(Press-News.org) The road that connects also divides.
This dichotomy – half-century-old roads connecting portions of Bahamian islands while fragmenting the tidal waters below – leads to rapid and interesting changes in the fish living in those fragmented sections, according to a new study from North Carolina State University.
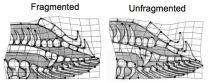
NC State Ph.D. student Justa Heinen-Kay and assistant professor of biological sciences R. Brian Langerhans show, in a paper published in the journal Evolutionary Applications, that the male genitalia of three different species of Bahamian mosquitofish (Gambusia) living in fragmented waters differ markedly from the genitalia of fish living in unfragmented waters.
Fragmentation limits the number of mosquitofish predators, which appears to have a link to the shape of the male fish's genitalia. Fish coexisting with predators in unfragmented areas have bonier and more elongated gonopodium tips than fish living without threat of predation in fragmented areas. The gonopodium is the sperm-transferring organ in these livebearing fish.
"This study shows that human-induced habitat alteration results in changes in fish genitalia in just 35 to 50 years – the time elapsed since the fragment-causing roads were built," Heinen-Kay said. "While we expected to see some changes, we were surprised to see the consistency with which each species changed in accordance with our predictions based on earlier work that focused on how ecological factors, such as predation, affected the evolution of male genitalia over the course of thousands of years."
The authors said that these findings indicate that sometimes the impacts of human activities on the traits of organisms can be predictable, suggesting that management, restoration and conservation efforts could be useful.
Langerhans added that the study could provide particular insight into speciation, or how different species develop.
"Because genitalia have an obvious and direct influence on reproduction, these findings beg the question of whether human-induced environmental change might facilitate speciation. As populations become more and more different in their genital morphology, their ability to interbreed can decline, leading to speciation," Langerhans said. "How common this sort of rapid change in genital shape might be in other species, and its consequences for the formation of new species, are some of the questions we'll ask in future studies."
INFORMATION:
Dr. Craig Layman, an NC State associate professor of applied ecology, and Holly Noel, an undergraduate student in biological sciences at NC State, co-authored the paper. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation and NC State.
Note to editors: An abstract of the paper follows.
Human-caused habitat fragmentation can drive rapid divergence of male genitalia
Authors: Justa L. Heinen-Kay, Holly G. Noel, Craig A. Layman and Brian Langerhans, North Carolina State University
Published: November 2014 in Evolutionary Applications
DOI: 10.1111/eva.12223
Abstract: The aim of this study rests on three premises: (i) Humans are altering ecosystems worldwide, (ii) environmental variation often influences the strength and nature of sexual selection, and (iii) sexual selection is largely responsible for rapid and divergent evolution of male genitalia. While each of these assertions has strong empirical support, no study has yet investigated their logical conclusion that human impacts on the environment might commonly drive rapid diversification of male genital morphology. We tested whether anthropogenic habitat fragmentation has resulted in rapid changes in the size, allometry, shape, and meristics of male genitalia in three native species of livebearing fishes (genus: Gambusia) inhabiting tidal creeks across six Bahamian islands. We found that genital shape and allometry consistently and repeatedly diverged in fragmented systems across all species and islands. Using a model selection framework, we identified three ecological consequences of fragmentation that apparently underlie observed morphological patterns: decreased predatory fish density, increased conspecific density, and reduced salinity. Our results demonstrate that human modifications to the environment can drive rapid and predictable divergence in male genitalia. Given the ubiquity of anthropogenic impacts on the environment, future research should evaluate the generality of our findings and potential consequences for reproductive isolation. END
Mosquitofish genitalia change rapidly due to human impacts
2014-11-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Direct writing' of diamond patterns from graphite a potential technological leap
2014-11-05
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – What began as research into a method to strengthen metals has led to the discovery of a new technique that uses a pulsing laser to create synthetic nanodiamond films and patterns from graphite, with potential applications from biosensors to computer chips.
"The biggest advantage is that you can selectively deposit nanodiamond on rigid surfaces without the high temperatures and pressures normally needed to produce synthetic diamond," said Gary Cheng, an associate professor of industrial engineering at Purdue University. "We do this at room temperature ...
Piglet brain atlas new tool in understanding human infant brain development
2014-11-05
URBANA, Ill. – A new online tool developed by researchers at the University of Illinois will further aid studies into postnatal brain growth in human infants based on the similarities seen in the development of the piglet brain, said Rod Johnson, a U of I professor of animal sciences.
