(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - The bacteria that helped cause the near-ruin of two large oyster hatcheries in the Pacific Northwest have been mistakenly identified for years, researchers say in a recent report.
In addition, the study shows that the bacteria now believed to have participated in that problem are even more widespread and deadly than the previous suspect.
Although the hatchery industry has largely recovered, primarily by better control of ocean water acidity that was also part of the problem, the bacterial pathogens remain a significant concern for wild oysters along the coast, researchers said.
For many years, it had been believed that the primary bacteria causing oyster larval death in the Pacific Northwest was Vibrio tubiashii. Now, scientists say that most, or possibly all of the bacterial problem was caused by a different pathogen, Vibrio coralliilyticus, a close cousin that's now known to be even more virulent to Pacific oysters.
The findings were published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, by researchers from the College of Veterinary Medicine at Oregon State University, the U.S. Department of Agriculture, and Rutgers University. The research was supported by the USDA.
"These bacteria are very similar, they're close cousins," said Claudia Häse, an OSU associate professor and expert in microbial pathogenesis. "V. coralliilyticus was believed to primarily infect warm water corals and contributes to coral bleaching around the world. It shares some gene sequences with V. tubiashii, but when we finally were able to compare the entire genomes, it became apparent that most of what we're dealing with in the Pacific Northwest is V. coralliilyticus."
Scientists now say that V. coralliilyticus is not only far more widespread than previously believed, but that it can infect a variety of fish, shellfish and oysters, including rainbow trout and larval brine shrimp. And it appears to be the primary offender in bacterial attacks on Pacific Northwest oyster larvae.
OSU experts have developed a rapid diagnostic assay for this bacteria that is nearing commercialization, and it may help assess problems both in oyster and coral health, Häse said.
"Although we've largely addressed the problems the hatcheries face, these bacteria continue to pose threats to wild oysters," Häse said. "And corals are still declining in many places, the Great Barrier Reef in Australia is dying at an alarming rate. Better diagnostics might help in all of these situations."
In what's now understood to be a problem with multiple causes, these pathogenic bacteria were involved in major crashes of oyster hatcheries, causing shortages in seed oysters for commercial producers. Dramatic losses were suffered in a Netarts Bay, Oregon, hatchery in 2005, and Washington hatcheries were also hard hit. Bacterial infection, water acidity, oxygen depletion and rising seawater temperatures are all believed to have been part of the problem.
By better monitoring and control of water acidity, which was one serious concern, hatcheries have been able to regain most of their productive capabilities. Wild oysters, however, continue to face the multiple pressures from rising acidity, pathogenic bacteria and other forces that have led to serious hatchery mortality.
Those problems have not been made any easier by the lack of funding for identification and studies of the bacteria that researchers now know to be causing infection.
In laboratory tests, strains of V. tubiashii did not show significant pathogenicity to Pacific oysters. V. coralliilyticus, by contrast, is highly infectious to both Pacific and Eastern oyster larvae, and perhaps other shellfish species.
"The Vibrio genus and many bacteria associated with it are a huge problem in fish and shellfish aquaculture, and we should be studying them more aggressively," Häse said. "V. coralliilyticus, in particular, has a very powerful toxin delivery system, and vibrios are some of the smartest of all bacteria. They can smell, sense things and swim toward a host."
It's believed that increasing environmental stresses may make oysters and other marine life more vulnerable to these types of bacterial infection, researchers say.
INFORMATION:
Editor's Note: A digital image of oyster larvae is available to illustrate this story: https://flic.kr/p/evUSy9
Findings play important role in understanding impact of oral health on heart
35 extra cases of serious heart infection every month in the UK
Prescription of antibiotic prophylaxis has fallen by 89 per cent
Scientists at the University of Sheffield have identified a significant rise in the number of people diagnosed with a serious heart infection alongside a large fall in the prescribing of antibiotic prophylaxis to dental patients.
The pioneering study is the largest and most comprehensive to be conducted with regards to the National Institute for Health and Care ...
