New technique to help produce next-generation photonic chips
2014-11-17
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Southampton have developed a new technique to help produce more reliable and robust next generation photonic chips.
Photonic chips made from silicon will play a major role in future optical networks for worldwide data traffic. The high refractive index of silicon makes optical structures the size of a fraction of the diameter of a human hair possible. Squeezing more and more optical structures for light distribution, modulation, detection and routing into smaller chip areas allows for higher data rates at lower fabrication costs.
As the complexity of optical chips increases, testing and characterising such chips becomes more difficult. Light traveling in the chip is confined in the silicon, that is, it cannot be 'seen' or measured from the outside.
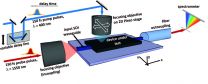
Southampton researchers have now developed a new method, which will help solve this problem, to find out at which time the light in the chip is at which position. The technique, called Ultrafast photomodulation spectroscopy (UPMS), uses ultraviolet laser pulses of femtosecond duration to change the refractive index of silicon in a tiny area on the photonic chip.
Non-contact characterization tools like UPMS are vital for scientist designing complex photonic chips. The UPMS technique is fast and robust and has the potential to be used for industrial testing in the photonics industry.
The research is published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Photonics.
Dr Roman Bruck, from Physics and Astronomy at the University of Southampton and lead author of the study, says: "Monitoring the transmission of the chip while the refractive index is locally changed gives a precise picture of how the light flows through it. This allows testing of individual optical elements on the chip, a crucial step in the design optimisation to ensure its flawless operation. Because the changes induced by the technique are fully reversible, this testing method is non-destructive and after testing, the chip can be used for its intended application."
The research team, from Physics and Astronomy and the Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) at the University, expects to establish the technique as a standard characterisation tool, making photonic chips under development more reliable and bringing them into the market quicker. The work has been funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-17
WASHINGTON, DC--Maritime traffic on the world's oceans has increased four-fold over the past 20 years, likely causing more water, air and noise pollution on the open seas, according to a new study quantifying global ship traffic.
The research used satellite data to estimate the number of vessels on the ocean every year between 1992 and 2012. The number of ships traversing the oceans grew by 60 percent between 1992 and 2002. Shipping traffic grew even faster during the second decade of the study, peaking at rate of increase of 10 percent per year in 2011.
Traffic went ...
2014-11-17
We're entering the era of big neuroscience. In a little over a year, the United States, Europe, Japan and Israel have launched brain research projects with big budgets and bold ambitions. Several other countries are expected to follow suit. But what has propelled neuroscience to the vanguard, and what impact will these initiatives have on the field?
Leaders from three of these projects--the U.S. BRAIN Initiative, Europe's Human Brain Project and Japan's Brain/MINDS--discussed these and other questions ahead of this week's special session on global brain initiatives at ...
2014-11-17
KNOXVILLE, TN -- In the nursery and landscape industries, flowering dogwood (Cornus florida), kousa dogwood (Cornus kousa), and their hybrids are the most popular and economically significant members of the genus Cornus. The deciduous trees are highly valued for their spring display of pink, red, or white bracts, brilliant red fall foliage, and exfoliating bark. In the United States alone, retail and wholesale sales of dogwoods account for more than $30 million dollars annually.
In the past, flowering dogwoods were severely affected by dogwood anthracnose and powdery ...
2014-11-17
Cambridge, Mass. - November 17, 2014 - A vast majority of scientists believe that the Earth is warming at an unprecedented rate and that human activity is almost certainly the dominant cause. But on the topics of response and mitigation, there is far less consensus.
One of the most controversial propositions for slowing the increase in temperatures here on Earth is to manipulate the atmosphere above. Specifically, some scientists believe it should be possible to offset the warming effect of greenhouses gases by reflecting more of the sun's energy back into space.
The ...
2014-11-17
This news release is available in German. The Malt1 protein carries out a variety of tasks in immune cells, known as lymphocytes. Among other things, it acts as an enzyme - specifically, a protease - that breaks down messenger substances and thus controls their quantity. Until now it was not known what role the specific protease function plays in the development of immune cells. Several years ago Prof. Jürgen Ruland and his team at TUM's Klinikum rechts der Isar turned their attention to this question.
Blockade as a therapeutic approach
The scientists were ...
2014-11-17
COLUMBIA, MO -- Black walnut (Juglans nigra L.) is native to much of the eastern United States and is highly valued for its nuts and timber. Black walnut fruit generally reach most of their size by mid-August and mature by late September or early October. The fruit are then harvested, hulled, and dried in-shell before cracking for commercial markets. Walnut growers use the term "ambers" to describe poorly filled, shriveled eastern black walnut kernels. These "ambered kernels" are not marketable, resulting in economic loss to commercial growers. Although researchers have ...
2014-11-17
University of Adelaide research has for the first time shown how much of a critical role the natural antioxidant selenium plays at the earliest stages of a woman's fertility.
The discovery has been made in joint research involving the University's School of Chemistry and Physics and the Robinson Research Institute.
For her PhD in Chemistry at the University of Adelaide, Melanie Ceko investigated the role and location of selenium in the ovary, and a specific protein that includes selenium. The results of her study show how important selenium is to the development of ...
2014-11-17
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Good news for savvy businesses: Customers who walk through your doors unhappy with another firm's service can be won back with simple gestures of goodwill.
Consider a dissatisfied airline passenger. A hotel can score loyalty points by providing the traveler a room upgrade or perhaps even a simple apology for the airline's failure, said Clay Voorhees, associate professor of marketing at Michigan State University.
In a study published online in the Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, Voorhees and fellow researchers refute past findings ...
2014-11-17
For nearly three decades, researchers have pondered the Hispanic Mortality Paradox -- why Hispanics in the U.S. tend to outlive non-Hispanic whites by several years, despite having, in general, lower income and educational attainment levels that are associated with shorter lives.
New research suggests that the Hispanic Mortality Paradox may be related to illness survival and recovery advantages. A study by researchers from the University of North Texas and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center found that Hispanics were hospitalized significantly fewer total ...
2014-11-17
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - An international team of researchers including Jon Klein, M.D., Ph.D., and Michael Merchant, Ph.D., of the University of Louisville has identified a protein that turns a person's immune system against itself in a form of kidney disease called membranous nephropathy (MN). The findings are published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This is the second protein associated with MN and the development of an autoimmune response.
Through the identification of this second protein, a new blood test can be developed to diagnose this common form of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New technique to help produce next-generation photonic chips





