(Press-News.org) VCU Massey Cancer Center and VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine (VIMM) researchers discovered a unique approach to treating pancreatic cancer that may be potentially safe and effective. The treatment method involves immunochemotherapy - a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy, which uses the patient's own immune system to help fight against disease. This pre-clinical study, led by Paul B. Fisher, M.Ph., Ph.D., and Luni Emdad, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., found that the delivery of [pIC]PEI - a combination of the already-established immune-modulating molecule, polyinosine-polycytidylic acid (pIC), with delivery molecule polyethlenimine (PEI), a polymer often used in detergents, adhesives and cosmetics - inside pancreatic cancer cells triggers cancer cell death without harming normal pancreatic cells.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers, with an overall five-year survival rate of less than six percent. Its high fatality is attributed to failure to diagnose the disease before it spreads to other organs, as well as its resistance to current therapies. Surgical removal of the cancer, chemotherapy and radiation each offer little resistance against this aggressive disease.
"Pancreatic cancer is currently the fourth leading cause of cancer death in the US. Developing an effective treatment is a vital step, and immunochemotherapy may be the key," said Emdad, member of the Cancer Molecular Genetics research program at VCU Massey, assistant professor in the Department of Human and Molecular Genetics at VCU School of Medicine and member of the VIMM.
Published in Cancer Research, this is the first study that links the proteins involved in programmed cell death as prime mediators in cancer-specific killing by [pIC]PEI. Emdad and Fisher have found that, in vitro (in cell cultures), [pIC]PEI selectively induces cell death in pancreatic cancer cells, and that, in vivo (in animal models), [pIC]PEI also inhibited tumor growth via cell death.
"Since [pIC]PEI is extremely and selectively toxic to pancreatic cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo, the use of this compound, alone and in combination with other therapeutic agents, could potentially lead to a novel, safe and effective approach for treating pancreatic cancer by directly attacking the cancer cell chemotherapeutically and stimulating the immune system to confront the cancer, an immunochemotherapy approach," said Fisher, Thelma Newmeyer Corman Chair in Cancer Research and co-leader of the Cancer Molecular Genetics research program at VCU Massey, professor and chair of the VCU Department of Human and Molecular Genetics, and director of the VIMM . "The results are promising, and we look forward to conducting more extensive pre-clinical studies. Our ultimate hope is to bring this innovative scheme into the clinic to treat patients with pancreatic cancer."
As the need exists for newer and more effective strategies to treat pancreatic cancer, these findings are critical. And while the current focus of this research is on pancreatic cancer, this approach also has applications for melanoma, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. Several important questions related to [pIC]PEI will be explored in future research, including assessing its efficacy in additional and expanded in vitro and in vivo studies, and testing it in new combinations with conventional chemotherapies.
INFORMATION:
Other VCU School of Medicine investigators contributing to this research include: First author Praveen Bhoopathi, Ph.D., postdoctoral research scientist, Human and Molecular Genetics Department; Bridget A. Quinn, a graduate student in the M.D./Ph.D. and Molecular Biology Genetics programs; Qin Gui, M.S., and Xue-Ning Shen, M.D., both research technicians in the Human and Molecular Genetics Department; Steven R. Grossman, M.D., Ph.D., professor and chair of the Division of Hematology, Oncology and Palliative Care, deputy director of Massey and member of the Cancer Molecular Genetics and Developmental Therapeutics research programs at Massey; Swadesh K. Das, Ph.D., member of the Cancer Molecular Genetics program at Massey, VIMM member and assistant professor of the Human and Molecular Genetics Department; Devanand Sarkar, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., Harrison Scholar and member of the Cancer Molecular Genetics research program at Massey, associate scientific director of Cancer Therapeutics at the VIMM, and associate professor and Blick Scholar in the Human and Molecular Genetics Department.
This study was supported by NIH, NCI grant 1R01 CA127641 (PBF), VCU Massey Cancer Center Developmental Funds (PBF), VCU Massey Cancer Center Pilot Project (LE, SRG, PBF) and, in part, by VCU Massey Cancer Center's NIH-NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA016059.
The full study is available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25205107.
High blood pressure - already a massive hidden killer in Nigeria - is set to sharply rise as the country adopts western lifestyles, a study suggests.
