(Press-News.org) Stanford, CA--Photosynthesis is probably the most well-known aspect of plant biochemistry. It enables plants, algae, and select bacteria to transform the energy from sunlight during the daytime into chemical energy in the form of sugars and starches (as well as oils and proteins), and it involves taking in carbon dioxide from the air and releasing oxygen derived from water molecules. Photosynthetic organisms undergo other types of biochemical reactions at night, when they generate energy by breaking down those sugars and starches that were stored during the day.
Cells often face low-oxygen conditions at night, when there's no photosynthesis releasing oxygen into the air and all photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic organisms in the environment are respiring oxygen.
When this happens, some organisms such as the single-cell alga Chlamydomonas are able to generate cellular energy from the breakdown of sugars without taking up oxygen. They do this using a variety of fermentation pathways, similar to those used by yeast to create alcohol. Although critical to the survival of common aquatic and terrestrial organisms that are found all over the planet, many of the details regarding this low-oxygen energy creation process are poorly understood.
New work from a team including Carnegie's Wenqiang Yang and Arthur Grossman, and in collaboration with Matt Posewitz at the Colorado School of Mines, hones in on the biochemical pathways underlying the special flexibility of Chlamydomonas in responding to oxygen-free and low-oxygen conditions. Other Carnegie co-authors include Claudia Catalanotti, Tyler Wittkopp, Luke Mackinder, and Martin Jonikas. It is published by The Plant Cell.
In an arduous and exacting step-by-step process, the team used a series of specially created mutants to determine the importance of two identical branches of the fermentation pathway that are located in different compartments in the cell, both believed to be essential to dark, low-oxygen fermentation in Chlamydomonas. The pathways are dependent on four proteins, PAT1 and PAT2 and ACK1 and ACK2.
ACK1 and PAT2 are located in a part of the plant cell called the chloroplast, which is the compartment where photosynthesis takes place. ACK2 and PAT1 are located in the mitochondria, the organelle in plant and animal cells where sugar breakdown takes place.
"Surprisingly, we found that the chloroplast pathway is much more critical than the mitochondrial pathway for sustaining fermentation metabolism, even though generating energy from the breaking down of sugars is generally considered a mitochondrial process," Grossman said.
What's more, they found that although the PAT- and ACK-controlled pathways are indeed crucial to generating energy under these conditions, and to producing an important metabolite called acetate, there appear to be other undiscovered biochemical pathways that are participating in this process as well and capable of picking up at least some of the slack in the system.
"The system needs more work, especially if we are going to understand the ways in which the day-night cycle and environmental oxygen levels impact the productivity of photosynthetic organisms on our planet," Grossman added.
INFORMATION:
This work was funded by the Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Chemical Sciences, Geosciences and Biosciences Division, US Department of Energy grants, the National Science Foundation Award, and South Carolina Experiment Station project. It is designated as technical contribution of the Clemson University Experiment Station.
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
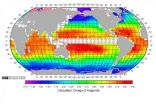
A team of scientists has published the most comprehensive picture yet of how acidity levels vary across the world's oceans, providing a benchmark for years to come as enormous amounts of human-caused carbon emissions continue to wind up at sea.
"We have established a global standard for future changes to be measured," said Taro Takahashi, a geochemist at Columbia's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory who published the maps with his colleagues in the August issue of the journal Marine Chemistry. The maps provide a monthly look at how ocean acidity rises and falls by season ...
Research scientists at VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland have demonstrated a new technique for generating electrical energy. The new method can be used in harvesting energy from mechanical vibrations of the environment and converting it into electricity. Energy harvesters are needed, for example, in wireless self-powered sensors and medical implants, where they could ultimately replace batteries. In the future, energy harvesters can open up new opportunities in many application areas such as wearable electronics.
Research scientists at VTT have successfully generated ...
New Rochelle, NY, November 10, 2014--To understand their risk for hereditary forms of cancer, such as breast and colon cancer, women need to know their family history. The design and effectiveness of a 20-minute skills-based intervention that can help women better communicate with relatives and gather and share information about cancer family history is described in a study in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jwh.2014.4754 ...
A new drug combination for rheumatoid arthritis treats the disease just as well as other intensive treatment strategies but with less medication and fewer side effects at a significantly lower cost. Doctoral researcher Diederik De Cock (KU Leuven) describes the strategy in a new study published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic auto-immune disease that causes pain and stiffness in the joints, fatigue, bone damage and, eventually, loss of mobility. RA afflicts around 1% of people in the western world; in Belgium, 80,000 to 100,000 ...
Hidden away in the tropical darkness of nocturnal Madagascar, scientists have discovered a new species of gecko which has been described in the open access journal Zoosystematics and Evolution.
A master of disguise, the new species Paroedura hordiesi has camouflage pattern to blend with its natural habitat, while climbing on rocks and the ruins of an old fort, where it was spotted by scientists.
Home of the new gecko, the karstic limestone massifs in the region of northern Madagascar are believed to still harbour further undescribed reptile species, some of which might ...
BOSTON - The innate immune system serves as the body's specialized armed forces division, comprised of a host of defense mechanisms used to battle bacterial infections. Among the system's warriors are white blood cells including the specialized macrophages, which maintain constant surveillance for foreign intruders or pathogens, functioning as the body's first line of defense, poised to attack at barrier sites including the skin, lungs and intestines.
Now, a research team led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) finds that naturally occurring ...
Recognizing the emotions other people feel is crucial for establishing proper interpersonal relations. To do so, we look at (amongst other things) facial expressions and body posture. Unfortunately, in some neurological disorders this ability is heavily impaired. This happens, for example, in multiple sclerosis where scientific evidence shows that people affected by the disease often have trouble recognizing expressions that communicate emotions. A new study now demonstrates that the same difficulty may also be encountered with emotions conveyed by posture. In addition, ...
A newly identified signaling pathway that stimulates glucose uptake in brown fat cells might be useful for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity, according to a study in The Journal of Cell Biology.
When the body encounters cold temperatures, the sympathetic nervous system activates adrenoceptors on the surface of brown fat cells to stimulate glucose uptake from the bloodstream. Brown fat cells then use this glucose as a fuel source to generate body heat. Glucose uptake also can be induced by insulin. However, although insulin-stimulated glucose-uptake is well understood, ...
THE term 'spirituality' is now widely used to describe the qualities that give people hope, meaning and purpose. In the case of patients, it can aid their recovery. The University of Huddersfield has become a key centre for research into spirituality and how it can be integrated into health care teaching and practice.
Articles, overseas conference presentations and now close links with an NHS trust are among the recent outputs and activities of the University's Spirituality Special Interest Group, based in the School of Human and Heath Sciences. Established for ten ...
WASHINGTON, Nov. 10, 2014 -- Throughout the history of science, many major discoveries came accidentally. Sometimes they came from recognizing potential in an unexpected product or even a failed recipe's waste. Other times, discovery came out of pure desperation from a seemingly dead-end experiment. This week, Reactions celebrates those happy accidents that ended up changing the world in the first episode of a new sub-series, "Legends of Chemistry." Check out the video here: http://youtu.be/Xowen_a787Y.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter ...