(Press-News.org) In the largest study of its kind to date, researchers have used DNA sequencing to uncover dozens of genes that heighten the risk for autism. Joseph Buxbaum, Ph.D., Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, Mark Daly, Ph.D., Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, and their colleagues examined more than 14,000 DNA samples from affected children, parents and unrelated people. They identified changes in 107 genes that are likely to contribute to the risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) – a jump from the nine genes implicated in earlier studies using these approaches. The findings, reported online October 29, 2014, in Nature, provide a better understanding of some of the genetic and cellular changes in pathways and processes thought to be involved in ASD, and eventually may help lead to potential therapies. ASD, a complex disorder that affects one in 68 children in the United States, frequently affects a person's behavior and ability to interact with others.
The scientists identified variations and mutations in genes in three pathways that are important to normal development. In each case, the changes in these pathways were linked to autism risk. They include:
Synaptic function. Synapses are the spaces between nerve cells over which brain messages must travel. Mutations in synaptic genes and synapse formation and function can alter these messages.
Chromatin remodeling. DNA is packaged into chromatin in cells. Changes in this packaging can affect which genes are turned on and off, and the formation of neural connections in the brain.
Transcription. Instructions embedded in genes must be transcribed, or read, to build proteins, the workhorse of the cell. Transcription mistakes can affect a wide range of important processes in the brain, from controlling gene activity to transmitting messages.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and other funding sources. NHGRI and NIMH are parts of NIH.
ARTICLE:
De Rubeis, et al. Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature. DOI: 10.1038/nature13772.
WHO:
Adam Felsenfeld, Ph.D., program director, Genome Sequencing Program, Division of Genome Sciences, NHGRI.
CONTACT:
To schedule an interview, please contact Steven Benowitz, NHGRI, 301-451-8325, or steven.benowitz@nih.gov
NHGRI is one of the 27 institutes and centers at the National Institutes of Health. The NHGRI Extramural Research Program supports grants for research and training and career development at sites nationwide. Additional information about NHGRI can be found at http://www.genome.gov.
About the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): The mission of the NIMH is to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses through basic and clinical research, paving the way for prevention, recovery and cure. For more information, visit the NIMH website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 institutes and centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
Researchers uncover new evidence revealing molecular paths to autism
2014-10-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Changes in scores of genes contribute to autism risk
2014-10-29
Small differences in as many as a thousand genes contribute to risk for autism, according to a study led by Mount Sinai researchers and the Autism Sequencing Consortium (ASC), and published today in the journal Nature.
The new study examined data on several types of rare, genetic differences in more than 14,000 DNA samples from parents, affected children, and unrelated individuals – by far the largest number to date – to dramatically expand the list of genes identified with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Most of the genes that contribute to autism remain ...
Planet-forming lifeline discovered in a binary star system
2014-10-29
A research group led by Anne Dutrey from the Laboratory of Astrophysics of Bordeaux, France, and the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) observed the distribution of dust and gas in a binary star system called GG Tau-A. It was recently discovered that one of GG Tau-A's components is itself a double star. This object is only a few million years old and lies approximately 460 light-years from Earth in the constellation Taurus.
Like a wheel in a wheel, GG Tau-A contains a large, outer disk encircling the entire system as well as an inner disk around the main central ...
Teeth, sex and testosterone reveal secrets of aging in wild mouse lemurs
2014-10-29
Mouse lemurs can live at least eight years in the wild – twice as long as some previous estimates, a long-term longitudinal study finds.
PLOS ONE published the research on brown mouse lemurs (Microcebus rufus) led in Madagascar by biologist Sarah Zohdy, a post-doctoral fellow in Emory University's Department of Environmental Sciences and the Rollins School of Public Health. Zohdy conducted the research while she was a doctoral student at the University of Helsinki.
"It's surprising that these tiny, mouse-sized primates, living in a jungle full of predators that ...
Tiny carbon nanotube pores make big impact
2014-10-29
A team led by the Lawrence Livermore scientists has created a new kind of ion channel based on short carbon nanotubes, which can be inserted into synthetic bilayers and live cell membranes to form tiny pores that transport water, protons, small ions and DNA.
These carbon nanotube "porins" have significant implications for future health care and bioengineering applications. Nanotube porins eventually could be used to deliver drugs to the body, serve as a foundation of novel biosensors and DNA sequencing applications, and be used as components of synthetic cells.
Researchers ...
Study identifies potential treatment target for cocaine addiction
2014-10-29
A study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has identified a potential target for therapies to treat cocaine addiction. In their study receiving advance online publication in Molecular Psychiatry, the investigators find evidence that changing one amino acid in a subunit of an important receptor protein alters whether cocaine-experienced animals will resume drug seeking after a period of cocaine abstinence. Increasing expression of the enzyme responsible for that change within the ...
Researchers track ammonium source in open ocean
2014-10-29
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To understand the extent to which human activities are polluting Earth's atmosphere and oceans, it's important to distinguish human-made pollutants from compounds that occur naturally. A recent study co-authored by a Brown University professor does just that for ammonium, a compound that is produced by human activities like agriculture, as well as by natural processes that occur in the ocean.
The research, based on two years of rainwater samples taken in Bermuda, suggests that ammonium deposited over the open ocean comes almost ...
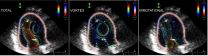
Engineers develop novel ultrasound technology to screen for heart conditions
2014-10-29
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego have determined for the first time the impact of a ring-shaped vortex on transporting blood flow in normal and abnormal ventricles within the human heart. They worked with cardiologists at the Non-Invasive Cardiology Laboratory at Gregorio Marañon Hospital, in Madrid, Spain.
In order to make the study possible, researchers have developed a novel ultrasound technology that makes screening cheaper and much easier, making it possible to reach a large number of people and even infants. Intra-ventricular flow imaging ...
HPV infections in women eradicated by AHCC, Japanese mushroom extract
2014-10-29
VIDEO:
AHCC (Active Hexose Correlated Compound) is a natural immune-modulating compound derived from a unique fraction of specially-cultured medicinal mushroom mycelia which has been clinically shown to strengthen the body's immune...
Click here for more information.
(October 29, 2014, Beaverton, OR) New research presented at the Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) 11th International Conference in Houston, TX showed for the first time that it is possible to eliminate HPV ...
Penn vet professor investigates parasite-schizophrenia connection
2014-10-29
Many factors, both genetic and environmental, have been blamed for increasing the risk of a diagnosis of schizophrenia. Some, such as a family history of schizophrenia, are widely accepted. Others, such as infection with Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite transmitted by soil, undercooked meat and cat feces, are still viewed with skepticism.
A new study by Gary Smith, professor of population biology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania's School of Veterinary Medicine, used epidemiological modeling methods to determine the proportion of schizophrenia cases that ...
Clean smell doesn't always mean clean air
2014-10-29
Some of the same chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere as a result of smog and ozone are actually taking place in your house while you are cleaning. A researcher in Drexel's College of Engineering is taking a closer look at these reactions, which involve an organic compound -called limonene- that provides the pleasant smell of cleaning products and air fresheners. His research will help to determine what byproducts these sweet-smelling compounds are adding to the air while we are using them to remove germs and odors.
Secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) are microscopic ...