(Press-News.org) Yasuo Ikeda, M.D., of Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan, and colleagues examined whether once-daily, low-dose aspirin would reduce the total number of cardiovascular (CV) events (death from CV causes, nonfatal heart attack or stroke) compared with no aspirin in Japanese patients 60 years or older with hypertension, diabetes, or poor cholesterol or triglyceride levels. The study appears in JAMA and is being released to coincide with its presentation at the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2014.
The World Health Organization estimates that annual global mortality due to cardiovascular diseases (including heart attack and stroke) will approach 25 million by 2030. A recent study of trends in cardiovascular disease in Japan indicated that there has been, from 1960 to 2000, a steep increase in the prevalence of glucose intolerance, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity, probably due to the adoption of Western diets and lifestyles. By 2030, it is estimated that 32 percent of the Japanese population will be 65 years or older. Prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases is an important public health priority in Japan due to an aging population, according to background information in the article.
This study included 14,464 patients (60 to 85 years of age) with hypertension, dyslipidemia (poor cholesterol or triglyceride levels), or diabetes mellitus who were randomized to aspirin (100 mg/d) or no aspirin in addition to ongoing medications. The patients were recruited by primary care physicians at 1,007 clinics in Japan. The study was terminated early by the data monitoring committee after a median follow-up of 5.02 years based on likely futility.
The researchers found that there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in time to the primary end point (a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal stroke, and nonfatal heart attack). At 5 years after randomization, the cumulative primary event rate was similar in participants in the aspirin group (2.77 percent) and those in the no aspirin group (2.96 percent).
Aspirin significantly reduced incidence of nonfatal heart attack and transient ischemic attack, and significantly increased the risk of extracranial hemorrhage requiring transfusion or hospitalization.
The authors write that despite inconsistent evidence for the benefit of aspirin in primary prevention of cardiovascular events, the benefits in secondary prevention are well documented, including in Japanese patients. "There is also a growing body of evidence to suggest benefits for aspirin in the prevention of colorectal and other cancers, and the prevention of cancer recurrence, including in the Japanese population. Reduction in the incidence of colorectal cancer may influence the overall benefitrisk profile of aspirin. Further analyses of [this] study data are planned, including analysis of deaths associated with cancers, to allow more precise identification of the patients for whom aspirin treatment may be most beneficial."
J. Michael Gaziano, M.D., M.P.H., of the Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Associate Editor, JAMA, and Philip Greenland, M.D., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, and Senior Editor, JAMA, write in an accompanying editorial that the findings from this study adds to the body of evidence that helps refine the answer to the question of when aspirin should be used to prevent vascular events.
"Decision making involves an assessment of individual risk-to-benefit that should be discussed between clinician and patient. However, at present the choice of aspirin remains clear in several situations. Aspirin is indicated for patients at high short-term risk due to an acute vascular event and those undergoing certain vascular procedures; patients with any evidence of vascular disease should be given daily aspirin. On the other hand, patients at very low risk of vascular events should not take aspirin for prevention of vascular events, even at low dose."
"However, some individuals who do not have overt vascular disease will have risk levels that approach those of patients with CVD (such as patients with multiple risk factors). It remains likely that there is some level of risk of CVD events that would result in a positive trade-off of benefit and risk for the use of aspirin, but the precise level of risk is uncertain."
INFORMATION:
Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
doi:10.1001/jama.2014.15690
doi:10.1001/jama.2014.16047
Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com
DALLAS - November 17, 2014 - Using next generation gene sequencing techniques, cancer researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have identified more than 3,000 new mutations involved in certain kidney cancers, findings that help explain the diversity of cancer behaviors.
"These studies, which were performed in collaboration with Genentech Inc., identify novel therapeutic targets and suggest that predisposition to kidney cancer across species may be explained, at least in part, by the location of tumor suppressor genes with respect to one another in the genome," said ...
