The body's emotions
Recognizing other people's emotions: A problem in multiple sclerosis
2014-11-10
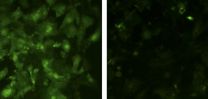
(Press-News.org) Recognizing the emotions other people feel is crucial for establishing proper interpersonal relations. To do so, we look at (amongst other things) facial expressions and body posture. Unfortunately, in some neurological disorders this ability is heavily impaired. This happens, for example, in multiple sclerosis where scientific evidence shows that people affected by the disease often have trouble recognizing expressions that communicate emotions. A new study now demonstrates that the same difficulty may also be encountered with emotions conveyed by posture. In addition, the study shows that this difficulty recognizing other people's emotions is unrelated to difficulties identifying one own's emotions, a disorder known as alexithymia, which may be present in patients with multiple sclerosis.
"The finding on posture is new, and even though this symptom is less pronounced than the inability to read facial expressions, it is nonetheless important" explains Marilena Aiello, a SISSA researcher. "Studies on the identification of expressions in neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis are important. In this type of disease the relationship between patients and carers is crucial to guarantee the patient the best quality of life. It's thus vital to identify the factors that may influence and improve this relationship".
In addition to Aiello, the other SISSA researchers who participated in the study, published in the Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, are Cinzia Cecchetto (first author) and Raffaella Rumiati, a SISSA neuroscientist who coordinated the research project.
INFORMATION:
USEFUL LINKS:
Original paper in the Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society: http://goo.gl/e9Po1f
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-10
A newly identified signaling pathway that stimulates glucose uptake in brown fat cells might be useful for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity, according to a study in The Journal of Cell Biology.
When the body encounters cold temperatures, the sympathetic nervous system activates adrenoceptors on the surface of brown fat cells to stimulate glucose uptake from the bloodstream. Brown fat cells then use this glucose as a fuel source to generate body heat. Glucose uptake also can be induced by insulin. However, although insulin-stimulated glucose-uptake is well understood, ...
2014-11-10
THE term 'spirituality' is now widely used to describe the qualities that give people hope, meaning and purpose. In the case of patients, it can aid their recovery. The University of Huddersfield has become a key centre for research into spirituality and how it can be integrated into health care teaching and practice.
Articles, overseas conference presentations and now close links with an NHS trust are among the recent outputs and activities of the University's Spirituality Special Interest Group, based in the School of Human and Heath Sciences. Established for ten ...
2014-11-10
WASHINGTON, Nov. 10, 2014 -- Throughout the history of science, many major discoveries came accidentally. Sometimes they came from recognizing potential in an unexpected product or even a failed recipe's waste. Other times, discovery came out of pure desperation from a seemingly dead-end experiment. This week, Reactions celebrates those happy accidents that ended up changing the world in the first episode of a new sub-series, "Legends of Chemistry." Check out the video here: http://youtu.be/Xowen_a787Y.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter ...
2014-11-10
A darting mouse may hold an important clue in the development of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), autism and bipolar disorder, according to a study by a Vanderbilt University-led research team recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The transgenic mouse, into which was inserted a rare human genetic variation in the dopamine transporter (DAT), could lead to improvements in the diagnosis and treatment of these all-too-common brain disorders, said Randy Blakely, Ph.D., the report's senior author.
The mutation, which has ...
2014-11-10
AUGUSTA, Ga. - A gene known to play a major role in constricting blood vessels also appears to be a major player in the aberrant blood vessel growth that can destroy the vision of premature babies.
Endothelin gene expression is greatly increased in the retinal tissue of a mouse model of retinopathy of prematurity, a condition that significantly affects about 1,500 infants annually, resulting in blindness in about half those babies, according to researchers at the Medical College of Georgia at Georgia Regents University.
The finding points toward a new therapy to help ...
2014-11-10
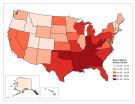
Ann Arbor, MI, November 10, 2014 -- Public health researchers seeking to determine an individual's risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD), coronary heart disease (CHD), or stroke have previously relied on national US data, such as that provided by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES). Now, new data compiled and evaluated by researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide information at the state level for the first time, paving the way for targeted intervention programs. Their results appear in the American ...
2014-11-10
(Boston)--A new study has found it is possible to distinguish between different hemorrhagic fevers, including Marburg (Ebola cousin) and Lassa before the person becomes symptomatic.
The study, which appears in the journal BMC Genomics will allow for the development of better diagnostics, especially during the early stages of disease, when treatments have a greater chance of being effective.
Hemorrhagic fevers include Lassa, which is endemic in Western Africa and Marburg, which causes sporadic outbreaks in Africa associated with high rates of mortality. The early symptoms ...
2014-11-10
Researchers from North Carolina State University and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology have found that temperature-controlled aggregation in a family of new semi-conducting polymers is the key to creating highly efficient organic solar cells that can be mass produced more cheaply. Their findings also open the door to experimentation with different chemical mixtures that comprise the active layers of the cells.
Polymer solar cells are a delicately controlled mixture of a polymer donor and a fullerene acceptor. The cell is created by adding a solvent to the ...
2014-11-10
SEATTLE--Group Health patients with a positive screening test for colon cancer (a stool test or sigmoidoscopy) tended to be more likely to get the recommended follow-up test, a diagnostic colonoscopy, if nurse navigators contacted them than if they got usual care. This is according to "Results of Nurse Navigator Follow-up After Positive Colorectal Cancer Screening Test: A Randomized Trial" in the November-December Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine, led by Beverly B. Green, MD, MPH, a Group Health physician and a Group Health Research Institute associate investigator. ...
2014-11-10
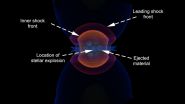
In research published today in the Astrophysical Journal, an Australian led team of astronomers has used radio telescopes in Australia and Chile to see inside the remains of a supernova.
The supernova, known as SN1987A, was first seen by observers in the Southern Hemisphere in 1987 when a giant star suddenly exploded at the edge of a nearby dwarf galaxy called the Large Magellanic Cloud.
In the two and a half decades since then the remnant of Supernova 1987A has continued to be a focus for researchers the world over, providing a wealth of information about one of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The body's emotions
Recognizing other people's emotions: A problem in multiple sclerosis