(Press-News.org) Washington, DC, October 27, 2014—New results from a safety and immunogenicity study, which included a challenge phase to test efficacy, indicate that a live attenuated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine candidate, given in combination with a novel adjuvant, provided significant protection against disease. This represents the first efficacy data for this vaccine/adjuvant combination, which was 58.5 percent efficacious in protecting against diarrhea of any severity using a highly rigorous ETEC human challenge model. The vaccine/adjuvant combination was also protective against severe ETEC diarrhea in this model with a protective efficacy of 65.9 percent.
Each year, nearly 600,000 children die from severe, dehydrating diarrhea and millions more are hospitalized, mostly in low-resource countries. ETEC may be the first enteric illness encountered by many infants, and it causes several hundred million cases of diarrhea each year, mainly in children. This high rate of ETEC disease in early life contributes to the faltering of infant development common in many parts of the developing world. ETEC is also the most common cause of travelers' diarrhea that affects individuals from industrialized countries visiting endemic areas. Currently, no licensed vaccines targeting ETEC exist.
The study was conducted by PATH in collaboration with Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health (JHU) to study the ACE527 ETEC vaccine candidate, which is an orally administered mixture of three different strains of weakened bacteria. It was administered in combination with genetically detoxified double-mutant E. coli heat-labile toxin (dmLT) adjuvant, which may enhance the anti-LT response induced by the vaccine and could contribute to protection.
The two-part Phase 1/2b study enrolled healthy US adults to receive ACE527 alone, ACE527 with the dmLT adjuvant, or a placebo. After demonstrating comparable safety and immunogenicity of both vaccine arms in the first part of the trial, the study was amended to include a challenge phase involving more than half of the original volunteers while the data were still blinded. Volunteers who were immunized with three doses of ACE527 coadministered with dmLT at the time of immunization were protected from severe diarrhea when challenged orally six to seven months later with live ETEC organisms, meeting the primary endpoint of the study.
"These promising study results point to the great potential that ETEC vaccines hold for saving young children's lives and preventing illness in the developing world," said Dr. Richard Walker, director of PATH's enteric vaccine development project. "We are greatly encouraged by these positive data and hope to see the development of this ETEC vaccine/adjuvant combination continued."
Given these very encouraging new results, PATH is interested in accelerating the development of this promising vaccine/adjuvant for use in infants and young children in low-resource settings. PATH is currently in discussion with several developing-country vaccine manufacturers about the ACE527 candidate, and is interested in pursuing other partnership opportunities to conduct further evaluation of the vaccine/adjuvant combination.
The Phase 1/2b study results were shared publically for the first time yesterday in an oral presentation by Dr. Clayton Harro of JHU at the 8th Vaccine & ISV Congress in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Harro served as principal investigator for the study, which was conducted at JHU's Center for Immunization Research in Baltimore, Maryland.
INFORMATION:
About PATH
PATH is the leader in global health innovation. An international nonprofit organization, PATH saves lives and improves health, especially among women and children. Accelerating innovation across five platforms—vaccines, drugs, diagnostics, devices, and system and service innovations—PATH harnesses its entrepreneurial insight, scientific and public health expertise, and passion for health equity. By mobilizing partners around the world, PATH takes innovation to scale, working alongside countries primarily in Africa and Asia to tackle their greatest health needs. With these key partners, PATH delivers measurable results that disrupt the cycle of poor health. Learn more at http://www.path.org.
Clinical results indicate vaccine candidate highly efficacious against bacterial diarrhea
Vaccine/adjuvant combination against a leading cause of bacterial diarrhea shows great promise for saving children's lives
2014-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How cells know which way to go
2014-10-27
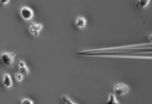
VIDEO:
In this video, lab-grown human leukemia cells move toward a pipette tip holding an attractive chemical.
Click here for more information.
Amoebas aren't the only cells that crawl: Movement is crucial to development, wound healing and immune response in animals, not to mention cancer metastasis. In two new studies from Johns Hopkins, researchers answer long-standing questions about how complex cells sense the chemical trails that show them where to go — and the ...
The Ebola epidemic: Is there a way out?
2014-10-27
Berlin, 27 October 2014. Not everyone who contracts the Ebola virus dies, the survival rate is around 30% suggesting that some kind of immunity to the disease is possible. Experimental treatments and vaccines against Ebola exist but have not yet been tested in large groups for safety and efficacy (phase 2 trials).
