Finding 'lost' languages in the brain
Study has far-reaching implications for unconscious role of infant experiences on adult development
2014-11-17
(Press-News.org) MONTREAL: An infant's mother tongue creates neural patterns that the unconscious brain retains years later even if the child totally stops using the language, (as can happen in cases of international adoption) according to a new joint study by scientists at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital - The Neuro and McGill University's Department of Psychology. The study offers the first neural evidence that traces of the "lost" language remain in the brain.
"The infant brain forms representations of language sounds, but we wanted to see whether the brain maintains these representations later in life even if the person is no longer exposed to the language," says Lara Pierce, a doctoral candidate at McGill University and first author on the paper. Her work is jointly supervised by Dr. Denise Klein at The Neuro and Dr. Fred Genesee in the Department of Psychology. The article, "Mapping the unconscious maintenance of a lost first language," is in the November 17 edition of scientific journal PNAS.
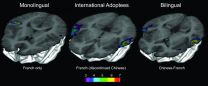
The Neuro conducted and analyzed functional MRI scans of 48 girls between nine and 17 years old who were recruited from the Montreal area through the Department of Psychology. One group was born and raised unilingual in a French-speaking family. The second group had Chinese-speaking children adopted as infants who later became unilingual French speaking with no conscious recollection of Chinese. The third group were fluently bilingual in Chinese and French.
Scans were taken while the three groups listened to the same Chinese language sounds.
"It astounded us that the brain activation pattern of the adopted Chinese who 'lost' or totally discontinued the language matched the one for those who continued speaking Chinese since birth. The neural representations supporting this pattern could only have been acquired during the first months of life," says Ms. Pierce. "This pattern completely differed from the first group of unilingual French speakers."
The study suggests that early-acquired information is not only maintained in the brain, but unconsciously influences brain processing for years, perhaps for life - potentially indicating a special status for information acquired during optimal periods of development. This could counter arguments not only within the field of language acquisition, but across domains, that neural representations are overwritten or lost from the brain over time.
The implications of this finding are far reaching, and open the door for questions relating both to the re-learning of an early acquired, but forgotten, language or skill, as well as the unconscious influence of early experiences on later developmental outcomes.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada, the Fonds de recherche sur la société et la culture, the G.W. Stairs Foundation and the Centre for Research on Brain Language and Mind.
About the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital
The Neuro is an academic medical centre dedicated to neuroscience. As a research and teaching institute of McGill University, The Neuro is at the centre of the neuroscience mission of the McGill University Health Centre. The eminent neurosurgeon Wilder Penfield founded The Neuro in 1934. Since then, The Neuro has achieved international renown for its integration of research, outstanding patient care and advanced training. The Neuro has a world-class staff in cellular and molecular neuroscience, brain imaging, cognitive neuroscience, as well as in the study and treatment of epilepsy, multiple sclerosis and neuromuscular disorders. For more information, please visit http://www.mni.mcgill.ca
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-17
November 17, 2014--Museum biological collections are the records of life on Earth and as such, they are frequently used to investigate serious environmental issues. When public health officials were concerned about the levels of mercury in fish and birds, for example, scientists studied museum specimens to assess historical changes in mercury contamination. Eggs in museum collections were analyzed to establish the connection between DDT, thinning eggshells, and the decline in bird populations. And now, specimens from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County (NHM) ...
2014-11-17
CHICAGO - Black patients who have been diagnosed with heart failure are no less likely than white patients to get atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia), according to a new study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which was presented today at the 2014 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association. These findings run counter to previous studies, which have found that black patients with heart failure tend to have less atrial fibrillation problems than white patients.
"Even though ...
2014-11-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- The investigational drug ixazomib taken orally in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone shows promise in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to the results of a phase 1/2 study published in the journal Lancet Oncology.
"Ixazomib is an investigational, oral proteasome inhibitor with promising anti-myeloma effects and low rates of peripheral neuropathy," says Shaji Kumar, M.D., a hematologist at Mayo Clinic and lead author of the study. "While it is well known that a combination of bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone ...
2014-11-17
iRhythm Technologies, Inc. announced today that study results presented during the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions showed an association between a high burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and lower cognitive function, specifically executive and verbal function. Previous studies have shown a relationship between AFib, cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia. However, this study, which was led by researchers at the University of Minnesota, demonstrates for the first time a correlation between high AFib burden - the percent of time a person has ...
2014-11-17
Amsterdam, NL, 17 November 2014 - Two simple tests conducted during the neurological exam can help clinicians differentiate between early-stage Parkinson's disease (PD) and atypical parkinsonism. By asking patients to perform a tandem gait test and inquiring whether they are still able to ride a bicycle, clinicians can ascertain whether medio-lateral balance is impaired, a defining characteristic of atypical parkinsonism. These findings are published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease.
This issue of the Journal of Parkinson's Disease also marks the inauguration of ...
2014-11-17
Why is Jamaica, with a population smaller than that of Los Angeles, home to so many of the world's elite sprinters - runners who compete in the 100, 200, 400 and 800-meter races?
Robert Trivers, an evolutionary biologist and professor of anthropology and biology in the School of Arts and Sciences, set out with his colleagues to find out if there was something about the symmetry of their knees that might partly explain this phenomenon. They already knew from their earlier research that the symmetry of children's knees at age 8 predicts how fast a person runs 14 years later ...
2014-11-17
The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 12:48 p.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured an image of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, ...
2014-11-17
Here's another reason to pay close attention to microbes: Current climate models probably overestimate the amount of carbon that will be released from soil into the atmosphere as global temperatures rise, according to research from the US Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
The findings are from a new computer model that explores the feedbacks between soil carbon and climate change. It's the first such model to include several physiologically realistic representations of how soil microbes break down organic matter, a process that ...
2014-11-17
Fruit flies do not always conform to the norm. When female fruit flies have to decide where to lay their eggs, they take their lead from what they see most others in their group do. However, some do take their personal preferences into account. So says Marine Battesti of the Université Paris-Sud in France, lead author of a study in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
The site on which an insect chooses to lay her eggs is very important for the development and survival of future generations. Such choices are not fixed, but are influenced by the ...
2014-11-17
UC Davis researchers are getting a new look at the workings of HIV and other viruses thanks to new techniques in electron microscopy developed on campus.
The envelope (or Env) protein of HIV is a key target for vaccine makers: it is a key component in RV144, an experimental vaccine that is so far the only candidate to show promise in clinical trials. Also called gp120, the Env protein associates with another protein called gp41 and three gp120/gp41 units associate to form the final trimeric structure. The gp120 trimer is the machine that allows HIV to enter and attack ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Finding 'lost' languages in the brain
Study has far-reaching implications for unconscious role of infant experiences on adult development