Orange is not the new black: Just highly allergenic for one toddler
Study highlights first report of severe allergic response to orange
2014-11-06
(Press-News.org) ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) – Many people don't realize allergies and asthma go hand-in-hand, and about 90 percent of kids with asthma also have allergies. Even more important, when asthma is undiagnosed or poorly controlled, children are at risk for suffering difficult-to-treat allergic reactions to food.
According to a study presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, a two and-a-half year-old girl in Pennsylvania suffered a life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to eating an orange – the first time such a case has been reported in a toddler.
"She ate an orange, and within a few minutes had developed severe anaphylaxis," said allergist and ACAAI member Sigrid DaVeiga, MD, study author. "Her lips and tongue swelled, she broke out in hives and couldn't breathe well. Her parents immediately got her to an emergency room, and she was flown by helicopter to a pediatric intensive care unit."
Following treatment and a 48-hour hospital stay, the girl recovered and was able to go home. Upon examination of her medical history, doctors discovered that she had previously had orange juice with no reaction, but more importantly, that she had undiagnosed asthma. Later testing by allergists found that she was allergic to both orange and peach.
"Several recommendations were made following the allergic reaction, said allergist and ACAAI member Sayantani Sindher, MD, study author. "She was advised to avoid orange and peach, and also told to start asthma therapy, both of which will keep future allergic reactions under control."
According to ACAAI, it's very rare for anyone to have a severe allergic reaction to an orange.
It's more common for people who suffer from hay fever to sometimes suffer from oral allergy syndrome – an itchy mouth or scratchy throat after eating certain raw fruits or vegetables and some tree nuts. The response is caused by cross-reacting allergens found in both pollen, and the fruits and vegetables.
INFORMATION:
For more information about allergies and to locate an allergist in your area, visit AllergyandAsthmaRelief.org. The ACAAI Annual Meeting is being held Nov. 6-10 at the Georgia World Congress Convention Center in Atlanta. For more news and research being presented at the meeting, follow the conversation on Twitter #ACAAI. View the latest news online at ACAAI Annual Meeting Press Kit.
About ACAAI
The ACAAI is a professional medical organization of more than 6,000 allergists-immunologists and allied health professionals, headquartered in Arlington Heights, Ill. The College fosters a culture of collaboration and congeniality in which its members work together and with others toward the common goals of patient care, education, advocacy and research. ACAAI allergists are board-certified physicians trained to diagnose allergies and asthma, administer immunotherapy, and provide patients with the best treatment outcomes. For more information and to find relief, visit AllergyandAsthmaRelief.org. Join us on Facebook, Pinterest and Twitter.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-06
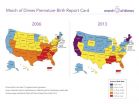
WHITE PLAINS, N.Y., Nov. 6, 2014 – The national preterm birth rate fell to 11.4 percent in 2013 – the lowest in 17 years -- meeting the federal Healthy People 2020 goal seven years early. Despite this progress, the U.S. still received a "C" on the 7th annual March of Dimes Premature Birth Report Card because it fell short of the more-challenging 9.6 percent target set by the March of Dimes, the group said today.
"Achieving the Healthy People 2020 goal is reason for celebration, but the U.S. still has one of the highest rates of preterm birth of any high ...
2014-11-06
WASHINGTON - Airport security agents using a new conversation-based screening method caught mock airline passengers with deceptive cover stories more than 20 times as often as agents who used the traditional method of examining body language for suspicious signs, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
In experiments spanning eight months, security agents at eight international airports in Europe detected dishonesty in 66 percent of the deceptive mock passengers using the new screening method, compared to just 3 percent for agents ...
2014-11-06
New Rochelle, NY, November 6, 2014—Screening large cell culture collections containing plant samples obtained from diverse geographic regions, climates, and soil and growing conditions for biological activity can reveal a wealth of natural compounds with potential applications for crop improvement and protection. The capability to do reproducible screening and genomic analysis of the more than 2,000 plant cell lines maintained in culture at the Institute of Cell Biology and Genetic Engineering, in Kiev, Ukraine is describe in an article in Industrial Biotechnology, ...
2014-11-06
A recently launched European satellite could reveal tens of thousands of new planets within the next few years, and provide scientists with a far better understanding of the number, variety and distribution of planets in our galaxy, according to research published today.
Researchers from Princeton University and Lund University in Sweden calculated that the observational satellite Gaia could detect as many as 21,000 exoplanets, or planets outside of Earth's solar system, during its five-year mission. If extended to 10 years, Gaia could detect as many as 70,000 exoplanets, ...
2014-11-06
November 5, 2014, Hong Kong, China –Today, the international open-access open-data journal GigaScience (a BGI and BioMed Central journal) announced publication of an article that presents GWATCH1, a new web-based platform that provides visualization tools for identifying disease-associated genetic markers from privacy-protected human data without risk to patient privacy. This dynamic online tool, developed by an international team of researchers from Russia, Australia, Canada, and the US, allows and facilitates disease gene discovery via automation and presentation ...
2014-11-06
Fast, on-the-spot tests for bacterial infections may help to reduce excessive antibiotic use. A systematic review published in The Cochrane Library, found that when doctors tested for the presence of bacterial infections they prescribed fewer antibiotics.
Antibiotics treat infections caused by bacteria but not those caused by viruses. Most patients who visit their doctors with acute respiratory infections are suffering from viral infections like the common cold. However, because doctors usually have no immediate way of knowing whether an infection is bacterial or viral, ...
2014-11-06
Teenagers are much more likely to take up smoking if they live in neighbourhoods with a large number of shops that sell tobacco products, a study suggests.
Adolescents with the most tobacco outlets in their neighbourhood are almost 50% more likely to smoke than those with no outlets nearby, researchers say.
The study also found that teenagers living in areas with the highest density of retailers are 53 per cent more likely to try smoking at least once.
Based on their findings, researchers argue that anti-smoking strategies among teenagers should include reducing ...
2014-11-06
PRINCETON, N.J.—Life satisfaction dips around middle age and rises in older age in high-income, English-speaking countries, but that is not a universal pattern, according to a new report published in The Lancet as part of a special series on ageing. In contrast, residents of other regions — such as the former Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa — grow increasingly less satisfied as they age.
The study — conducted by researchers from Princeton University's Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, ...
2014-11-06
A major new Series on health and ageing, published in The Lancet, warns that unless health systems find effective strategies to address the problems faced by an ageing world population, the growing burden of chronic disease will greatly affect the quality of life of older people. As people across the world live longer, soaring levels of chronic illness and diminished wellbeing are poised to become a major global public health challenge.
Worldwide, life expectancy of older people continues to rise. By 2020, for the first time in history, the number of people aged 60 years ...
2014-11-06
Multicenter patient-safety study reduces injuries from hospital medical errors by 30% with improved handoff communications
I-PASS bundle improves safety, quality of care at nine medical centers
BOSTON (Nov. 6, 2014) – Improvements in verbal and written communication between health care providers during patient handoffs can reduce injuries due to medical errors by 30 percent, according to a multicenter study led by researchers from Boston Children's Hospital. Reported Nov. 6 in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), study results show that I-PASS—an ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Orange is not the new black: Just highly allergenic for one toddler
Study highlights first report of severe allergic response to orange