(Press-News.org) OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Nov. 6, 2014 - For much the same reason LCD televisions offer eye-popping performance, a thermomagnetic processing method developed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory can advance the performance of polymers.
Polymers are used in cars, planes and hundreds of consumer products, and scientists have long been challenged to create polymers that are immune to shape-altering thermal expansion. One way to achieve this goal is to develop highly directional crystalline structures that mimic those of transparent liquid crystal diode, or LCD, films of television and computer screens. Unfortunately, polymers typically feature random microstructures rather than the perfectly aligned microstructure - and transparency - of the LCD film.
ORNL's Orlando Rios and collaborators at Washington State University have pushed this barrier aside with a processing system that changes the microstructure and mechanical properties of a liquid crystalline epoxy resin. Their finding, outlined in a paper published in the American Chemical Society journal Applied Materials and Interfaces, offers a potential path to new structural designs and functional composites with improved properties.
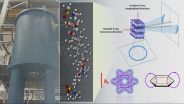
The method combines conventional heat processing with the application of powerful magnetic fields generated by superconducting magnets. This provides a lever researchers can use to control the orientation of the molecules and, ultimately, the crystal alignment.
"In this way, we can achieve our goal of a zero thermal expansion coefficient and a polymer that is highly crystalline," said Rios, a member of ORNL's Deposition Science Group. "And this means we have the potential to dial in the desired properties for the epoxy resin polymers that are so prevalent today."
Epoxy is commonly used in structural composites, bonded magnets and coatings. Rios noted that thermosets such as epoxy undergo a chemical cross-linking reaction that hardens or sets the material. Conventional epoxy typically consists of randomly oriented molecules with the molecular chains pointing in every direction, almost like a spider web of atoms.
"Using thermomagnetic processing and magnetically responsive molecular chains, we are able to form highly aligned structures analogous to many stacks of plates sitting on a shelf," Rios said. "We confirmed the directionality of this structure using X-ray measurements, mechanical properties and thermal expansion."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the paper, "Thermomagnetic processing of liquid crystalline epoxy resins and their mechanical characterization using nanoindentation," are Yuzhan Li and Michael Kessler of Washington State's School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering. The ORNL portion of the research was supported by the Critical Materials Institute, an Energy Innovation Hub funded by DOE's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. Washington State's research was funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the Department of Energy's Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit http://science.energy.gov/.
Image: http://www.ornl.gov/Image%20Library/Main%20Nav/ORNL/News/News%20Releases/2014/Rios_web01_A_hr.jpg?code=d676387b-8bef-46e5-b634-3dce3427450c
Cutline: The high magnetic field environments are provided by fully recondensing commercial prototype superconducting magnet processing system. The electromagnetic fields turn and align the liquid crystal phase forming a pseudo super-structure of ordered domains. This leads to advanced physical properties such as near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion.
NOTE TO EDITORS: You may read other press releases from Oak Ridge National Laboratory or learn more about the lab at http://www.ornl.gov/news. Additional information about ORNL is available at the sites below:
Twitter - http://twitter.com/ornl
RSS Feeds - http://www.ornl.gov/ornlhome/rss_feeds.shtml
Flickr - http://www.flickr.com/photos/oakridgelab
YouTube - http://www.youtube.com/user/OakRidgeNationalLab
LinkedIn - http://www.linkedin.com/companies/oak-ridge-national-laboratory
Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/Oak.Ridge.National.Laboratory
ORNL thermomagnetic processing method provides path to new materials
2014-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The tiger beetle: Too fast to see
2014-11-06
PITTSBURGH--Speed is an asset for a predator. Except when that predator runs so fast that it essentially blinds itself.
The tiger beetle, relative to its size, is the fastest creature on Earth. Some of these half-inch-long beetles cover about 120 body lengths per second (at about five miles per hour). The fastest human can do about five body lengths. To take the sprinting gold from the tiger beetle, a person would have to hit 480 miles per hour.
BUT! The tiger beetle has a problem. At peak speeds, everything becomes a blur. They can't gather enough light with their ...
Black, Hispanic kids underrepresented in autism identification
2014-11-06
LAWRENCE -- The number of children diagnosed with autism has increased in recent years, but a new study co-authored by a University of Kansas professor shows that while the number of students with autism increased in every state from 2000 to 2007, black and Hispanic children were significantly underrepresented.
