A new genetic cause for a progressive form of epilepsy identified
2014-11-17
(Press-News.org) A study led by researchers at University of Helsinki, Finland and Universities of Melbourne and South Australia has identified a new gene for a progressive form of epilepsy. The findings of this international collaborative effort have been published today, 17 November 2014, in Nature Genetics.
Progressive myoclonus epilepsies (PME) are rare, inherited, and usually childhood-onset neurodegenerative diseases whose core symptoms are epileptic seizures and debilitating involuntary muscle twitching (myoclonus). The goal of the international collaborative study was to identify underlying genetic causes in 84 PME patients using DNA sequencing targeting the protein coding elements of the human genome.
Overall, a genetic diagnosis was reached for almost one third of these hitherto unsolved patients. Findings of the study shed light on molecular genetic basis of progressive epilepsy, which aids in diagnostics and potential therapeutic interventions of the disease. The study also shows that modern DNA technologies are powerful in dissecting the underlying genetic causes of severe diseases.
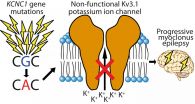
The most important and surprising finding of the study was that a single mutation in a potassium channel encoding gene KCNC1 explains a significant proportion of unsolved PME cases. The mutation was found in a total of 13 patients and was not inherited from parents - instead it has emerged in a germ cell of one of the parents or in the fertilized egg. Each individual has dozens of these new, "de novo", mutations but they are rarely disease causing. The researchers estimate that this mutation occurs in approximately 1 out of every 5.7 million conceptions, indicating that at least hundreds of patients could have this mutation globally.
"A fascinating aspect of this finding is that this single mutation can be found in several patients all over the world. The mutation site is an example of a 'mutation hotspot' of the genome - a DNA nucleotide which is more prone for alterations", says Professor Anna-Elina Lehesjoki, the corresponding principal investigator of the study in University of Helsinki and Folkhälsan Research Center, Finland.
The new mutation identified in the study disrupts the function of a potassium channel, KV3.1, which has a central role in signal transmission in the brain. The likely consequence of the mutation is that inhibitory signals in certain parts of patient brain are reduced, which makes patients susceptible to epileptic seizures and myoclonus starting in childhood. In addition, the mutation causes degeneration of the cerebellum and subtle cognitive decline in some of the patients.
"The fact that the mutation occurs in a well-characterized ion channel gives hope to development of targeted therapy. There are anti-epileptic drugs in the market that target other similar ion channels and follow-up research aims to discover a way to rescue the function of the channel in PME patients", says Professor Lehesjoki.
The researchers of the project emphasize the importance of international collaboration for the study. "This study shows the power of combining sample collections and knowledge from different countries", says Professor Samuel Berkovic, University of Melbourne, who coordinated the patient sample collection spanning over 20 years and involving multiple epilepsy centers worldwide.
INFORMATION:
The central research institutes participating in the study were University of Helsinki, Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland FIMM and Folkhälsan Research Center (Finland), Universities of Melbourne and South Australia (Australia), Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (UK), University of Tübingen (Germany) and several universities in Italy.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-17
Scientists have found that altering members of the p53 gene family, known as tumor suppressor genes, causes rapid regression of tumors that are deficient in or totally missing p53. Study results suggest existing diabetes drugs, which impact the same gene-protein pathway, might be effective for cancer treatment.
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center investigation showed that, in vivo, the genes p63 and p73 can be manipulated to upregulate or increase levels of IAPP, a protein important for the body's ability to metabolize glucose. IAPP is found in some diabetes ...
2014-11-17
BALTIMORE, MD - As the world's diminishing fresh water resources are increasing allocated for human use, agricultural and horticultural production operations must rely more often on the use of brackish, saline, or reclaimed water for irrigation. These saline-rich water sources often contain electrical conductivities that can negativity affect plants' ability to thrive. Salinity is particularly problematic for ornamental plants such as daffodils because of the potential for damage to plants' aesthetics and visual qualities.
In the September 2014 issue of HortScience, Maren ...
2014-11-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- One of the family of drugs prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions is called TNF inhibitors. They act by dampening part of the immune system called tumor necrosis factor (TNF). In one of the balancing acts of medicine, the anti-inflammatory action of the drug also increases the risk for other conditions, in this case, a rare form of eye cancer, uveal melanoma. Mayo Clinic researchers make the case and alert physicians in an article in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Mayo researchers studied three patients -- two women and a ...
2014-11-17
Who says your kids don't listen to you?
An Indiana University study has found that setting specific family rules about healthy eating and sedentary behavior actually leads to healthier practices in children.
Data analyzed for the study was originally part of a data set used to evaluate the Wellborn Baptist Foundation's HEROES program, a K-12 school-based obesity prevention initiative set in the Illinois, Indiana and Kentucky tri-state area. However, lead author Alyssa M. Lederer, doctoral candidate and associate instructor in the Department of Applied Health Science ...
2014-11-17
CINCINNATI--Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) have found that a gene abundant in the kidneys may actually play a role in the regulation of blood pressure and hypertension in experimental male mouse models.
The study led by Manoocher Soleimani, MD, James F. Heady Professor of Medicine and associate chair of research in the Department of Internal Medicine at UC, was presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology, held Friday, Nov. 15, 2014, in Philadelphia.
The gene, a kidney androgen-regulated protein (KAP) that is abundantly ...
2014-11-17
New Rochelle, NY, November 17, 2014--In the future, as space exploration takes astronauts on longer missions and more female astronauts participate, "The Impact of Sex and Gender on Adaptation to Space" will become increasingly critical to astronaut safety and mission success, as explored in a special collection of articles published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles are available Open Access on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/toc/jwh/23/11.
In the Executive ...
2014-11-17
LOGAN, UT - Urban landscape plants are often subjected to environmental conditions well beyond those of their native habitat. Differences in precipitation, along with stress caused by increased salinity resulting from irrigation with brackish reclaimed water, can have devastating impacts on trees and plants. Use of salt-tolerant species and implementation of proper management strategies can reduce the incidence of plant stress and loss. Researchers in Utah looked to plants' native habitats for ways to identify salt tolerance among tree species used in urban landscapes in ...
2014-11-17
An international team of scientists led by Uppsala University has developed a high-throughput method of imaging biological particles using an X-ray laser. The images show projections of the carboxysome particle, a delicate and tiny cell compartment in photosynthetic bacteria.
The experiment, described in a paper published today in the scientific journal Nature Photonics, represents a major milestone for studies of individual biological structures using X-ray lasers. The technique paves the way for 3D imaging of parts of the cell, and even small viruses, to develop a ...
2014-11-17
November 17, 2014 - A growing body of research evidence shows that complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) has health benefits for US military veterans and active duty personnel, according to a special December supplement to Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The special issue presents new studies and commentaries on the benefits and increasing use of CAM techniques in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and other military health settings. "The papers in this supplement represent promising ...
2014-11-17
Fatigue, increased irritability, and feeling demoralized, may raise a healthy man or woman's risk of first-time cardiovascular disease by 36 percent, according to a study led by researchers at Mount Sinai St. Luke's and Mount Sinai Roosevelt hospitals presented on Nov. 17 at the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2014 in Chicago, IL.
The combination of fatigue, increased irritability, and feeling demoralized is medically known as vital exhaustion. In their study, Mount Sinai researchers found that vital exhaustion was associated with a dramatic increase ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new genetic cause for a progressive form of epilepsy identified





