INFORMATION:
Paschall, M. J., Lipperman-Kreda, S., Grube, J. W., & Thomas, S. (November 2014). Relationships Between Social Host Laws and Underage Drinking: Findings From a Study of 50 California Cities. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 75(6), 901–907.
To arrange an interview with Mallie J. Paschall, Ph.D., members of the media may reach him at paschall@PREV.org or 510-883-5753.
The Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs is published by the Center of Alcohol Studies at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. It is the oldest substance-related journal published in the United States.
To learn about education and training opportunities for addiction counselors and others at the Rutgers Center of Alcohol Studies, please visit AlcoholStudiesEd.rutgers.edu.
Social host laws tied to less underage drinking
2014-10-28
(Press-News.org) PISCATAWAY, NJ – Teenagers who live in communities with strict "social host" laws are less likely to spend their weekends drinking at parties, according to a study in the November issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Many U.S. states and local communities have passed social host laws, which hold adults responsible when underage drinkers imbibe on their property. The details of the laws vary, however, and research has been mixed as to whether they actually keep kids from drinking.
In the new study, investigators focused on 50 communities in California, half of which had social host laws. (The state has no law on the books, but local governments are free to devise their own.) The researchers found that teenagers were less likely to report drinking at parties when they lived in communities with particularly strong social host laws.
However, the findings indicate a correlation and not necessarily a direct effect of the laws, said lead researcher Mallie J. Paschall, Ph.D., a senior research scientist at the Prevention Research Center in Oakland, California.
"These findings are preliminary. We can't say that social host laws definitely prevent kids from drinking at parties," Paschall said.
Still, the results are encouraging, according to Paschall. "Most kids get alcohol from social sources, not commercial ones," he pointed out. So, in theory, laws aimed at those social sources--in this case, parents or other adults of legal drinking age--should help reduce underage drinking.
"It does look like there is less-frequent drinking among teenagers in cities with stringent social host laws, even when other city and youth characteristics that are related to underage drinking are controlled for" Paschall said. "So these laws might be an effective strategy for reducing hazardous drinking."
"Strong" social host laws have some key provisions, according to Paschall: They specifically target underage drinking; there is a civil penalty (such as a hefty fine) that's swiftly administered; and property owners are held responsible, even if they claim they didn't know about the underage drinking.
Those types of laws are controversial, Paschall acknowledged. And in some communities, police do not enforce them--sometimes because there is little support for the policies from the public or the local prosecutor's office.
But enforcement is necessary for the laws to work, Paschall noted--as is public knowledge. If adults don't know they could be held responsible for underage drinking, the policies won't be much of a deterrent, he said.
In future studies, the researchers plan to look at rates of teen drinking before and after the passage of social host laws to get a better idea of whether the policies themselves have an impact.
Paschall said it will also be important to see whether the laws reduce problems related to teen drinking, including drunk driving.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robotically assisted bypass surgery reduces complications after surgery and cuts recovery
2014-10-28
VANCOUVER ─ Robotically assisted coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery is a rapidly evolving technology that shortens hospital stays and reduces the need for blood products, while decreasing recovery times, making the procedure safer and less risky, says a study presented at the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress.
"Robotically assisted CABG is a safe and feasible alternative approach to standard bypass surgery in properly selected patients. It is a less traumatic and less invasive approach than regular CABG," says cardiac surgeon and researcher Dr. Richard ...
Radiation exposure linked to aggressive thyroid cancers
2014-10-28
For the first time, researchers have found that exposure to radioactive iodine is associated with more aggressive forms of thyroid cancer, according to a careful study of nearly 12,000 people in Belarus who were exposed when they were children or adolescents to fallout from the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident.
Researchers examined thyroid cancers diagnosed up to two decades after the Chernobyl accident and found that higher thyroid radiation doses estimated from measurements taken shortly after the accident were associated with more aggressive tumor features.
"Our ...
