(Press-News.org) Using two drugs was no more effective than a single drug in slowing disease progression in people with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), according to two studies funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). One of the studies also showed that rigorous blood pressure treatment slowed growth of kidney cysts, a marker of ADPKD, but had little effect on kidney function compared to standard blood pressure treatment.
The results of the HALT-PKD Clinical Trials Network studies will be published online November 15 in two papers in the New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with presentation at the American Society of Nephrology annual meeting.
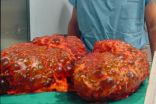
"Enlarged cysts in kidneys can lead to reduced kidney function and eventually kidney failure, where the only treatment is dialysis or transplantation," said study author Michael Flessner, M.D., Ph.D., a program director at the NIH's National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, which funded the trial. "The HALT-PKD findings show that people with polycystic kidney disease do not need to take both of the drugs studied to slow their rate of kidney cyst growth and decline in kidney function."
The HALT-PKD trial enrolled volunteers to test whether a combination of commonly used FDA-approved drugs, lisinopril and telmisartan, could shrink kidney cysts and therefore slow progression of ADPKD, a genetic disorder characterized by growth of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Within the trial, one study examined 558 people with early-stage ADPKD and relatively healthy kidneys. The other study treated 486 people with more advanced disease and decreased kidney function. In each study, half of participants were randomly assigned to receive lisinopril and telmisartan, while the other half received lisinopril plus a placebo. In both studies, adding the second drug did not change kidney function or rate of increase in kidney cyst size.
In the study of people with early ADPKD and healthy kidneys, researchers also tested if decreasing blood pressure below usual targets would slow progression of ADPKD and preserve kidney function. High blood pressure is a common and damaging effect of ADPKD. Half the participants were assigned to a standard blood pressure group (between 120-130 over 70-80), and half to a lower blood pressure group (between 95-110 over 60-75) but still within the normal range.
Participants in the lower blood pressure group received more rigorous treatment, taking more medication to maintain a lower blood pressure. The lower blood pressure group had a 14 percent decrease in kidney cyst size compared to those in the standard blood pressure group. However, kidney function - measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) - was about the same as the standard group at the end of the trial, yielding no clinical benefit. About 15 percent more of the people in the lower blood pressure group experienced lightheadedness and dizziness.
"The HALT-PKD studies were well performed and the largest of their kind," said Robert Star, M.D., director of the Division of Kidney, Urologic, and Hematologic Diseases within NIDDK. "More research is needed to better understand how polycystic kidney disease destroys kidney function over time, and what combination of medications can most safely and effectively prevent or undo the damage caused by this devastating condition."
ADPKD is the most common kind of polycystic kidney disease, representing 90 percent of the approximately 600,000 U.S. cases. PKD is the fourth leading cause of kidney failure.
INFORMATION:
HALT-PKD (tkNCT#) was supported by NIDDK under grants DK62408, DK62401, DK62410, DK62402, DK62411 and DK082230, with additional support from the NIH's NCATS under grants RR000039, RR000585, RR000054, RR000051, RR023940, RR001032, RR025008, TR000454, RR024150, TR00135, RR025752, TR001064, RR025780, TR001082, RR025758, TR001102, RR033179, TR000001, RR024989 and TR000439 and the PKD Foundation. Study drugs were donated by Boehringer Ingelheim and Merck & Co., Inc.
The NIDDK, a component of the NIH, conducts and supports research on diabetes and other endocrine and metabolic diseases; digestive diseases, nutrition and obesity; and kidney, urologic and hematologic diseases. Spanning the full spectrum of medicine and afflicting people of all ages and ethnic groups, these diseases encompass some of the most common, severe and disabling conditions affecting Americans. For more information about the NIDDK and its programs, see http://www.niddk.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
In patients undergoing noncardiac surgery, neither aspirin nor clonidine (a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure) taken before and after surgery reduced the risk of acute kidney injury, according to a study appearing in JAMA. The study is being released to coincide with its presentation at the American Society of Nephrology's annual Kidney Week meeting.
