The artificial pancreas shown to improve the treatment of type 1 diabetes
The world's first clinical trial comparing three alternative diabetes treatments
2014-11-27
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in French.
The world's first clinical trial comparing three alternative treatments for type 1 diabetes was conducted in Montréal by researchers at the IRCM and the University of Montreal, led by endocrinologist Dr. Rémi Rabasa-Lhoret. The study confirms that the external artificial pancreas improves glucose control and reduces the risk of hypoglycemia compared to conventional diabetes treatment. The results, published today in the scientific journal The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, could have a significant impact on the treatment of type 1 diabetes, a chronic disease that can cause vision loss and cardiovascular diseases.
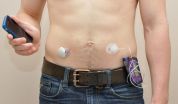
An emerging technology to treat type 1 diabetes, the external artificial pancreas is an automated system that simulates the normal pancreas by continuously adapting insulin delivery based on changes in glucose levels. Two configurations exist: the single-hormone artificial pancreas that delivers insulin alone and the dual-hormone artificial pancreas that delivers both insulin and glucagon. While insulin lowers blood glucose levels, glucagon has the opposite effect and raises glucose levels.
"Our clinical trial was the first to compare these two configurations of the artificial pancreas with the conventional diabetes treatment using an insulin pump," says Dr. Rabasa-Lhoret, Director of the Obesity, Metabolism and Diabetes research clinic at the IRCM and professor at the University of Montreal's Department of Nutrition. "We wanted to determine the usefulness of glucagon in the artificial pancreas, especially to prevent hypoglycemia, which remains the major barrier to reaching glycemic targets."
People living with type 1 diabetes must carefully manage their blood glucose levels to ensure they remain within a target range in order to prevent serious long-term complications related to high glucose levels (such as blindness or kidney failure) and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood glucose that can lead to confusion, disorientation and, if severe, loss of consciousness, coma and seizure).
"Our study confirms that both artificial pancreas systems improve glucose control and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia compared to conventional pump therapy," explains engineer Ahmad Haidar, first author of the study and postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Rabasa-Lhoret's research unit at the IRCM. "In addition, we found that the dual-hormone artificial pancreas provides additional reduction in hypoglycemia compared to the single-hormone system."
"Given that low blood glucose remains very frequent during the night, the fear of severe nocturnal hypoglycemia is a major source or stress and anxiety, especially for parents with young diabetic children," adds Dr. Laurent Legault, paediatric endocrinologist at the Montreal Children's Hospital, and co-author of the study. "The artificial pancreas has the potential to substantially improve the management of diabetes and the quality of life for patients and their families."
IRCM researchers are pursuing clinical trials on the artificial pancreas to test the system for longer periods and with larger patient cohorts. The technology should be available commercially within the next five to seven years, with early generations focusing on overnight glucose control.
According to the Canadian Diabetes Association, an estimated 285 million people worldwide are affected by diabetes, approximately 10 per cent of which have type 1 diabetes. With a further 7 million people developing diabetes each year, this number is expected to hit 438 million by 2030, making it a global epidemic. Today, more than nine million Canadians - or one if four - are living with diabetes or prediabetes.
About the Study
The randomized controlled trial compared the dual-hormone artificial pancreas, the single-hormone artificial pancreas and the conventional insulin pump therapy in 30 adult and adolescent patients with type 1 diabetes, who had been using an insulin pump for at least three months. Patients were admitted to the IRCM's clinical research facility three times. Each visit included three meals, chosen social activities, an evening exercise, a bedtime snack and an overnight stay, throughout which blood glucose levels were monitored.
INFORMATION:
This project was funded by the Canadian Diabetes Association, Dr. Haidar's postdoctoral fellowship from JDRF, and Dr. Rabasa-Lhoret's J.A. De Sève Chair in clinical research. The study's other authors include Virginie Messier and Catherine Leroux from the IRCM, as well as Tina Maria Mitre from the Department of Mathematics and Statistics at McGill University. The University of Montreal is officially known as Université de Montréal. For more information on the study, please refer to the article summary published online by The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-27
Leading medical experts today [Thursday 27 November] warn that rising numbers of deaths from liver disease - already the UK's third commonest cause of premature death - will be unavoidable without radical improvements in treatment and detection services, and tougher government policies to control the excessive alcohol use and obesity responsible for much of the national burden of liver disease.
