The Chilean abortion paradox: Even when prohibited by law, abortion rates decrease
2014-11-07
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in Spanish.
Legal restriction of abortion has a negative connotation since the idea of women resorting to illegal abortion -risking their own lives- is strongly rooted in the public opinion worldwide. However, a series of independently peer-reviewed articles, challenge this notion in some countries. The latest data in this subject have been discussed by the Chilean epidemiologist Elard Koch, Director of Research of the MELISA Institute, in the current issue of the official journal of the Chilean Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. The research shows that not only abortion-related mortality continued its decreasing trend in Chile after its prohibition by law in 1989, but also hospital discharges due to abortion have significantly decreased during the last decade.
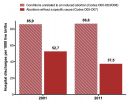
According to more recent evidence from official data, Chile displays a continuous decreasing trend of hospital discharges due to complications of abortions suspected to be illegally induced -represented by specific codes of the World Health Organisation classification- at a rate of 2% per year since 2001. In contrast, a decreasing trend was not observed in hospital discharges due to other types of abortion, such as spontaneous abortion or ectopic pregnancies, which have remained constant during the same period. The high quality of Chilean vital statistics indicates these findings are unlikely to be the result of an artifact of the registry system. Rather, a decrease in hospital discharges due to complications from illegal abortion appears to explain virtually all the reduction in hospital discharges due to any type of abortion in Chile during the last decade.
The Chilean experience represents a paradox in our times: even under a less permissive abortion legislation, maternal health indicators can be significantly improved by other factors, including a noteworthy reduction in mortality and morbidity associated to abortion.
In addition to a summary of the previously published research conducted at the MELISA Institute, showing that Chile is a paragon of maternal health in the entire American continent, the editorial article presents previously unpublished data of an ongoing study on the vulnerability profile of 3,134 Chilean women with unplanned pregnancies at risk of induced abortion. This research suggests that women at high risk of abortion display a vulnerability profile marked by coercion and fear, which together account for nearly 70% of the reasons for declaring the intention to terminate the pregnancy. Moreover, data suggest that support programs directed to vulnerable women can prevent most illegal abortions, with an outcome of live birth (with or without adoption) ranging between 69% and 94% depending on the risk group.
In Chile, it is estimated occur 13,000 to 18,000 illegal abortions each year, representing a death risk of 1 in 4 million women of fertile age and leading to about 16% of hospital discharges due to any type of abortion. It is thought that most illegal abortions are provoked through the self-administration of misoprostol. However, several authors agree that the Chilean progress in this matter is likely to be explained by the success of maternal health policy interventions, the access to modern methods of family planning, the increase in women's educational level and, more recently, to the emergence of support programs for vulnerable women with unplanned pregnancies at risk of abortion.
INFORMATION:
"Koch E. Epidemiología del aborto y su prevención en Chile [Epidemiology of abortion and its prevention in Chile]. Rev Chil Obstet Ginecol (in press)
Koch E, Thorp J, Bravo M, Gatica S, Romero CX, Aguilera H, Ahlers I. Women's education level, maternal health facilities, abortion legislation and maternal deaths: a natural experiment in Chile from 1957 to 2007. PLoS ONE 7(5):e36613. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0036613. Available here.
For more information about this subject and to request a press-embargoed copy of the article (certified translation to English) or an interview with Dr. Elard Koch, please contact the Division of Public Relations of the MELISA Institute at comunicaciones@melisainstitute.org or call to +56 41 234 5814"
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-07
SALT LAKE CITY, Utah, Nov. 7, 2014 - Myriad Genetics, Inc. (Nasdaq: MYGN) today presented results from a prospective clinical utility study of its Myriad myPath Melanoma test at the 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology (ASDP) annual meeting in Chicago, Ill. Myriad myPath Melanoma is a genetic test that differentiates malignant melanoma from benign skin lesions across all major melanoma subtypes. Key findings of this clinical utility study included a 43 percent reduction in indeterminate diagnoses and a 49 percent change in physicians' treatment recommendations for ...