About 10 percent of the 200 million adults estimated to undergo major noncardiac surgery each year develop acute kidney injury (a sudden loss of kidney function). Perioperative (around the time of surgery) ...
Among kidney transplant recipients, a 3-month course of the antibiotic levofloxacin following transplantation did not prevent the major complication known as BK virus from appearing in the urine. The intervention was associated with an increased risk of adverse events such as bacterial resistance, according to a study appearing in JAMA. The study is being released to coincide with its presentation at the American Society of Nephrology's annual Kidney Week meeting.
Kidney transplantation is the preferred treatment for endstage renal disease. The development of potent ...
Taipei, November 15, 2014 - While a low body mass index (BMI) of less than 20 kg/m2 has been shown to be an independent risk factor for hip fractures, far less is known about the relationship of body weight changes on hip fracture risk.
The findings of a new study presented today at the IOF Regionals Asia-Pacific Osteoporosis Meeting in Taipei, show that among middle-aged to elderly Singapore Chinese, weight loss of 10% or more was associated with a 56% higher hip fracture risk.
The researchers used data from the Singapore Chinese Health Study, a population-based cohort ...
Taipei, November 15, 2014 - An epidemiological study presented today at the 5th Asia-Pacific Osteoporosis Meeting is one of the first to project the immense and growing economic cost of osteoporotic fractures in China.
The study, by investigators from the University of Tasmania, Anhui Medical University and Nanjing Medical University, used decision analytic modelling to estimate the burden of osteoporotic fractures. The researchers estimated that in 2010 more than 2.3 million osteoporosis-related hip, clinical vertebral and wrist fractures occurred in the population ...
DALLAS - November 15, 2014 - A novel looping mechanism that involves the end caps of DNA may help explain the aging of cells and how they initiate and transmit disease, according to new research from UT Southwestern Medical Center cell biologists.
The UT Southwestern team found that the length of the endcaps of DNA, called telomeres, form loops that determine whether certain genes are turned off when young and become activated later in life, thereby contributing to aging and disease.
"Our results suggest a potential novel mechanism for how the length of telomeres may ...
Philadelphia, PA (November 14, 2014) -- In addition to helping patients shed pounds, weight loss surgery may also improve kidney function, according to a study that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Weight loss, or bariatric, surgery is highly effective for rapid weight loss in patients with morbid obesity, who are at markedly increased risk for kidney failure. Because the effect of bariatric surgery-induced weight loss on kidney function is unknown, Alex Chang, MD (Geisinger Medical ...
Philadelphia, PA (November 14, 2014) -- The majority of individuals in the United States are not eligible to donate a kidney, even if they wanted to, according to a study that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
There is a shortage of living kidney donors in the United States, but no one has previously examined the general population to see who would be eligible to be donors. To assess the potential US donor pool, researchers led by Anthony Bleyer, MD (Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center) ...
Philadelphia, PA (November 14, 2014) -- Simple exercises can help improve the health of patients with kidney disease, according to studies that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Because exercise capacity is significantly reduced in CKD patients, Sharlene Greenwood, MD (King's College Hospital, in London) and her colleagues examined the effect of 12 months of exercise training on kidney function ...
DARIEN, IL - A new study suggests that teen drivers who start class earlier in the morning are involved in significantly more motor vehicle accidents than peers with a later high school start time. The results underscore the importance of the "Awake at the Wheel" campaign of the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project.
Results show that the weekday crash rate for teen drivers during the 2009 to 2010 school year was about 29 percent higher in Chesterfield County, Va., where high school classes began at 7:20 a.m., than in adjacent Henrico County, Va., where classes started ...
VIDEO:
What is Nutrigenomix? Here's a primer.
Click here for more information.
Researchers from the University of Toronto (U of T) report that personalized dietary advice based on a person's genetic makeup improves eating habits compared to current "one-size-fits-all" dietary recommendations. The findings were published online today in the journal PLoS One.
"We conducted the first randomized controlled trial to determine the impact of disclosing DNA-based dietary advice on ...