Through a cooperative effort between researchers in animal sciences, bioengineering, and U of I's Beckman Institute, Johnson and colleagues Ryan Dilger and Brad Sutton have developed a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain atlas for the four-week old piglet that offers a three-dimensional ...
Expansion of gambling does not lead to more problem gamblers, study finds
2014-11-05
BUFFALO, N.Y. – In the past decade, online gambling has exploded and several states, including New York, have approved measures to legalize various types of gambling. So, it's only natural that the number of people with gambling problems has also increased, right?
Wrong, say researchers at the University at Buffalo Research Institute on Addictions (RIA).
"We compared results from two nationwide telephone surveys, conducted a decade apart. We found no significant increase in the rates of problem gambling in the U.S., despite a nationwide increase in gambling opportunities," ...
Financial experts may not always be so expert new Notre Dame study reveals
2014-11-05
When in doubt, an expert always knows better. Except in the case of mutual-fund managers. There may be some room for doubt in their case a new study by Andriy Bodnaruk, an assistant finance professor at the University of Notre Dame, and colleague Andrei Simonov from Michigan State University, suggests.
Bodnaruk and Simonov studied 84 mutual-fund managers in Sweden to determine how well they manage their own finances.
"We asked the question whether financial experts make better investment decisions than ordinary investors," Bodnaruk said. "We identified a group of investors ...
ADHD-air pollution link
2014-11-05
Prenatal exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or PAH, a component of air pollution, raises the odds of behavior problems associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, or ADHD, at age 9, according to researchers at the Columbia Center for Children's Environmental Health at the Mailman School of Public Health. Results are published online in the journal PLOS ONE.
The researchers followed 233 nonsmoking pregnant women and their children in New York City from pregnancy into childhood, and found that children born to mothers exposed to high levels of PAH ...
Small New Zealand population initiated rapid forest transition c. 750 years ago
2014-11-05
Human-set fires by a small Polynesian population in New Zealand ~750 years ago may have caused fire-vulnerable forests to shift to shrub land over decades, rather than over centuries, as previously thought, according to a study published November 5, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David McWethy from Montana State University and colleagues.
Human impacts on forest composition and structure have been documented worldwide; however, the rate at which ancient human activities led to permanent deforestation is poorly understood. In South Island, New Zealand, the ...
Ah-choo! Expect higher grass pollen and allergen exposure in the coming century
2014-11-05
AMHERST, Mass. – Results of a new study by scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst strongly suggest that there will be notable increases in grass pollen production and allergen exposure up to 202 percent in the next 100 years, leading to a significant, worldwide impact on human health due to predicted rises in carbon dioxide (CO2) and ozone (O3) due to climate change.
While CO2 stimulates reproduction and growth in plants, ozone has a negative impact on plant growth, the authors point out. In this study in Timothy grass, researchers led by environmental ...
Scientists on NOAA-led mission discover new coral species off California
2014-11-05
A NOAA-led research team has discovered a new species of deep-sea coral and a nursery area for catsharks and skates in the underwater canyons located close to the Gulf of Farallones and Cordell Bank national marine sanctuaries off the Sonoma coast.
In the first intensive exploration of California's offshore areas north of Bodega Head, a consortium of federal and state marine scientists used small submersibles and other innovative technologies to investigate, film and photograph marine life that has adapted to survive in offshore waters reaching 1,000 feet deep.
The ...
A fraction of the global military spending could save the planet's biodiversity
2014-11-05
A fundamental step-change involving an increase in funding and political commitment is urgently needed to ensure that protected areas deliver their full conservation, social and economic potential, according to an article published today in Nature by experts from Wildlife Conservation Society, the University of Queensland, and the IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA).
The paper, The performance and potential of protected areas, comes ahead of the IUCN World Parks Congress 2014 – a once-in-a-decade global forum on protected areas opening next week in ...
UW study shows direct brain interface between humans
2014-11-05
Sometimes, words just complicate things. What if our brains could communicate directly with each other, bypassing the need for language?
University of Washington researchers have successfully replicated a direct brain-to-brain connection between pairs of people as part of a scientific study following the team's initial demonstration a year ago. In the newly published study, which involved six people, researchers were able to transmit the signals from one person's brain over the Internet and use these signals to control the hand motions of another person within a split ...