2014-11-07
Scientists from the RIKEN BioResource Center in Tsukuba, Japan, have discovered that a single mutation in the beta-catenin gene, which codes a protein known to be deeply involved in a number of developmental and homeostatic processes, can lead to infertility not through a disruption of the production of egg or sperm cells, but rather by leading to abnormalities in the morphology of the sexual organs, making natural reproduction impossible.
Beta-catenin is an essential protein in the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, which has been shown in mice to be involved in the ...
2014-11-07
It arises from what scientists previously described as "junk DNA" or "the dark matter of the genome," but this gene is definitely not junk.
The gene GAS5 acts as a brake on steroid hormone receptors, making it a key player in diseases such as hormone-sensitive prostate and breast cancer.
Unlike many genes scientists are familiar with, GAS5 does not encode a protein. It gets transcribed into RNA, like other genes, but with GAS5 the RNA is what's important, not the protein. The RNA accumulates in cells subjected to stress and soaks up steroid hormone receptors, preventing ...
2014-11-07
The present-day extinct ancestors of turtles had a flexible ribcage and breathed, like us, by alternately expanding and contracting the lungs and thorax. The development of a solid shell on the back and belly, however, rendered this kind of respiratory process impossible. Today's turtles breathe with the aid of a muscle sling attached to the shell, which contracts and relaxes to aerate the lungs. An international team of researchers from North American, African and European institutes and museums have now discovered the origin of this muscle sling: in Eunotosaurus africanus, ...
2014-11-07
New research published today in the journal Nature Communications, has demonstrated how glass can be manipulated to create a material that will allow computers to transfer information using light. This development could significantly increase computer processing speeds and power in the future.
The research by the University of Surrey, in collaboration with the University of Cambridge and the University of Southampton, has found it is possible to change the electronic properties of amorphous chalcogenides, a glass material integral to data technologies such as CDs and ...
2014-11-07
A new study suggests that the flightless birds named moa were completely extinct by the time New Zealand's human population had grown to two and half thousand people at most.
The new findings, which appear in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, incorporate results of research by international teams involved in two major projects led by Professor Richard Holdaway (Palaecol Research Ltd and University of Canterbury) and Mr Chris Jacomb (University of Otago), respectively.
The researchers calculate that the Polynesians whose activities caused moa extinction ...
2014-11-07
ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) - Many people have been told, incorrectly, that they're allergic to penicillin, but have not had allergy testing. These people are often given alternative antibiotics prior to surgery to ward off infection. But when antibiotic choices are limited due to resistance, treatment alternatives may be more toxic, more expensive and less effective.
According to two studies presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, people who believe they have a penicillin allergy would benefit from consultation ...
2014-11-07
ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) - Asthma symptoms affect an estimated 26 million Americans and are one of the leading causes of work and school absences. People who suffer from asthma know it's a challenge to make sure symptoms are under control at all times. And it's even a challenge to know where to get the best information on how to do that.
According to a study presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, teens and caregivers have different levels of health literacy, and teens don't necessarily get their information ...
2014-11-07
ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) - Last year's long, harsh winter was brutal, and caused some experts to predict the "polar vortex" would turn into the "pollen vortex," and make allergy sufferers more miserable than ever before. But the "pollen vortex" didn't happen - at least not everywhere.
According to a study presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, the spring pollen count in Ontario, Canada was not higher than usual, and in fact, was down considerably - and far lower than at any other time in the previous ...
2014-11-07
ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) - People who suffer from allergies want to keep up-to-date on the latest information regarding treatment, but it's not always easy. Some doctors don't even know fact from fiction when it comes to treating allergies.
According to a study presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, prevailing allergy myths have a long shelf life. The study surveyed 409 physicians - either in internal medicine or pediatrics - on the topic of treating allergies. The physicians all received six questions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The Chilean abortion paradox: Even when prohibited by law, abortion rates decrease

