Early intervention could boost education levels
2014-10-22
(Press-News.org) Taking steps from an early age to improve childhood education skills could raise overall population levels of academic achievement by as much as 5%, and reduce socioeconomic inequality in education by 15%, according to international research led by the University of Adelaide.
In a study now published in the journal Child Development, researchers from the University of Adelaide's School of Population Health and colleagues at the University of Bristol in the UK have modelled the likely outcomes of interventions to improve academic skills in children up to school age. They considered what effect these interventions would have on education by age 16.
Lead author Dr Catherine Chittleborough from the University of Adelaide says socioeconomic disadvantage is a known risk factor for education and related outcomes.
"Childhood socioeconomic disadvantage is associated with reduced ability to benefit from schooling, poorer educational outcomes, a lower likelihood of continuing to tertiary education, and less job success. A poor education is associated with increased welfare dependence and lower skilled jobs with lower pay, helping to continue the cycle of disadvantage," Dr Chittleborough says.
"We've known for some time that intervening before the age of five can improve skills necessary for educational success, but the effect of these interventions on socioeconomic inequalities has remained unknown," she says.
Using data of almost 12,000 children from the UK, the researchers found that progressive educational interventions – and more intense interventions for those with greater need – could improve school entry academic skills and later educational outcomes.
"Based on our models, population levels of educational achievement could rise by 5%, and absolute socioeconomic inequality in poor educational achievement could be reduced by 15%," Dr Chittleborough says.
"That is an important finding, especially when you consider that in 2012 there were more than 620,000 pupils aged 15-16 in secondary education in the UK. A 5% improvement in their educational outcomes means that 13,500 students would be better off. This would then impact on their future employability and their ability to contribute to society economically. I expect we would see similar outcomes on education if we used Australian data."
Dr Chittleborough says pre-school education is extremely important to set children on the right path. "By providing the appropriate educational support, we could make a difference to a lot of children's lives," she says.
INFORMATION:
This research is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC).
Media contact:
Dr Catherine Chittleborough
Lecturer
School of Population Health
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8 8313 1684
catherine.chittleborough@adelaide.edu.au
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-22
Philadelphia, Oct. 22, 2014 – New work by a pioneering scientist details how subtle changes in mitochondrial function may cause a broad range of common metabolic and degenerative diseases. Mitochondria are tiny energy-producing structures within our cells that contain their own DNA.
The new research shows that small changes in the ratio of mutant to normal mitochondrial DNA within the thousands of mitochondrial DNAs inside each cell can cause abrupt changes in the expression of numerous genes within the nuclear DNA. Furthermore, the different proportions of mutant ...
2014-10-22
Using loan level data matched to consumer credit records, researchers have been able to determine that a reduction in mortgage payments of as little as $150 a month spurred a reduction in mortgage defaults and an increase in consumer spending (particularly the financing of automobile purchases), while improving household credit ratings.
University of Chicago Booth School of Business Professor Amit Seru, together with Benjamin J. Key of UChicago's Harris School of Public Policy, Tomasz Piskorski of the Columbia Business School and Vincent Yao of Fannie Mae authored "Mortgage ...
2014-10-22
New Rochelle, NY, October 22, 2014—A panel of leading clinicians and researchers across various general and specialty pediatric fields developed a consensus statement recommending how to evaluate youngsters in whom neuropsychiatric symptoms suddenly develop, including the abrupt, dramatic onset of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). This difficult diagnosis is typically made by pediatricians or other primary care clinicians and child psychiatrists, who will benefit from the guidance provided in the recommendations published in Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, ...
2014-10-22
Researchers from Princeton University and other institutions may have hit upon an answer to a climate-change puzzle that has eluded scientists for years, and that could help understand the future availability of water for hundreds of millions of people.
In a phenomenon known as the "Karakoram anomaly," glaciers in the Karakoram mountains, a range within the Himalayas, have remained stable and even increased in mass while many glaciers nearby — and worldwide — have receded during the past 150 years, particularly in recent decades. Himalayan glaciers provide ...
2014-10-22
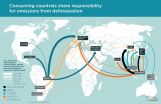
International trade with agricultural and wood products is an increasingly important driver of tropical deforestation. More than a third of recent deforestation can be tied to production of beef, soy, palm oil and timber. "The trend is clear, the drivers of deforestation have been globalized and commercialized", says assistant professor Martin Persson, Chalmers University of Technology.
In a report commissioned by US think-tank Center for Global Development (CGD) Martin Persson and colleagues in Linköping, Sweden, and Vienna, Austria, have investigated to which extent ...
2014-10-22
Major leaks from oil and gas pipelines have led to home evacuations, explosions, millions of dollars in lawsuit payouts and valuable natural resources escaping into the air, ground and water. But in a report in ACS' journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, scientists say they have developed a new software-based method that finds leaks even when they're small, which could help prevent serious incidents — and save money for customers and industry.
Gary Valtinson and Miguel Bagajewicz note that using pipelines to move oil, gas and even water from one place ...
2014-10-22
Selver Demic and his colleagues from the Mercator Research Group have set out to find out more about the causes of depression. "Approx. 20 per cent of the population will suffer a de-pressive episode in the course of their lives," says Demic. "This cohort of 20 per cent includes people who will never again experience any problems after that one-time episode is over. The others, however, will suffer repeatedly or chronically under the disorder, despite taking appropriate medication. We want to use our model to explain the occurrence and recurrence rates."
Unfortunate ...
2014-10-22
INDIANAPOLIS -- Indiana is at the forefront of providing mental health screening and services to juvenile offenders, but more efforts are needed to improve the services provided to detained youths, according to Indiana University School of Medicine research findings published in the October issue of the American Journal of Public Health.
"A Statewide Collaboration to Initiate Mental Health Screening and Assess Services for Indiana Detained Youths" reviewed 25,265 detention visits of 15,461 youths occurring in 2008 to 2011. The youths were incarcerated in 16 detention ...
2014-10-22
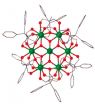
This news release is available in German. An international team of scientists have become the first ever researchers to successfully reach temperatures below minus 272.15 degrees Celsius – only just above absolute zero – using magnetic molecules. The physicists and chemists are presenting their new investigation today (22 October 2014) in the scientific journal Nature Communications. It was developed by six scientists from Bielefeld University, the University of Manchester (Great Britain), and the Universidad de Zaragoza (Spain).
Scientists usually express ...
2014-10-22
Though most NCAA colleges and universities have created programs to help athletes deal with concussions, a new Harvard study has found that, when it comes to specific components of those plans, many institutions still lag behind accepted standards.
The study, the first-ever comprehensive examination of how colleges and universities have complied with the Concussion Policy and Legislation adopted by the NCAA in 2010, is based on the results of a survey sent to all 1,066 NCAA member institutions. Of those institutions, 907 schools responded.
The results, according to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Early intervention could boost education levels