How cells defend themselves against antibiotics and cytostatic agents
Structure of the ABC transporter, elucidated thanks to pioneering structure analysis/Publication in Nature
2014-11-04
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
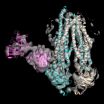
"On the one hand, ABC transporters causes diseases such as cystic fibrosis, while on the other hand they are responsible for the immune system recognising infected cells or cancer cells," explains Professor Robert Tampé from the Institute for Biochemistry at the Goethe University. The considerable medical, industrial and economic significance of ABC transporters is also based on the fact that they cause bacteria and other pathogens to become resistant to antibiotics. Likewise, they can help cancer cells to defend themselves against cytostatic agents and thus determine whether chemotherapy will succeed.
For the first time, the group led by Robert Tampé, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of California in San Francisco, succeeded in determining the structure of an asymmetrical ABC transporter complex with the aid of a high-resolution cryo-electron microscope. "Over a period of five years, we have successfully implemented a number of innovative, methodological developments. These have enabled us to gain insights that previously were unimaginable," says Tampé.
The researchers report in the current issue of the renowned scientific journal, Nature that they have succeeded in investigating a single frozen ABC transport complex at a subnanometer resolution that has never before been achieved. For this purpose, they used a newly developed single electron camera, new imaging processes and specific antibody fragments in order to determine the structure and conformation of the dynamic transport machine.
"The combination of physical, biotechnological, biochemical and structural biological methods has led to a quantum leap in the elucidation of the structure of macromolecular complexes," says Tampé. The method facilitates the targeted development of a trend-setting therapeutic approach.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-04
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (November 4, 2014) — Think about the way our bodies are assembled during early development and ask: How do neighboring cells know that they are supposed to become a nerve or a bone cell and how do these tissues find the correct place and alignment? Researchers at the University of Miami (UM) are answering these crucial questions.
In a new study, UM researchers describe the signaling systems that tissues use to communicate with their surrounding neighbors, at the head-trunk region. Their discovery may have important implications for the treatment ...
2014-11-04
Sublingual misoprostol is inferior to intramuscular oxytocin for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) in women undergoing uncomplicated birth at a regional hospital in Uganda, according to trial results published in PLOS Medicine. The randomized non-inferiority trial, conducted by Esther Cathyln Atukunda at the Mbarara University of Science and Technology, Uganda, and colleagues, showed that PPH incidence in the misoprostol arm exceeded that in the oxytocin arm by 11.2% (95% confidence interval 6.44%-16.1%).
PPH is responsible for 25–30% of maternal deaths. ...
2014-11-04
In an analysis of the 2003–2010 MarketScan US database, Rakesh Bhattacharjee and coauthors (University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois) compared hospital admissions and prescriptions for children with asthma who underwent adenotonsillectomy before and after surgery to determine whether their asthma control improved (based on ICD-9-CM and CPT codes, as well as drug prescriptions) in the year after compared with the year before surgery. They also compared the children with children with asthma who did not undergo adenotonsillectomy who were the same age and sex and lived ...
2014-11-04
Surgical removal of the tonsils and adenoids in children suffering from sleep apnea is associated with decreased asthma severity, according to the first large study of the connection, published in the journal PLOS Medicine.
Researchers from the University of Chicago found that in the first year after the operation, children who had the surgery had a 30 percent reduction in acute asthma exacerbations and a 38 percent decrease in acute status asthmaticus—a medical emergency.
They also found pediatric patients who received the surgery had a 36 percent reduction ...
2014-11-04
Asthma may be more harmful than was previously thought, according to UCLA researchers who found that genetic damage is present in circulating, or peripheral, blood. Doctors previously thought that the genetic damage it caused was limited to the lungs.
In the study, researchers looked for the overexpression of a cytokine called interleukin 13 (IL-13), which is known to mediate inflammation, a critical problem for people with asthma.
The study, which was conducted in an animal model that mimicked human asthma, was the first to assess the role of IL-13 in genetic damage ...
2014-11-04
RENO, Nev. – The puzzle pieces of tectonic plates that make up the outer layer of the earth are not rigid and don't fit together as nicely as we were taught in high school.
A study published in the journal Geology by Corné Kreemer, an associate professor at the University of Nevada, Reno, and his colleague Richard Gordon of Rice University, quantifies deformation of the Pacific plate and challenges the central approximation of the plate tectonic paradigm that plates are rigid.
Using large-scale numerical modeling as well as GPS velocities from the largest ...
2014-11-04
WASHINGTON, D.C., November 4, 2014--If you took the junk from the back of your closet and combined it with the dirty laundry already on your floor, you would have an even bigger mess. While this principle will likely always hold true for our bedrooms, it turns out that in certain situations, combining messes can actually reduce the disorder of the whole. An international team of researchers from Slovenia and Iran has identified a set of conditions in which adding disorder to a system makes it more orderly. This behavior is known as antifragility, a concept introduced recently ...
2014-11-04
A newly published research study examining only marketing directed at children on the interior and exterior of fast food restaurants has found that the majority of black, middle-income and rural communities are disproportionately exposed to such marketing tactics.
Authored by Arizona State University researcher Punam Ohri-Vachaspati and her colleagues, the study is the first to examine the use of child-directed marketing on the interior and exterior of fast food restaurants and its relationship to demographics. It adds to a substantial body of literature on the effects ...
2014-11-04
PITTSBURGH—It's commonly believed that creativity is a process that involves connecting ideas and building on the past to create something new. But is it better to "think outside the box," using unrelated concepts to get the creative juices flowing, or to build on something more closely related to the problem one is trying to solve?
In a paper newly published in Design Studies, recent University of Pittsburgh graduate Joel Chan and his mentor Christian Schunn of Pitt's Learning Research and Development Center, along with Carnegie Mellon University's Steven Dow, ...
2014-11-04
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Vance on Nov. 3 as it started moving in a northeasterly direction toward the northwestern coast of Mexico. On Nov. 4, a Tropical Storm Watch was in effect from Mazatlan northward to Topolobampo, Mexico. Hurricane Vance is forecast to make landfall in northwestern mainland Mexico on Nov. 5.
On Nov. 3 at 20:50 UTC (3:50 p.m. EST) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Hurricane Vance off Mexico's west coast. The eastern quadrant of the storm ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How cells defend themselves against antibiotics and cytostatic agents
Structure of the ABC transporter, elucidated thanks to pioneering structure analysis/Publication in Nature




