every 24 months. The estimate has helped guide many developments in the computer industry.
In a new study, Rolf Halden, PhD, a researcher at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute, examines the trajectory of chemicals appearing as emergent threats to human or environmental health.
Halden's meta-analysis of 143,000 peer-reviewed research papers ...
2014-10-20
About 20% of younger siblings of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) will develop the condition by age 3. A new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers has found that 57% of these younger siblings who later develop the condition already showed symptoms at age 18 months.
Published in the October Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, this is the first large-scale, multi-site study aimed at identifying specific social-communicative behaviors that distinguish infants with ASD from their typically and atypically developing high-risk ...
2014-10-20
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Obesity affects individual patient care, the healthcare system and nearly every organ in the body. People with obesity often have other health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, certain tumors and cancers, and psychiatric disorders. However, the role of obesity in orthopaedic conditions and their treatment is less well-publicized.
According to orthopaedic surgeon William M. Mihalko, MD, PhD, of Campbell Clinic Orthopaedics in Memphis, Tenn., "obesity can accompany a multitude of comorbidities that can have a significant impact on a patient's ...
2014-10-20
Older individuals who are subliminally exposed to positive stereotypes about aging showed improved physical functioning that can last for several weeks, a new study led by the Yale School of Public Health has found.
Researchers used a novel intervention method to examine for the first time whether exposure to positive age stereotypes could weaken negative age stereotypes and their effects over time, and lead to healthier outcomes.
The study, to be published online in an upcoming issue of the journal Psychological Science, consisted of 100 older individuals (average ...
2014-10-20
Antibiotics—one of modernity's great success stories—are charms that come with a curse. Their overuse in human and animal populations can lead to the development of resistant microbial strains, posing a dire threat to global health.
In a new study, Hansa Done, PhD candidate, and Rolf Halden, PhD, researchers at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute, examine antibiotic use in the rapidly expanding world of global aquaculture.
Done and Halden measured the presence of antibiotics in shrimp, salmon, catfish, trout, tilapia and swai, originating from ...
2014-10-20
This news release is available in German. Physical exercise in old age can improve brain perfusion as well as certain memory skills. This is the finding of Magdeburg neuroscientists who studied men and women aged between 60 and 77. In younger individuals regular training on a treadmill tended to improve cerebral blood flow and visual memory. However, trial participants who were older than 70 years of age tended to show no benefit of exercise. Thus, the study also indicates that the benefits of exercise may be limited by advancing age. Researchers of the German Center ...
2014-10-20
ATLANTA (October 20, 2014) – New data presented today indicate that consumers of frozen meals (1) had higher daily intakes of dietary fiber, potassium, calcium and protein, and lower daily intakes of calories and saturated fat than consumers of quick service restaurant (QSR) meals (2). The poster, Consumption of Frozen Meals as Compared to Quick Service Restaurant Meals is Associated with Better Nutrient Intakes in Adult Participants of The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2003-2010), was presented at the 2014 Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Food ...
2014-10-20
Boulder, CO, USA — Ryan McKellar's research sounds like it was plucked from Jurassic Park: he studies pieces of amber found buried with dinosaur skeletons. But rather than re-creating dinosaurs, McKellar uses the tiny pieces of fossilized tree resin to study the world in which the now-extinct behemoths lived.
New techniques for investigating very tiny pieces of fragile amber buried in dinosaur bonebeds could close the gaps in knowledge about the ecology of the dinosaurs, said McKellar, who is a research scientist at the Royal Saskatchewan Museum in Saskatchewan, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The quick life and death of Tropical Storm Trudy