Jason Travers, assistant professor of special education, co-authored a study that analyzed administrative identification of autism in every state under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act for the years 2000 and 2007. The disparity in the odds of white ...
Who will come to your bird feeder in 2075?
2014-11-06
The distribution of birds in the United States today will probably look very different in 60 years as a result of climate, land use and land cover changes.
A new U.S. Geological Survey study predicts where 50 bird species will breed, feed and live in the conterminous U.S. by 2075. While some types of birds, like the Baird's sparrow, will likely lose a significant amount of their current U.S. range, other ranges could nearly double. Human activity will drive many of these shifts. The study was published today in the journal PLOS ONE.
"Habitat loss is a strong predictor ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Nuri resemble a frontal system
2014-11-06
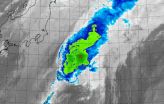
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nuri on Nov. at captured an infrared picture of the storm. The storm looked more like a frontal system as it stretched from northeast to southwest.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite flew over Nuri on Nov. 6 at 1240 UTC (7:40 a.m. EST). The MODIS image showed some strong thunderstorms remaining in a small area around Nuri's center, but the storm appeared stretched out from northeast to southwest. Wind shear was affecting the storm, stretching it ...
'Rewriting' the way to make natural drug compounds
2014-11-06
(SALT LAKE CITY)--One of the big hurdles in bringing drugs to market is the difficulty of producing large enough quantities of potential compounds to conduct clinical trials. This is particularly true with compounds made by organisms, which usually are produced in exceedingly small amounts and are difficult to synthesize in the laboratory.
Researchers from the University of Utah College of Pharmacy have made an important stride in addressing those problems. In a study in ACS Synthetic Biology, researchers led by Eric W. Schmidt, Ph.D., professor of medicinal chemistry, ...
NASA see birth of Tropical Cyclone 5B in Bay of Bengal
2014-11-06
The fifth tropical cyclone of the Northern Indian Ocean season formed in the Bay of Bengal as NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead and captured an image of the storm.
When Terra passed over Tropical Cyclone 5B on Nov. 6 at 05:05 UTC (12:05 a.m. EST), the MODIS instrument aboard took a visible image of the storm. The MODIS image showed a concentrated storm with strong thunderstorms circling tight around the center and in the northeastern quadrant.
By 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST), Tropical Cyclone 5B was located near 13.4 north latitude and 87.9 east longitude. That's about ...
Study highlights prevalence of mistreatment between nursing home residents
2014-11-06
NEW YORK (November 6, 2014) -- Inappropriate, disruptive, or hostile behavior between nursing home residents is a sizable and growing problem, according to new research from Weill Cornell Medical College and Cornell University.
The study found that nearly one in five nursing home residents were involved in at least one negative and aggressive encounter with one or more fellow residents over the previous four weeks. These included acts of verbal or physical abuse, inappropriate sexual behavior, or invasion of privacy, among other incidents, known collectively as resident-to-resident ...
Denying problems when we don't like the political solutions
2014-11-06
DURHAM, N.C. -- There may be a scientific answer for why conservatives and liberals disagree so vehemently over the existence of issues like climate change and specific types of crime.
A new study from Duke University finds that people will evaluate scientific evidence based on whether they view its policy implications as politically desirable. If they don't, then they tend to deny the problem even exists.
"Logically, the proposed solution to a problem, such as an increase in government regulation or an extension of the free market, should not influence one's belief ...
Koala study reveals clues about origins of the human genome
2014-11-06
Eight percent of your genome derives from retroviruses that inserted themselves into human sex cells millions of years ago. Right now the koala retrovirus (KoRV) is invading koala genomes, a process that can help us understand our own viral lineage and make decisions about managing this vulnerable species.
In a recent study scientists from the University of Illinois discovered that 39 different KoRVs in a koala's genome were all endogenous, which means passed down to the koala from one parent or the other; one of the KoRVs was found in both parents.
Koalas are the ...
Retaining military veteran employees is all about the right fit
2014-11-06
It's a difficult career transition that can lead to more professional frustration and shorter tenure on the job for many of the newest generation of veterans employed with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) compared to their non-veteran co-workers.
New research from the University of Cincinnati is helping VA analyze the process of reintegrating veterans into civilian careers and evaluate methods for easing that transition. That's good news for all veterans as the nation prepares to observe Veterans Day on Nov. 11.
"This period of time within our labor force ...