(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
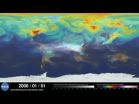
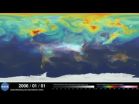
An ultra-high-resolution NASA computer model has given scientists a stunning new look at how carbon dioxide in the atmosphere travels around the globe. Plumes of carbon dioxide in the simulation...
Click here for more information.
An ultra-high-resolution NASA computer model has given scientists a stunning new look at how carbon dioxide in the atmosphere travels around the globe.
Plumes of carbon dioxide in the simulation swirl and shift as winds disperse the greenhouse gas away from its sources. The simulation also illustrates differences in carbon dioxide levels in the northern and southern hemispheres and distinct swings in global carbon dioxide concentrations as the growth cycle of plants and trees changes with the seasons.
Scientists have made ground-based measurements of carbon dioxide for decades and in July NASA launched the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite to make global, space-based carbon observations. But the simulation - the product of a new computer model that is among the highest-resolution ever created - is the first to show in such fine detail how carbon dioxide actually moves through the atmosphere.
"While the presence of carbon dioxide has dramatic global consequences, it's fascinating to see how local emission sources and weather systems produce gradients of its concentration on a very regional scale," said Bill Putman, lead scientist on the project from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. "Simulations like this, combined with data from observations, will help improve our understanding of both human emissions of carbon dioxide and natural fluxes across the globe."
The carbon dioxide visualization was produced by a computer model called GEOS-5, created by scientists at NASA Goddard's Global Modeling and Assimilation Office. In particular, the visualization is part of a simulation called a "Nature Run." The Nature Run ingests real data on atmospheric conditions and the emission of greenhouse gases and both natural and man-made particulates. The model is then is left to run on its own and simulate the natural behavior of the Earth's atmosphere. This Nature Run simulates May 2005 to June 2007.
While Goddard scientists have been tweaking a "beta" version of the Nature Run internally for several years, they are now releasing this updated, improved version to the scientific community for the first time. Scientists are presenting a first look at the Nature Run and the carbon dioxide visualization at the SC14 supercomputing conference this week in New Orleans.
"We're very excited to share this revolutionary dataset with the modeling and data assimilation community," Putman said, "and we hope the comprehensiveness of this product and its ground-breaking resolution will provide a platform for research and discovery throughout the Earth science community."
In the spring of 2014, for the first time in modern history, atmospheric carbon dioxide - the key driver of global warming - exceeded 400 parts per million across most of the northern hemisphere. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, carbon dioxide concentrations were about 270 parts per million. Concentrations of the greenhouse gas in the atmosphere continue to increase, driven primarily by the burning of fossil fuels.
Despite carbon dioxide's significance, much remains unknown about the pathways it takes from emission source to the atmosphere or carbon reservoirs such as oceans and forests. Combined with satellite observations such as those from NASA's recently launched OCO-2, computer models will help scientists better understand the processes that drive carbon dioxide concentrations.
The Nature Run also simulates winds, clouds, water vapor and airborne particles such as dust, black carbon, sea salt and emissions from industry and volcanoes.
The resolution of the model is approximately 64 times greater than that of typical global climate models. Most other models used for long-term, high-resolution climate simulations resolve climate variables such as temperatures, pressures, and winds on a horizontal grid consisting of boxes about 50 kilometers (31 miles) wide. The Nature Run resolves these features on a horizontal grid consisting of boxes only 7 kilometers (4.3 miles) wide.
The Nature Run simulation was run on the NASA Center for Climate Simulation's Discover supercomputer cluster at Goddard Space Flight Center. The simulation produced nearly four petabytes (million billion bytes) of data and required 75 days of dedicated computation to complete.
In addition to providing a striking visual description of the movements of an invisible gas like carbon dioxide, as it is blown by the winds, this kind of high-resolution simulation will help scientists better project future climate. Engineers can also use this model to test new satellite instrument concepts to gauge their usefulness. The model allows engineers to build and operate a "virtual" instrument inside a computer.
Using GEOS-5 in tests known as Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSE) allows scientists to see how new satellite instruments might aid weather and climate forecasts.
"While researchers working on OSSEs have had to rely on regional models to provide such high-resolution Nature Run simulations in the past, this global simulation now provides a new source of experimentation in a comprehensive global context," Putman said. "This will provide critical value for the design of Earth-orbiting satellite instruments."
