University of Kentucky reports HIV/AIDS drugs could be repurposed to treat AMD
2014-11-20
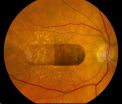
(Press-News.org) LEXINGTON, Ky. (Nov. 20, 2014) - A landmark study published today in the journal Science by an international group of scientists, led by the laboratory of Dr. Jayakrishna Ambati, professor & vice chair of the Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences at the University of Kentucky, reports that HIV/AIDS drugs that have been used for the last 30 years could be repurposed to treat age-related macular degeneration (AMD), as well as other inflammatory disorders, because of a previously undiscovered intrinsic and inflammatory activity those drugs possess.
AMD is a progressive condition that is untreatable in up to 90 percent of patients and is a leading cause of blindness in the elderly worldwide. The two forms of AMD, wet and dry, are classified based on the presence or absence of blood vessels that have invaded the retina. A detailed understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying wet AMD has led to several robust FDA-approved therapies. In contrast, there are no approved treatments for dry AMD thus far.
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) are the most widely used class of anti-HIV drugs. NRTIs are thought to be therapeutic in HIV/AIDS patients because they target the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is critical for replication of HIV. Previous work from the Ambati lab found that a type of toxic molecule called Alu RNA accumulate in the retina to cause dry AMD; interestingly, Alu RNA and HIV are similar in that they both require reverse transcriptase to fulfill their life cycle.
In their Science publication, Fowler et al. report that multiple FDA-approved NRTIs prevented retinal degeneration in a mouse model of dry AMD. Surprisingly, this effect of NRTIs in the eye was not due to the well-known function of these drugs to inhibit reverse transcriptase. Instead, NRTIs blocked an innate immune pathway called the "inflammasome", even in experimental systems in which the NRTIs were not capable of blocking reverse transcriptase. In their report, they also showed that NRTIs were effective in other disease models that share common signaling pathways with the dry AMD model, including the "wet" form of AMD - a disease that when treated still does not lead to substantial vision improvement in two-thirds of patients - and graft-versus-host disease which is the major obstacle preventing successful allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
"Repurposing of NRTIs could be advantageous, for one, because they are very inexpensive. Moreover, through decades of clinical experience, we know that some of the drugs we tested are incredibly safe. Since these NRTIs are already FDA-approved, they could be rapidly and inexpensively translated into therapies for a variety of untreatable or poorly treatable conditions," said Benjamin Fowler, the lead author and a postdoctoral fellow in the Ambati lab. Ambati added, "We are excited at the prospect of testing whether NRTIs could be effective in halting the progression of AMD in patients."
NRTIs were originally designed to treat cancer in the 1960s. They re-emerged in the late 1980s and became the first drugs the FDA-approved to treat HIV/AIDS.
INFORMATION:
MEDIA CONTACT: Ann Blackford at 859-323-6442 or ann.blackford@uky.edu, or Kristi Lopez at 859-806-0445.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-20
Scientists developed a new method which allows to estimate the magnetic field of a distant exoplanet, i.e., a planet, which is located outside the Solar system and orbits a different star. Moreover, they managed to estimate the value of the magnetic moment of the planet HD 209458b.The group of scientists including one of the researchers of the Lomonosov Moscow State University (Russia) published their article in the Science magazine.
In the two decades which passed since the discovery of the first planet outside the Solar system, astronomers have made a great progress ...
2014-11-20
MADISON, Wis. -- As real as that daydream may seem, its path through your brain runs opposite reality.
Aiming to discern discrete neural circuits, researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have tracked electrical activity in the brains of people who alternately imagined scenes or watched videos.
"A really important problem in brain research is understanding how different parts of the brain are functionally connected. What areas are interacting? What is the direction of communication?" says Barry Van Veen, a UW-Madison professor of electrical and computer engineering. ...
2014-11-20
MADISON, Wis. - The influenza virus, like all viruses, is a hijacker. It quietly slips its way inside cells, steals the machinery inside to make more copies of itself, and then -- having multiplied -- bursts out of the cell to find others to infect.
Most drugs currently used to treat influenza are designed to attack the virus, to render it incapacitated. But influenza viruses are sneaky, capable of mutating to avoid destruction by the drug.
In a comprehensive new study published today in the journal Cell Host and Microbe, the University of Wisconsin-Madison's Yoshihiro ...
2014-11-20
EUGENE, Ore. -- Nov. 20, 2014 -- A potential path to identify imperfections and improve the quality of nanomaterials for use in next-generation solar cells has emerged from a collaboration of University of Oregon and industry researchers.
To increase light-harvesting efficiency of solar cells beyond silicon's limit of about 29 percent, manufacturers have used layers of chemically synthesized semiconductor nanocrystals. Properties of quantum dots that are produced are manipulated by controlling the synthetic process and surface chemical structure.
This process, however, ...
2014-11-20
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- The majority of preschoolers may not be getting the amount of sleep they need each night, placing them at higher risk of being overweight or obese within a year, according to a new study.
Published online by the journal Sleep Medicine, the study investigated links between mothers' employment status and their children's weight over time, exploring the impact of potential mediators, such as children's sleep and dietary habits, the amount of time they spent watching TV and family mealtime routines.
"The only factor of the four that we investigated that ...
2014-11-20
Washington, DC--Levels of testosterone and other naturally-occurring reproductive hormones play a limited role in driving menopausal women's interest in sex and sexual function, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
While testosterone is the main sex hormone in men, women also have small amounts of it. The ovaries naturally produce testosterone. Researchers set out to examine the role the hormone plays in sexual function as women go through menopause.
"While levels of testosterone and other reproductive ...
2014-11-20
Washington, DC--As many as one in five people with Type 2 diabetes do not see any improvement in blood sugar management when they engage in a supervised exercise regimen, according to a new scientific review published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
People develop Type 2 diabetes when their bodies become resistant to the hormone insulin, which carries sugar from the blood to cells. This leads to excess sugar in the bloodstream. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention projects about 40 percent of Americans will develop ...
2014-11-20
Enzymes carry out fundamental biological processes such as photosynthesis, nitrogen fixation and respiration, with the help of clusters of metal atoms as "active" sites. But scientists lack basic information about their function because the states thought to be critical to their chemical abilities cannot be experimentally observed.
Now, researchers at Princeton University have reported the first direct observation of the electronic states of iron-sulfur clusters, common to many enzyme active sites. Published on August 31 in the journal Nature Chemistry, the states were ...
2014-11-20
LIVERMORE, California -- Using ocean observations and a large suite of climate models, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists have found that long-term salinity changes have a stronger influence on regional sea level changes than previously thought.
"By using long-term observed estimates of ocean salinity and temperature changes across the globe, and contrasting these with model simulations, we have uncovered the unexpectedly large influence of salinity changes on ocean basin-scale sea level patterns," said LLNL oceanographer Paul Durack, lead author of a paper ...
2014-11-20
BANGALORE, INDIA (November 20, 2014) - Participation of non-scientists as volunteers in conservation can play a significant role in saving wildlife, finds a new scientific research led by Duke University, USA, in collaboration with Wildlife Conservation Society and Centre for Wildlife Studies, Bengaluru.
The study has shown that citizen science projects greatly contribute to 'increased environmental awareness among the general public'. It also reported direct impacts on conservation including - shift in formal profession by volunteers to become conservationists, initiation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] University of Kentucky reports HIV/AIDS drugs could be repurposed to treat AMD