Washington, D.C.--Silicon is the second most-abundant element in the earth's crust. When purified, it takes on a diamond structure, which is essential to modern electronic devices--carbon is to biology as silicon is to technology. A team of Carnegie scientists led by Timothy Strobel has synthesized an entirely new form of silicon, one that promises even greater future applications. Their work is published in Nature Materials.
Although silicon is incredibly common in today's technology, its so-called indirect band gap semiconducting properties prevent it from being ...
HOUSTON -- (Nov. 17, 2014) - A compound called calcein may act to inhibit topoisomerase IIβ-binding protein 1 (TopBP1), which enhances the growth of tumors, said researchers from Baylor College of Medicine in a report that appears online in the journal Nature Communications.
"The progression of many solid tumors is driven by de-regulation of multiple common pathways," said Dr. Weei-Chin Lin, associate professor of medicine- hematology & oncology, and a member of the NCI-designated Dan L. Duncan Cancer Center at Baylor. Among those are the retinoblastoma (Rb), PI(3)K/Akt ...
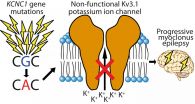
A study led by researchers at University of Helsinki, Finland and Universities of Melbourne and South Australia has identified a new gene for a progressive form of epilepsy. The findings of this international collaborative effort have been published today, 17 November 2014, in Nature Genetics.
Progressive myoclonus epilepsies (PME) are rare, inherited, and usually childhood-onset neurodegenerative diseases whose core symptoms are epileptic seizures and debilitating involuntary muscle twitching (myoclonus). The goal of the international collaborative study was to identify ...
Scientists have found that altering members of the p53 gene family, known as tumor suppressor genes, causes rapid regression of tumors that are deficient in or totally missing p53. Study results suggest existing diabetes drugs, which impact the same gene-protein pathway, might be effective for cancer treatment.
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center investigation showed that, in vivo, the genes p63 and p73 can be manipulated to upregulate or increase levels of IAPP, a protein important for the body's ability to metabolize glucose. IAPP is found in some diabetes ...
BALTIMORE, MD - As the world's diminishing fresh water resources are increasing allocated for human use, agricultural and horticultural production operations must rely more often on the use of brackish, saline, or reclaimed water for irrigation. These saline-rich water sources often contain electrical conductivities that can negativity affect plants' ability to thrive. Salinity is particularly problematic for ornamental plants such as daffodils because of the potential for damage to plants' aesthetics and visual qualities.
In the September 2014 issue of HortScience, Maren ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- One of the family of drugs prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions is called TNF inhibitors. They act by dampening part of the immune system called tumor necrosis factor (TNF). In one of the balancing acts of medicine, the anti-inflammatory action of the drug also increases the risk for other conditions, in this case, a rare form of eye cancer, uveal melanoma. Mayo Clinic researchers make the case and alert physicians in an article in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Mayo researchers studied three patients -- two women and a ...
Who says your kids don't listen to you?
An Indiana University study has found that setting specific family rules about healthy eating and sedentary behavior actually leads to healthier practices in children.
Data analyzed for the study was originally part of a data set used to evaluate the Wellborn Baptist Foundation's HEROES program, a K-12 school-based obesity prevention initiative set in the Illinois, Indiana and Kentucky tri-state area. However, lead author Alyssa M. Lederer, doctoral candidate and associate instructor in the Department of Applied Health Science ...
CINCINNATI--Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) have found that a gene abundant in the kidneys may actually play a role in the regulation of blood pressure and hypertension in experimental male mouse models.
The study led by Manoocher Soleimani, MD, James F. Heady Professor of Medicine and associate chair of research in the Department of Internal Medicine at UC, was presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology, held Friday, Nov. 15, 2014, in Philadelphia.
The gene, a kidney androgen-regulated protein (KAP) that is abundantly ...
New Rochelle, NY, November 17, 2014--In the future, as space exploration takes astronauts on longer missions and more female astronauts participate, "The Impact of Sex and Gender on Adaptation to Space" will become increasingly critical to astronaut safety and mission success, as explored in a special collection of articles published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles are available Open Access on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/toc/jwh/23/11.
In the Executive ...