In a major new Lancet Commission, led by Professor Roger Williams, Director of the Institute of Hepatology, London, UK, doctors and medical scientists from across the UK call ...
2014-11-27
Boston, MA. Wednesday, November 26, 2014 -- Researchers from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Harvard Medical School, and Harvard-affiliated hospitals have uncovered an easily detectable, "pre-malignant" state in the blood that significantly increases the likelihood that an individual will go on to develop blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, or myelodysplastic syndrome. The discovery, which was made independently by two research teams affiliated with the Broad and partner institutions, opens new avenues for research aimed at early detection and prevention of ...
2014-11-27
TORONTO, Nov. 26, 2014--The nervous system may play a bigger role in infections and autoimmune diseases than previously known. If researchers can learn more about that role, it could provide insight into diagnosing and treating everything from the stomach flu to rheumatoid arthritis.
Researchers at St. Michael's Hospital in Toronto, in conjunction with the Feinstein Institute for Medical Research in Manhasset, N.Y., reviewed the latest, most vigorous pre-clinical trials on this topic in a commentary published Wednesday (Nov. 26) in the New England Journal of Medicine. ...
2014-11-27
An experimental vaccine to prevent Ebola virus disease was well-tolerated and produced immune system responses in all 20 healthy adults who received it in a Phase 1 clinical trial conducted by researchers from the National Institutes of Health. The candidate vaccine, which was co-developed by the NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), was tested at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. The interim results are reported online in advance of print in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"The unprecedented scale ...
2014-11-26
ANN ARBOR--The spaghetti-like internal structure of most plastics makes it hard for them to cast away heat, but a University of Michigan research team has made a plastic blend that does so 10 times better than its conventional counterparts.
Plastics are inexpensive, lightweight and flexible, but because they restrict the flow of heat, their use is limited in technologies like computers, smartphones, cars or airplanes--places that could benefit from their properties but where heat dissipation is important. The new U-M work could lead to light, versatile, metal-replacement ...
2014-11-26
MINNEAPOLIS - The majority of people with dementia have never seen a doctor about their memory and thinking problems, according to a new study published in the November 26, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
In the study, 55 percent of the people with dementia had never had an evaluation of their thinking and memory skills with a doctor.
"These results suggest that approximately 1.8 million Americans over the age of 70 with dementia have never had an evaluation of their cognitive abilities," said study author ...
2014-11-26
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Despite clear signs that their memory and thinking abilities have gone downhill, more than half of seniors with these symptoms haven't seen a doctor about them, a new study finds.
University of Michigan researchers and their colleagues say their findings suggest that as many as 1.8 million Americans over the age of 70 with dementia are not evaluated for cognitive symptoms by a medical provider, which in some patients can lead to a failure to uncover modifiable causes of thinking or memory impairment.
The study, published online in Neurology, the ...
2014-11-26
Juvenile offenders with multiple psychiatric disorders when they are incarcerated in detention centers appear to be at high risk for disorders five years after detention, according to a report published online by JAMA Psychiatry.
Psychiatric disorders are prevalent among juvenile detainees. However, far less is known about the young people after they leave detention.
Karen M. Abram, Ph.D., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, and co-authors looked at patterns of comorbidity (the presence of two or more disorders), how they change over ...
2014-11-26
FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. -- Nov. 26, 2014 -- An international team of scientists from the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) and The Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine (LCSB) have completed a first-of-its-kind microbial analysis of a biological wastewater treatment plant that has broad implications for protecting the environment, energy recovery and human health.
The study, published Nov. 26 in the scientific journal Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/ncomm6603), describes in unprecedented detail the complex relationships within a model ecosystem.
The ...
2014-11-26
Johns Hopkins researchers report that their test of an interventional X-ray guidance device approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2013 has the potential to reduce the radiation exposure of patients undergoing intra-arterial therapy (IAT) for liver cancer.
In a report prepared for presentation Dec. 3 at the 100th annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America in Chicago (abstract #SSM24-02), the researchers described the results of a clinical trial of the imaging system AlluraClarity, made by Philips Healthcare, on 50 patients with liver cancer. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The artificial pancreas shown to improve the treatment of type 1 diabetes
The world's first clinical trial comparing three alternative diabetes treatments