Women play dangerous waiting game with heart symptoms
2014-10-28
VANCOUVER ─ When heart symptoms strike, men and women go through similar stages of pain but women are more likely to delay seeking care and can put their health at risk, according to a study presented at the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress.
"The main danger is that when someone comes to the hospital with a more severe or advanced stage of heart disease, there are simply fewer treatment options available," says Dr. Catherine Kreatsoulas, lead author of the study and a Fulbright Scholar and Heart and Stroke Foundation Research Fellow at the Harvard School of Public ...
Prostate cancer risk reduced by sleeping with many women, but increased with many men
2014-10-28
This news release is available in French. Compared to men who have had only one partner during their lifetime, having sex with more than 20 women is associated with a 28% lower risk of one day being diagnosed with prostate cancer, according to researchers at the University of Montreal and INRS - Institut Armand-Frappier. However, having more than 20 male partners in one's lifetime is associated with a twofold higher risk of getting prostate cancer compared to those who have never slept with a man.
Marie-Elise Parent and Marie-Claude Rousseau, professors at university's ...
Future-focused women stand up to global warming with taxes, checkbook
2014-10-27
PULLMAN, Wash. - Politicians who discredit global warming risk losing a big chunk of the female vote. A new study found women who consider the long-term consequences of their actions are more likely to adopt a liberal political orientation and take consumer and political steps to reduce global warming.
Jeff Joireman, associate professor of marketing at Washington State University, demonstrated that "future-oriented" women are the voting bloc most strongly motivated to invest money, time and taxes toward reducing global warming.
Previous studies have shown that women ...
Placebo better than 'watchful waiting' when treating young children's coughs
2014-10-27
Both agave nectar and a placebo were more effective than no treatment for young children's cough symptoms, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine. The findings suggest that a placebo could help children more than "watchful waiting."
The Food and Drug Administration recommends against the use of over-the-counter cough and cold medications in children under two years old due to safety concerns and a lack of evidence for their effectiveness in this age group. As part of a voluntary change announced in 2008 by the Consumer Healthcare Products Association, ...
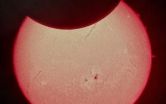
Spotlighting the sun
2014-10-27
Astronomers with the National Science Foundation (NSF)-funded National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) captured pictures not only of Thursday's partial solar eclipse, but also of the "monster" sized active region or sun spot that has many comparing it to one of a similar size that occurred 11 years ago.
The sun spots were earlier reported by scientists with the NSF-supported National Solar Observatory. According to astronomers Frank Hill and Kiran Jain, "As of Oct 21, 2014, a very large active region is currently on the solar disk and producing flares as strong as ...
NASA's SDO observes more flares erupting from giant sunspot
2014-10-27
A large active region on the sun erupted with another X-class flare on Oct. 27, 2014 -- its fourth since Oct. 24. The flare peaked at 10:47 a.m. EDT.
X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
Continuing a week's worth ...
Scientists' new analysis of plant proteins advances our understanding of photosynthesis
2014-10-27
A world without plants would be a world without oxygen, uninhabitable for us and for many creatures. We know plants release oxygen by absorbing carbon dioxide and breaking down water using sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. However, we know little about the mechanics of how plants create oxygen during photosynthesis. A breakthrough that will help advance our understanding of this critical ecological process was made recently by scientists at LSU.
"Without photosynthesis or oxygen, basically all recognizable life that we see in our landscape would be gone: ...
Two years after superstorm Sandy: Resilience in 12 neighborhoods
2014-10-27
Chicago, October 27, 2014—The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research today released the results of a major new study and related reports on the recovery from Superstorm Sandy in 12 New York and New Jersey neighborhoods hard hit by the 2012 storm.
It is the second AP-NORC study that has focused on the aftermath of Superstorm Sandy, with findings that emphasize the important role social factors play in a neighborhood's resilience: the ability of people and their social systems to survive, adapt and continue moving forward after a disaster. Funding ...