The International Union of Immunology Societies (IUIS) published a statement today in its official journal, Frontiers in Immunology calling for urgent and adequate funding of vaccine candidates in clinical trials and speedy implementation of immunisation in ...
Chest radiation to treat childhood cancer increases patients' risk of breast cancer
2014-10-27
A new study has found that patients who received chest radiation for Wilms tumor, a rare childhood cancer, face an increased risk of developing breast cancer later in life due to their radiation exposure. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings suggest that cancer screening guidelines might be re-evaluated to facilitate the early diagnosis and prompt treatment of breast cancer among Wilms tumor survivors.
Wilms tumor is a rare childhood kidney cancer that can spread to the lungs. When this spread occurs, patients ...
Latest bone research abstracts summarized in slides and videos
2014-10-27
Today, the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) has published an educational slide deck highlighting 60 original scientific abstracts presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) in September 2014.
The succinct slide kit can be downloaded free of charge by all individual IOF members (free sign up on the IOF website).
CEO Judy Stenmark stated, "IOF is pleased to provide this informative resource for healthcare professionals interested in the latest advances in bone and mineral research. While 10% of the featured ...
It's better for memory to make mistakes while learning
2014-10-27
Toronto, Canada – Making mistakes while learning can benefit memory and lead to the correct answer, but only if the guesses are close-but-no-cigar, according to new research findings from Baycrest Health Sciences.
"Making random guesses does not appear to benefit later memory for the right answer , but near-miss guesses act as stepping stones for retrieval of the correct information – and this benefit is seen in younger and older adults," says lead investigator Andrée-Ann Cyr, a graduate student with Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute and the Department ...
Study shows ethnic groups are at higher risk for heart disease yet many aren't aware
2014-10-27
VANCOUVER ─ Different ethnic groups have widely varying differences in both the prevalence and awareness of cardiovascular risk factors, a finding that highlights the need for specially designed education and intervention programs, according to a study presented today at the 2014 Canadian Cardiovascular Congress.
The conclusion comes from a study of more than 3,000 patients at an urgent-care clinic serving an ethnically diverse area of Toronto. Participants were asked to self-identify their ethnicity and, from a list of 20 activities or conditions, asked to identify ...
People with mental health disorders twice as likely to have heart disease or stroke
2014-10-27
VANCOUVER ─ People facing mental health challenges are significantly more likely to have heart disease or stroke, according to a study presented today at the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress.
"This population is at high risk, and it's even greater for people with multiple mental health issues," says Dr. Katie Goldie, lead author of the study and a postdoctoral fellow at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Toronto
Using data from the Canadian Community Health Survey, Dr. Goldie explored the associations between cardiovascular risk and disease, mental ...
Newly donated blood reduces complications from heart surgery, study shows
2014-10-27
VANCOUVER ─ Heart surgery patients who received newly donated blood have significantly fewer post-operative complications than those who received blood that had been donated more than two weeks before their surgery, a study presented at the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress has shown.
The study examined records at the New Brunswick Heart Centre (NBHC) in Saint John for non-emergency heart surgeries performed over almost nine years, from January 2005 to September 2013, on patients who received red blood cells either during their surgery or afterwards and who stayed ...
New nanodevice to improve cancer treatment monitoring
2014-10-27
This news release is available in French.
In less than a minute, a miniature device developed at the University of Montreal can measure a patient's blood for methotrexate, a commonly used but potentially toxic cancer drug. Just as accurate and ten times less expensive than equipment currently used in hospitals, this nanoscale device has an optical system that can rapidly gauge the optimal dose of methotrexate a patient needs, while minimizing the drug's adverse effects. The research was led by Jean-François Masson and Joelle Pelletier of the university's Department ...
Genetic predisposition to elevated LDL-C associated with narrowing of the aortic valve
2014-10-26
In an analysis that included approximately 35,000 participants, genetic predisposition to elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was associated with aortic valve calcium and narrowing of the aortic valve, findings that support a causal association between LDL-C and aortic valve disease, according to a study appearing in JAMA. The study is being released to coincide with its presentation at the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress.
Aortic valve disease remains the most common form of heart valve disease in Europe and North America and is the most common indication ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Clinical results indicate vaccine candidate highly efficacious against bacterial diarrheaVaccine/adjuvant combination against a leading cause of bacterial diarrhea shows great promise for saving children's lives