(Press-News.org) MAYWOOD, Ill. - Obesity is a known risk factor for atrial fibrillation, the most common heart rhythm disorder.
Obesity is commonly measured as a person's body mass index (BMI). But a Loyola University Medical Center study has found that the layer of fat around the outside of the heart is more closely associated with atrial fibrillation than BMI.
"Many people who would not be considered obese by their BMI nevertheless have high volumes of fat around their hearts, which could put them at risk for atrial fibrillation. Simple measures such as BMI may fail to completely inform us of a patient's true cardiovascular risk," said Mark Rabbat, MD, first author of the study and an assistant professor of medicine and radiology, Division of Cardiology, at Loyola University Medical Center.
Dr. Rabbat presented the intriguing findings Nov. 17 at the American Heart Association 2014 Scientific Sessions in Chicago.
The study found a statistically significant correlation between the fat layer and scarring in the left atrium that causes atrial fibrillation. By contrast, there was not a statistically significant correlation between BMI and scarring in the left atrium. (The left atrium is one of the four chambers of the heart.)
Atrial fibrillation, or a-fib, occurs when the atria (upper chambers of the heart) fibrillate (contract very fast and irregularly). A-fib is thought to be caused by inflammation and scarring (fibrosis) in the left atrium.
The fat layer around the outside of the heart is called epicardial adipose tissue (EAT). New innovations in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging enable physicians to precisely measure both EAT volume and the amount of fibrosis in the left atrium. "Our study is the first of its kind to demonstrate the association of EAT and the extent of left atrial fibrosis in patients with a-fib," Dr. Rabbat said.
The study included 54 patients who had a-fib. The average amount of fat around the heart (EAT volume) was 120 cubic centimeters. There was a statistically significant correlation of 0.45 between EAT volume and fibrosis. By comparison, there was only a 0.30 correlation between BMI and fibrosis - and this lower correlation was not statistically significant.
"Further studies are being planned by our group to clarify the association between EAT and a-fib and the interplay with other a-fib risk factors," said Mushabbar Syed, MD, Loyola's medical director of cardiovascular imaging and a co-author of the study.
For many years, EAT was believed to be harmless, inert fat tissue. But it now appears that EAT is a metabolically active organ, releasing proteins that may trigger the fibrosis that causes a-fib.
Weight loss, either through diet and exercise or through weight-loss surgery, has been shown to reduce the amount of EAT. But current medical treatments fail to specifically target EAT.
"Fat tissue around the heart may be a novel target to reduce the risk of a-fib and its recurrence," Dr. Rabbat said.
The study is titled "Epicardial adipose tissue volume predicts extent of left atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation."
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors of the study, all at Loyola, are Bassel Sayegh, MD; Andrew Stiff, MD; Brian Vetter, MS; Kim Chan, MBBS; Tonye Teme, MD; and senior author David Wilber, MD.
CHICAGO - Most patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs)--small devices placed in a person's chest to help treat irregular heartbeats with electrical pulses, or shocks--haven't thought about device deactivation if they were to develop a serious illness from which they were not expected to recover. But given changes in healthcare, there may be a new reason to do so. A new study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which was presented today at the 2014 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association, ...
We like to think of evolution as a fine-tuning process, one that whittles away genetic redundancies. The only problem is, we are not fine-tuned machines. Our bodies are chock-full of parts that either don't work anymore or are so buggy that our biology has Macgyvered a way to make it work.
Take our DNA. No, seriously, take our DNA. It's mostly garbage anyways. Fifty percent of our genome is comprised of genetic parasites, called transposable elements or transposons, that usually lie dormant. When they are allowed to move around the genome, they can wreak havoc on our ...
African Americans, Hispanics, and those who receive care at a community hospital are all significantly less likely than other patients to receive treatment for early stage non-small cell lung cancer, according to a report in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
"We found significant disparities for treatment of a curable cancer based on race, insurance status, and whether or not treatment was at an academic or community hospital," said Dr. Matthew Koshy, a physician in the department of radiation oncology at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, and ...
ANN ARBOR--In recent years, scientists have linked chemicals known as phthalates with complications of pregnancy and fetal development.
Now, a study led by researchers at the University of Michigan School of Public Health sheds light on the mechanism that may be to blame.
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastic materials more flexible and can also be found in personal care products such as perfumes, deodorants and lotions. They can enter the human body by being ingested, inhaled or through the skin. Most often phthalates are metabolized and excreted quickly, but ...
Increasing the amount of omega-3s in your diet, whether from fish or flax, will likely decrease your risk of getting heart disease, according to Penn State nutritionists.
A substantial amount of evidence exists supporting the heart-health benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid (EPA and DHA), marine-derived omega-3 fatty acids. However, much less evidence exists to demonstrate the positive effects of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid.
"The benefits reported for EPA and DHA are stronger because supplements of EPA and DHA ...
VIDEO:
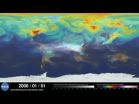
An ultra-high-resolution NASA computer model has given scientists a stunning new look at how carbon dioxide in the atmosphere travels around the globe. Plumes of carbon dioxide in the simulation...
Click here for more information.
An ultra-high-resolution NASA computer model has given scientists a stunning new look at how carbon dioxide in the atmosphere travels around the globe.
Plumes of carbon dioxide in the simulation swirl and shift as winds disperse the greenhouse ...
A team of 14 scientists led by David Williams of Arizona State University's School of Earth and Space Exploration has completed the first global geologic and tectonic map of the asteroid Vesta. The work reveals that Vesta's history has been dominated by impacts from large meteorites.
The mapping was carried out using images from NASA's Dawn spacecraft, which orbited Vesta between June 2011 and September 2012. The images let scientists create high-resolution geological maps, revealing the variety of Vesta's surface features in unprecedented detail.
"The geologic mapping ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Online retail sales totaled $75 billion in the second quarter of 2014, according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau. As consumers shop more using the Internet and cell phones, retailers must adjust their marketing strategies to reach these consumers. In a recently published study, a University of Missouri researcher found that consumers' preferences differ when they are shopping in a physical store compared to shopping online. Catering to shoppers' online and in-store preferences can increase the effectiveness of traditional marketing tactics such as direct ...
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine have found that a growth factor can regenerate damaged peripheral nerves without causing the growth of new blood vessels -- making it a unique candidate to treat nerve damage in areas of the body where the proliferation of blood vessels would be a drawback.
"One example would be in the cornea, which has a requirement for dense innervation but where the formation of new blood vessels would block vision," said Dr. Mark Rosenblatt, professor and head of ophthalmology and visual sciences at UIC and corresponding ...
Metastasis is bad news for cancer patients. Northwestern University scientists now have demonstrated a simple but powerful tool that can detect live cancer cells in the bloodstream, potentially long before the cells could settle somewhere in the body and form a dangerous tumor.
The NanoFlare technology is the first genetic-based approach that is able to detect live circulating tumor cells out of the complex matrix that is human blood -- no easy feat. In a breast cancer study, the NanoFlares easily entered cells and lit up the cell if a biomarker target was present, even ...