INFORMATION:
For detailed views of various parts of the world, visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/a-closer-look-at-carbon-dioxide
For more information about NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/oco or
http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov/
For more information about OSSEs, visit:
http://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/projects/osse/
A team of 14 scientists led by David Williams of Arizona State University's School of Earth and Space Exploration has completed the first global geologic and tectonic map of the asteroid Vesta. The work reveals that Vesta's history has been dominated by impacts from large meteorites.
The mapping was carried out using images from NASA's Dawn spacecraft, which orbited Vesta between June 2011 and September 2012. The images let scientists create high-resolution geological maps, revealing the variety of Vesta's surface features in unprecedented detail.
"The geologic mapping ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Online retail sales totaled $75 billion in the second quarter of 2014, according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau. As consumers shop more using the Internet and cell phones, retailers must adjust their marketing strategies to reach these consumers. In a recently published study, a University of Missouri researcher found that consumers' preferences differ when they are shopping in a physical store compared to shopping online. Catering to shoppers' online and in-store preferences can increase the effectiveness of traditional marketing tactics such as direct ...
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine have found that a growth factor can regenerate damaged peripheral nerves without causing the growth of new blood vessels -- making it a unique candidate to treat nerve damage in areas of the body where the proliferation of blood vessels would be a drawback.
"One example would be in the cornea, which has a requirement for dense innervation but where the formation of new blood vessels would block vision," said Dr. Mark Rosenblatt, professor and head of ophthalmology and visual sciences at UIC and corresponding ...
Metastasis is bad news for cancer patients. Northwestern University scientists now have demonstrated a simple but powerful tool that can detect live cancer cells in the bloodstream, potentially long before the cells could settle somewhere in the body and form a dangerous tumor.
The NanoFlare technology is the first genetic-based approach that is able to detect live circulating tumor cells out of the complex matrix that is human blood -- no easy feat. In a breast cancer study, the NanoFlares easily entered cells and lit up the cell if a biomarker target was present, even ...
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 17, 2014 - Whether birds are breathing in or out, air flows in a one-directional loop through their lungs. This pattern was unexpected and for decades, biologists assumed it was unique to birds, a special adaptation driven by the intense energy demands of flight.
But that view is wrong, according to University of Utah scientists who now have shown that bird-like breathing also developed in green iguanas - reptiles not known for high-capacity aerobic fitness. The finding bolsters the case that unidirectional bird-like flow evolved long before the first ...
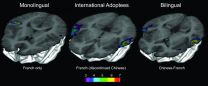
MONTREAL: An infant's mother tongue creates neural patterns that the unconscious brain retains years later even if the child totally stops using the language, (as can happen in cases of international adoption) according to a new joint study by scientists at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital - The Neuro and McGill University's Department of Psychology. The study offers the first neural evidence that traces of the "lost" language remain in the brain.
"The infant brain forms representations of language sounds, but we wanted to see whether the brain maintains ...
November 17, 2014--Museum biological collections are the records of life on Earth and as such, they are frequently used to investigate serious environmental issues. When public health officials were concerned about the levels of mercury in fish and birds, for example, scientists studied museum specimens to assess historical changes in mercury contamination. Eggs in museum collections were analyzed to establish the connection between DDT, thinning eggshells, and the decline in bird populations. And now, specimens from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County (NHM) ...
CHICAGO - Black patients who have been diagnosed with heart failure are no less likely than white patients to get atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia), according to a new study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which was presented today at the 2014 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association. These findings run counter to previous studies, which have found that black patients with heart failure tend to have less atrial fibrillation problems than white patients.
"Even though ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- The investigational drug ixazomib taken orally in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone shows promise in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to the results of a phase 1/2 study published in the journal Lancet Oncology.
"Ixazomib is an investigational, oral proteasome inhibitor with promising anti-myeloma effects and low rates of peripheral neuropathy," says Shaji Kumar, M.D., a hematologist at Mayo Clinic and lead author of the study. "While it is well known that a combination of bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone ...
iRhythm Technologies, Inc. announced today that study results presented during the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions showed an association between a high burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and lower cognitive function, specifically executive and verbal function. Previous studies have shown a relationship between AFib, cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia. However, this study, which was led by researchers at the University of Minnesota, demonstrates for the first time a correlation between high AFib burden - the percent of time a person has ...