Cellular extensions with a large effect
Study explains the link between cilia and diabetes
2014-11-06
(Press-News.org) Tiny extensions on cells, cilia, play an important role in insulin release, according to a new study, which is published in Nature Communications. The researchers report that the cilia of beta cells in the pancreas are covered with insulin receptors and that changed ciliary function can be associated with the development of type 2 diabetes.
Cilia are tiny extensions on cells and they are credited with many important functions, including transduction of signals in cells. Defects in cilia have been implied in several diseases and pathological conditions. Thus, scientists at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, University College London and the Helmholtz Zentrum München (HMGU) took interest in the role of cilia in blood glucose regulation and type 2-diabetes.
"It has been known for some time that the rate of type 2 diabetes is above average in people with ciliopathy, which is a pathological ciliary dysfunction", says Jantje Gerdes, previously at Karolinska Institutet and now at the Institute of Diabetes and Regeneration Research at the HMGU, first author of the study. "Our results confirm this observation and additionally explain how cilia are linked to glucose metabolism and diabetes."
The researchers investigated the function of ciliary cell extensions in the insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cells. Insulin is the hormone that reduces blood glucose levels. When the investigators stimulated the beta cells with glucose the number of insulin receptors on their cilia increased. When circulating insulin binds to the receptors it stimulates the release of more insulin into the blood. The cilia consequently play an important role in the release and signal transduction of insulin.
The investigators also studied what happens when the cilia are defective. They found that in mice with few or defective cilia the insulin release was reduced and the animals had significantly elevated blood glucose levels.
"Ciliary dysfunction and defective glucose utilization are directly linked", says Per-Olof Berggren at the Rolf Luft Research Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology at Karolinska Institutet, principal investigator of the study. "Ciliopathies therefore have a potential function as models in the investigation of many still unknown mechanisms that underlie diabetes."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by, among others, grants from the Swedish Research Council, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the European Research Council, The Family Erling-Persson Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, and the Stichting af Jochnick Foundation.
Publication: 'Ciliary dysfunction impairs pancreatic insulin secretion and promotes development of type 2 diabetes in rodents', Jantje M. Gerdes, Sonia Christou-Savina, Yan Xiong, Tilo Moede, Noah Moruzzi, Patrick Karlsson-Edlund, Barbara Leibiger, Ingo B. Leibiger, Claes-Göran Östenson, Philip L. Beales, and Per-Olof Berggren, Nature Communications, online 6 November 2014, doi: 10.1038/ncomms6308.
Contact the Press Office: ki.se/pressroom
Karolinska Institutet - a medical university: ki.se/english
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-06
VIDEO:
A 10-day-old zebrafish gets its stripes over the next 30 days, one image taken a day.
Click here for more information.
Within weeks of publishing surprising new insights about how zebrafish get their stripes, the same University of Washington group is now able to explain how to "erase" them.
The findings – the first published Aug. 28 in Science and the latest in the Nov. 6 issue of Nature Communications – give new understanding about genes and cell behaviors ...
2014-11-06
Berlin, Germany (November, 2014) – Closely related groups can differ dramatically in their diversity, but why this happens is a fundamental question in evolutionary biology, dating back to Darwin's observation that a few hyper-diverse groups dominate the modern biota. One of the most extreme examples of this observation is found in the comparison of rodents (Rodentia) and rabbits (Lagomorpha). These two mammalian orders are sister groups, but while rodents have diversified to over 2000 living species and an enormous range of body sizes, lagomorphs (rabbits, hares, ...
2014-11-06
ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) – Many people don't realize allergies and asthma go hand-in-hand, and about 90 percent of kids with asthma also have allergies. Even more important, when asthma is undiagnosed or poorly controlled, children are at risk for suffering difficult-to-treat allergic reactions to food.
According to a study presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, a two and-a-half year-old girl in Pennsylvania suffered a life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to eating an orange – ...
2014-11-06
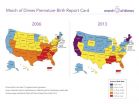
WHITE PLAINS, N.Y., Nov. 6, 2014 – The national preterm birth rate fell to 11.4 percent in 2013 – the lowest in 17 years -- meeting the federal Healthy People 2020 goal seven years early. Despite this progress, the U.S. still received a "C" on the 7th annual March of Dimes Premature Birth Report Card because it fell short of the more-challenging 9.6 percent target set by the March of Dimes, the group said today.
"Achieving the Healthy People 2020 goal is reason for celebration, but the U.S. still has one of the highest rates of preterm birth of any high ...
2014-11-06
WASHINGTON - Airport security agents using a new conversation-based screening method caught mock airline passengers with deceptive cover stories more than 20 times as often as agents who used the traditional method of examining body language for suspicious signs, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
In experiments spanning eight months, security agents at eight international airports in Europe detected dishonesty in 66 percent of the deceptive mock passengers using the new screening method, compared to just 3 percent for agents ...
2014-11-06
New Rochelle, NY, November 6, 2014—Screening large cell culture collections containing plant samples obtained from diverse geographic regions, climates, and soil and growing conditions for biological activity can reveal a wealth of natural compounds with potential applications for crop improvement and protection. The capability to do reproducible screening and genomic analysis of the more than 2,000 plant cell lines maintained in culture at the Institute of Cell Biology and Genetic Engineering, in Kiev, Ukraine is describe in an article in Industrial Biotechnology, ...
2014-11-06
A recently launched European satellite could reveal tens of thousands of new planets within the next few years, and provide scientists with a far better understanding of the number, variety and distribution of planets in our galaxy, according to research published today.
Researchers from Princeton University and Lund University in Sweden calculated that the observational satellite Gaia could detect as many as 21,000 exoplanets, or planets outside of Earth's solar system, during its five-year mission. If extended to 10 years, Gaia could detect as many as 70,000 exoplanets, ...
2014-11-06
November 5, 2014, Hong Kong, China –Today, the international open-access open-data journal GigaScience (a BGI and BioMed Central journal) announced publication of an article that presents GWATCH1, a new web-based platform that provides visualization tools for identifying disease-associated genetic markers from privacy-protected human data without risk to patient privacy. This dynamic online tool, developed by an international team of researchers from Russia, Australia, Canada, and the US, allows and facilitates disease gene discovery via automation and presentation ...
2014-11-06
Fast, on-the-spot tests for bacterial infections may help to reduce excessive antibiotic use. A systematic review published in The Cochrane Library, found that when doctors tested for the presence of bacterial infections they prescribed fewer antibiotics.
Antibiotics treat infections caused by bacteria but not those caused by viruses. Most patients who visit their doctors with acute respiratory infections are suffering from viral infections like the common cold. However, because doctors usually have no immediate way of knowing whether an infection is bacterial or viral, ...
2014-11-06
Teenagers are much more likely to take up smoking if they live in neighbourhoods with a large number of shops that sell tobacco products, a study suggests.
Adolescents with the most tobacco outlets in their neighbourhood are almost 50% more likely to smoke than those with no outlets nearby, researchers say.
The study also found that teenagers living in areas with the highest density of retailers are 53 per cent more likely to try smoking at least once.
Based on their findings, researchers argue that anti-smoking strategies among teenagers should include reducing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cellular extensions with a large effect
Study explains the link between cilia and diabetes