(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — They help fish swim, but fins also advertise a fish's social standing and health. In a new study, researchers report that for the male bluefin killifish (Lucania goodei), each colorful fin presents its own messages to other fish.
Researchers report their findings in the journal Behavioral Ecology.
They're called "bluefin" killifish, but the first thing University of Illinois animal biology professor Rebecca Fuller noticed while she was snorkeling in a Florida stream was the killifishes' differently colored fins. In addition to having reflective skin, the males sometimes had red, yellow and/or black markings on their anal, caudal (tail) and dorsal fins.
"In some of the males, the anal fin was yellow, and then some of them were red," she said. "And the field guide showed them as blue."
Some of the males had darker black markings on their anal fins than others, and some had bright yellow or orange tailfins.
Fuller immediately wanted to know what was driving the variation.
Previous studies suggested that melanin, the black pigment, is a badge of status among males; those with more prominent melanin markings tend to be more aggressive towards other males. In the new study, Fuller and her former graduate student Ashley Johnson, found that males with heavier melanin outlines on their anal fins dominated: They were more aggressive with other males – driving them off to gain exclusive access to females.
"Melanin is a signal to other males: 'I've been winning in the past and I'm doing well and get out of my way,'" Fuller said.
The red and yellow pigments on the anal fins and the yellow tints on the tailfins have different origins, the researchers found. Carotenoids color the tailfins, but another class of pigments, called pterins, tint the anal fins either yellow or red. Yellow and red pterins are tied to differences in a single gene, Fuller said.
Carotenoids (the same pigments that give carrots and apricots their color) are known antioxidants; they gobble up highly reactive ions or molecules that can damage cells and tissues. Because killifish obtain carotenoids only by eating, researchers hypothesize that a display of color derived from carotenoids signals to potential mates that they are gazing upon a particularly robust, well-fed individual.
In the new study, Fuller and Johnson discovered that richer carotenoid coloration on the tailfin was associated with better body condition, lower parasite infection and good spawning success. This suggests that females respond positively to the brightly pigmented tailfins of potential mates, Fuller said.
Much less is known about pterins, she said. They are associated with immune function and also have antioxidant characteristics, and so also may be a badge of health.
In the new study, the researchers found that the pterin and carotenoid color patterns were independent of one another: Carotenoids colored only the tailfin, while pterins appeared only on the anal fin. Brighter pterin coloration was associated with lower parasite infection and higher spawning success, the researchers found.
"We are finding that communication is complicated in nature and that animals have evolved ways to send different messages to different receivers," Fuller said. "In the case of bluefin killifish, multiple messages are being provided by three distinct pigments that are in three different areas of the body. Both females and males are getting these messages. Males are paying attention to the melanin, most likely, and females are paying attention to these more-colorful fins."
INFORMATION:
The National Science Foundation Division of Environmental Biology and the U. of I. provided funding for this study.
Editor's note: To reach Rebecca Fuller, call 217-328-2026; email rcfuller@illinois.edu
The paper, "The meaning of melanin, carotenoid, and pterin pigments in the bluefin killifish, Lucania goodei" is available online or from the U. of I. News Bureau.
Fairfax, Va., October 20, 2014—Tumor laterality (left-side vs. right-side) does not impact overall survival in breast cancer patients treated with breast-conserving surgery and adjuvant external beam radiation therapy, according to a study published in the October 1, 2014 issue of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Studies have shown that breast cancer patients treated with radiation therapy have improved local-regional recurrence, ...
VIDEO:
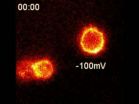
The movie is quantitative imaging of cells with potassium channels, bathed in dilute fluorescent tarantula toxin. Pixel color indicates intensity of tarantula toxin concentration. The circular shapes are cell surfaces,...
Click here for more information.
WOODS HOLE, Mass.--A novel probe that reports on the electrical activity of cells, made by fusing tarantula toxin with a fluorescent compound, is described in a paper today by scientists from the University of California, ...
PULLMAN, Wash.—Researchers led by a Washington State University biologist have found the optimal mechanism by which plants heal the botanical equivalent of a bad sunburn. Their work, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to the development of crops that can repair the sun's damage more easily, improving yields and profitability.
Helmut Kirchhoff, an assistant professor in WSU's Institute of Biological Chemistry and corresponding author of the PNAS paper, said plants have had to deal with solar damage since the evolution of photosynthesis ...
PHILADELPHIA — Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine and School of Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania and The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia have used graphene -- a two-dimensional form of carbon only one atom thick -- to fabricate a new type of microelectrode that solves a major problem for investigators looking to understand the intricate circuitry of the brain.
Pinning down the details of how individual neural circuits operate in epilepsy and other neurological disorders requires real-time observation of their locations, firing patterns, ...
Hurricane Gonzalo departed from Bermuda leaving power outages, downed trees, and damaged homes and buildings. An on-the ground account of the storm indicated the eye passed over the island. By Oct. 20, post-tropical storm Gonzalo was approaching the United Kindgom, sparking severe weather warnings.
By Sunday, Oct. 19 Gonzalo was affecting eastern Canada. Forecasters expect Gonzalo to hold together over while traveling east across the North Atlantic where it will affect Scotland as an extra-tropical storm on Tuesday, Oct. 21.
Camille Haley was former NASA intern and ...
Tropical Storm Trudy formed on Saturday, Oct. 17 and by Oct.19 the storm made landfall in southern Mexico and weakened to a remnant low pressure area.
Tropical Storm Trudy formed near the southwestern coast of Mexico during the morning of Oct. 18 triggering warnings and watches. A Hurricane Watch was posted from east of Acapulco to Laguna De Chacahua Mexico and a Tropical Storm Warning was posted for Tecpan De Galeana to Laguna De Chacahua Mexico.
On Sat. Oct. 18 at 8 a.m. EDT, radar from Mexico indicated that the center of Tropical Storm Trudy was located on the coast ...
VIDEO:
This video shows the movement of Tropical Storm Ana near the Hawaiian Islands from Oct. 17-20.
Click here for more information.
Tropical Storm Ana made a slow track west of the Hawaiian islands over the last couple of days, and by Oct. 20 was moving westward away from the main Hawaiian islands and heading toward the northwest Hawaiian islands. NASA's Terra satellite caught Ana on a flyby on Oct. 19 that showed the storm's clouds blanketing the chain of islands.
The ...
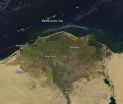
This NASA satellite image is of the Egyptian River Delta. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire. The location, widespread nature, and number of fires in this image and confirmation from the Ministry of Environment in Egypt. Fires are witnessed every year in October and November, caused ...
Looking forward in science often requires looking back, evaluating trends to extrapolate future outcomes. A classic case is Moore's Law, which predicts that the density of components on an integrated circuit will double every 24 months. The estimate has helped guide many developments in the computer industry.
In a new study, Rolf Halden, PhD, a researcher at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute, examines the trajectory of chemicals appearing as emergent threats to human or environmental health.
Halden's meta-analysis of 143,000 peer-reviewed research papers ...
About 20% of younger siblings of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) will develop the condition by age 3. A new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers has found that 57% of these younger siblings who later develop the condition already showed symptoms at age 18 months.
Published in the October Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, this is the first large-scale, multi-site study aimed at identifying specific social-communicative behaviors that distinguish infants with ASD from their typically and atypically developing high-risk ...