NEW YORK, NY - November 17, 2014 - A new study has identified an FDA approved cancer drug, crizotinib, as a possible new coating for drug-eluting stents. Researchers found that crizotinib in mice helped prevent the narrowing of blood vessels after stenting without affecting the blood vessel lining. Results of this study were published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
To find a more effective drug to use on stents, researchers used a computational biology or "big data" approach to better understand the genetic pathways of re-narrowing that occurs in stented ...
November 18, 2014 -- A study just released by Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health found that children who were exposed to antibiotics in the second or third trimester of pregnancy had a higher risk of childhood obesity at age 7. The research also showed that for mothers who delivered their babies by a Caesarean section, whether elective or non-elective, there was a higher risk for obesity in their offspring. Study findings are published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
Although previous studies have shown that antibiotics administered early ...
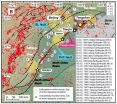
Boulder, Colo., USA - With a population of 11 million and located about 100 km from Beijing (22 million people) and Tangshan (7 million people), Tianjin lies on top of the Tangshan-Hejian-Cixian fault that has been the site of 15 devastating earthquakes in the past 1,000 years. An example of the disastrous events is the 1976 magnitude 7.6 Tangshan Earthquake, which killed a quarter million people.
To assess future seismic hazards along the fault, scientists from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Chinese Earthquake Administration (CEA) have reconstructed, ...
In an extensive, multi-institution study led by SUNY Downstate Medical Center, researchers have identified new evidence supporting the growing belief that Neanderthals were a distinct species separate from modern humans (Homo sapiens), and not a subspecies of modern humans.
The study looked at the entire nasal complex of Neanderthals and involved researchers with diverse academic backgrounds. Supported by funding from the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health, the research also indicates that the Neanderthal nasal complex was not adaptively ...
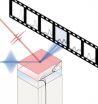
WASHINGTON D.C., November 18, 2014 -- A research team from Germany developed an analytical model to describe the structural dynamics of photoexcited thin films and verified it by ultrafast X-ray diffraction.
Lattice dynamics, atomic movements in a crystal structure, can influence the physical and chemical properties of a material. The phenomenon can be directly studied using ultrafast X-ray diffraction, in which femtosecond X-ray pulses take snapshots of the atomic positions in a crystal by interacting with the structure at the core electronic level.
However, no comprehensive ...
An investigational treatment for Marfan syndrome is as effective as the standard therapy at slowing enlargement of the aorta, the large artery of the heart that delivers blood to the body, new research shows. The findings indicate a second treatment option for Marfan patients, who are at high risk of sudden death from tears in the aorta.
The results are being presented Nov. 18 at the American Heart Association's annual meeting in Chicago and will appear online the same day in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"For years, standard medical therapy for Marfan syndrome ...
Each cell contains thousands of proteins, each one of which bears a unique signature. All proteins, distinct in shape and function, are built from the same amino acid strings. Many proteins are vital, as evidenced by the plethora of diseases linked to their absence or malfunction. But how exactly did proteins first come to be? Do they all share a single common ancestor? Or did proteins evolve from many different origins?
Forming a global picture of the protein universe is crucial to addressing these and other important questions, but it's nearly impossible to do. Such ...
URBANA, Ill. - Most Americans don't get the daily recommended amount of fiber in their diet, though research has shown that dietary fiber can cause a shift in the gut toward beneficial bacteria, reducing the risk of colon cancer, type 2 diabetes, and other diseases. A new study from the University of Illinois shows that two specific functional fibers may also have the potential to assist in weight loss when made part of a long-term, daily diet.
Kelly Swanson, a U of I professor of nutrition, and his team had previously been able to see a "snapshot" of what bacteria were ...
When NASA's Terra satellite passed over the Southern Indian Ocean, the MODIS instrument aboard captured a picture of Tropical Cyclone Adjali that showed it developed a "tail," which is actually band of thunderstorms extending south of the center.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite took a visible picture of Tropical Storm Adjali on Nov. 18 at 05:35 UTC (12:35 a.m. EST). The MODIS image showed a concentration of strong storms around the center of Adjali's circulation and a band of thunderstorms ...