(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC – October 20, 2014 -- Lactobacillus species, commonly seen in yogurt cultures, correlate, in the guts of mouse models, with mitigation of lupus symptoms, while Lachnospiraceae, a type of Clostridia, correlate with worsening, according to research published ahead of print in Applied and Environmental Microbiology. "Our results suggest that the same investigation shold be performed in human subjects with lupus," says principal investigator Xin Luo of Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA.
In the study, the investigators first showed that mouse models of lupus had higher levels of Lachnospiraceae (a type of Clostridia), and lower Lactobacillus than control mice. They also compared male and female mice, and found that the differences were present only in females. These results suggest that the gut bacteria may contribute to lupus, a disease which is nine times as prevalent in women as in men, says first author Husen Zhang.
They also monitored the gut microbiota over time in both lupus and control mice, and found that in the former, Clostridia increased in both early and late stages of the disease.
In further experiments, the investigators treated the symptoms in the lupus mice with either retinoic acid alone or vitamin A plus retinoic acid. The latter worsened the symptoms—surprisingly, Luo says, because it had been expected to reduce them—and in those mice, Clostridia increased, while Lactobacillus declined. Retinoic acid alone improved the symptoms, with opposite population changes in the gut bacteria.
The research suggests, but does not prove that altering the gut microbiota could mitigate lupus. Nonetheless, Luo suggests that people with lupus should eat Lactobacillus-containing probiotics, such as live culture yogurts, to reduce lupus flares. More generally, "The use of probiotics, prebiotics, and antibiotics has the potential to alter microbiota dysbiosis, which in turn could improve lupus symptoms," says co-principal investigator Husen Zhang. Ultimately, says Luo, fecal transplant might prove valuable as a treatment for lupus.
"We were inspired in part to perform this research by a study on type 1 diabetes, which found that that disease is dependent on gut microbiota," says Zhang. "Like type 1 diabetes, lupus is an autoimmune disease that is even more prevalent [than type 1 diabetes] in women."
INFORMATION:
Applied and Environmental Microbiology is a publication of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). The ASM is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. Its mission is to advance the microbiological sciences as a vehicle for understanding life processes and to apply and communicate this knowledge for the improvement of health and environmental and economic well-being worldwide.
Tropical Storm Gonzalo strengthened into a hurricane on Oct. 14 when it was near Puerto Rico and provided a natural laboratory for the next phase of NASA's HS3 or Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel mission.
The WB-57 aircraft flew over Hurricane Gonzalo on Oct. 15 carrying two HS3 mission instruments called HIWRAP and HIRAD in addition to a new Office of Naval Research sponsored dropsonde system.
The WB-57 is a mid-wing, long-range aircraft capable of operation for extended periods of time from sea level to altitudes in excess of 60,000 feet. Two crew members are positioned ...
For treating patients with prescription opioid dependence in primary care, buprenorphine maintenance therapy is superior to detoxification, according to a new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers published in the Oct. 20 issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
Prescription opioid dependence has been increasing for the last 15 years and now surpasses heroin dependence. Doctors are also writing more prescriptions for pain management, which has led to higher experimentation and addiction rates, according to lead author David Fiellin, M.D., professor of internal medicine ...
Scientists have developed new geochemical tracers that can identify hydraulic fracturing flowback fluids that have been spilled or released into the environment.
The tracers have been field-tested at a spill site in West Virginia and downstream from an oil and gas brine wastewater treatment plant in Pennsylvania.
"By characterizing the isotopic and geochemical fingerprints of enriched boron and lithium in flowback water from hydraulic fracturing, we can now track the presence of 'frac' fluids in the environment and distinguish them from wastewater coming from other ...
LIVERMORE, Calif. – New medications created by pharmaceutical companies have helped millions of Americans alleviate pain and suffering from their medical conditions. However, the drug creation process often misses many side effects that kill at least 100,000 patients a year, according to the journal Nature.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have discovered a high-tech method of using supercomputers to identify proteins that cause medications to have certain adverse drug reactions (ADR) or side effects. They are using high-performance computers ...
Preexisting differences in the sensitivity of a key part of each individual's immune system to stress confer a greater risk of developing stress-related depression or anxiety, according to a study conducted at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and published October 20 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Inflammation is the immune system's response to infection or disease, and has long been linked to stress. Previous studies have found depression and anxiety to be associated with elevated blood levels of inflammatory molecules ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — They help fish swim, but fins also advertise a fish's social standing and health. In a new study, researchers report that for the male bluefin killifish (Lucania goodei), each colorful fin presents its own messages to other fish.
Researchers report their findings in the journal Behavioral Ecology.
They're called "bluefin" killifish, but the first thing University of Illinois animal biology professor Rebecca Fuller noticed while she was snorkeling in a Florida stream was the killifishes' differently colored fins. In addition to having reflective ...
Fairfax, Va., October 20, 2014—Tumor laterality (left-side vs. right-side) does not impact overall survival in breast cancer patients treated with breast-conserving surgery and adjuvant external beam radiation therapy, according to a study published in the October 1, 2014 issue of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Studies have shown that breast cancer patients treated with radiation therapy have improved local-regional recurrence, ...
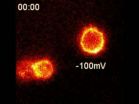
VIDEO:
The movie is quantitative imaging of cells with potassium channels, bathed in dilute fluorescent tarantula toxin. Pixel color indicates intensity of tarantula toxin concentration. The circular shapes are cell surfaces,...
Click here for more information.
WOODS HOLE, Mass.--A novel probe that reports on the electrical activity of cells, made by fusing tarantula toxin with a fluorescent compound, is described in a paper today by scientists from the University of California, ...
PULLMAN, Wash.—Researchers led by a Washington State University biologist have found the optimal mechanism by which plants heal the botanical equivalent of a bad sunburn. Their work, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to the development of crops that can repair the sun's damage more easily, improving yields and profitability.
Helmut Kirchhoff, an assistant professor in WSU's Institute of Biological Chemistry and corresponding author of the PNAS paper, said plants have had to deal with solar damage since the evolution of photosynthesis ...
PHILADELPHIA — Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine and School of Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania and The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia have used graphene -- a two-dimensional form of carbon only one atom thick -- to fabricate a new type of microelectrode that solves a major problem for investigators looking to understand the intricate circuitry of the brain.
Pinning down the details of how individual neural circuits operate in epilepsy and other neurological disorders requires real-time observation of their locations, firing patterns, ...