Researchers who conducted the first up-to-date nationwide estimate of the condition in Nigeria warn that this will strain the country's already-stretched health system.
Increased public awareness, lifestyle changes, screening and early detection are vital to tackle the increasing threat of the disease, they say.
High blood pressure - also known as hypertension - is twice as high in Nigeria compared with other East ...
Scientists have demonstrated for the first time that a single-dose, needleless Ebola vaccine given to primates through their noses and lungs protected them against infection for at least 21 weeks. A vaccine that doesn't require an injection could help prevent passing along infections through unintentional pricks. They report the results of their study on macaques in the ACS journal Molecular Pharmaceutics.
Maria A. Croyle and colleagues note that in the current Ebola outbreak, which is expected to involve thousands more infections and deaths before it's over, an effective ...
Geneticists at Heidelberg University Hospital's Department of Molecular Human Genetics have used a new mouse model to demonstrate the way a certain genetic mutation is linked to a type of autism in humans and affects brain development and behavior. In the brain of genetically altered mice, the protein FOXP1 is not synthesized, which is also the case for individuals with a certain form of autism. Consequently, after birth the brain structures degenerate that play a key role in perception. The mice also exhibited abnormal behavior that is typical of autism. The new mouse ...
An electronic "tongue" could one day sample food and drinks as a quality check before they hit store shelves. Or it could someday monitor water for pollutants or test blood for signs of disease. With an eye toward these applications, scientists are reporting the development of a new, inexpensive and highly sensitive version of such a device in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
S. V. Litvinenko and colleagues explain that an electronic tongue is an analytical instrument that mimics how people and other mammals distinguish tastes. Tiny sensors detect substances ...
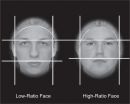
The structure of a soccer player's face can predict his performance on the field--including his likelihood of scoring goals, making assists and committing fouls--according to a study led by a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder.
The scientists studied the facial-width-to-height ratio (FHWR) of about 1,000 players from 32 countries who competed in the 2010 World Cup. The results, published in the journal Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology, showed that midfielders, who play both offense and defense, and forwards, who lead the offense, with higher FWHRs ...
Queensland University of Technology (QUT) researchers have found the habit of Googling for an online diagnosis before visiting the doctor can be a powerful predictor of infectious diseases outbreaks.
Now studies by the same Brisbane-based researchers show combining information from monitoring internet search metrics such as Baidu (China's equivalent of Google), with a web-based infectious disease alert system from reported cases and environmental factors hold the key to improving early warning systems and reducing the deadly effects of dengue fever in China.
Dr Wenbiao ...
A new peer-reviewed study found that people are contaminated with several toxic flame retardants rarely studied in the US, including one that has never before been detected in Americans called TCEP. Scientists tested urine samples of California residents for biomarkers of six chemicals, all of which were present.
The scientists discovered a way to test for this class of toxic flame retardants (phosphates), which could open up a new wave of research into a group of pervasive flame retardants that were previously not studied nearly as much as some other flame retardants. ...
Depression causes an average of 10 lost working days per episode
Managers report need for better legislation, training and counseling to tackle the problem
Right Direction Initiative developed to increase awareness of depression, reduce stigma associated with the disease in the workplace, and encourage employees to increase help-seeking behaviors
Canton, Ohio- November 12, 2014 - Nearly a quarter (23 percent) of U.S. respondents indicated they have been diagnosed with depression in their lifetime and two in five (nearly 40 percent) of those patients reported taking ...
Cities have more species diversity than you'd expect. A study of ants in Manhattan found not only a wide range of species, but also significant differences in the levels of biodiversity in different urban areas.
"People don't think of cities as having ecology, and urban environments haven't been well studied," says Dr. Amy Savage, a postdoctoral biological sciences researcher at North Carolina State University and lead author of a paper on the work. "But protected areas, such as national parks, have been well studied. So we wanted to see if the theories developed to predict ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- There's a cast of characters deep inside your ears -- many kinds of tiny cells working together to allow you to hear. The lead actors, called hair cells, play the crucial role in carrying sound signals to the brain.
But new research shows that when it comes to restoring lost hearing ability, the spotlight may fall on some of the ear's supporting actors - and their understudies.
In a new paper published online first by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from the University of Michigan Medical School, St. Jude Children's ...