(Press-News.org) CHICAGO - Changes in brain connections visible on MRI could represent an imaging biomarker of Alzheimer's disease, according to a new study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia. As many as 5 million Americans are affected, a number expected to grow to 14 million by 2050, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preventive treatments may be most effective before Alzheimer's disease is diagnosed, such as when a person is suffering from mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a decline in cognitive skills that is noticeable but not severe enough to affect independent function. Previous efforts at early detection have focused on beta amyloid, a protein found in abnormally high amounts in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease.
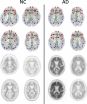
For the new study, researchers looked at the brain's structural connectome, a map of white matter tracts that carry signals between different areas of the brain.
"The structural connectome provides us with a way to characterize and measure these connections and how they change through disease or age," said study co-author Jeffrey W. Prescott, M.D., Ph.D., radiology resident at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
Dr. Prescott and colleagues analyzed results from 102 patients enrolled in a national study called the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) 2. The patients had undergone diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), an MRI method that assesses the integrity of white matter tracts in the brain by measuring how easy it is for water to move along them.
"It is known that water prefers moving along the defined physical connections between regions in the brain, which makes DTI a great tool for evaluating the structural connectome," Dr. Prescott said.
The researchers correlated changes in the structural connectome with results from florbetapir positron emission tomography (PET) imaging, a technique that measures the amount of beta amyloid plaque in the brain. Increased florbetapir uptake corresponds with greater amounts of the protein.
The results showed a strong association between florbetapir uptake and decreases in strength of the structural connectome in each of the five areas of the brain studied.
"This study ties together two of the major changes in the Alzheimer's brain--structural tissue changes and pathological amyloid plaque deposition--and suggests a promising role for DTI as a possible diagnostic adjunct," Dr. Prescott said.
Based on these findings, DTI may offer a role in assessing brain damage in early Alzheimer's disease and monitoring the effect of new therapies.
"Traditionally, Alzheimer's disease is believed to exert its effects on thinking via damage to the brain's gray matter, where most of the nerve cells are concentrated," said Jeffrey R. Petrella, M.D., professor of radiology at Duke and senior author on the study. "This study suggests that amyloid deposition in the gray matter affects the associated white matter connections, which are essential for conducting messages across the billions of nerve cells in the brain, allowing for all aspects of mental function."
"We suspect that as amyloid plaque load in the gray matter increases, the brain's white matter starts to break down or malfunction and lose its ability to move water and neurochemicals efficiently," added Dr. Prescott.
The researchers plan to continue studying this cohort of patients over time to gain a better understanding of how the disease evolves in individual patients. They also intend to incorporate functional imaging into their research to learn about how the relationship between function and structure is affected with increasing amyloid burden.
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors on the study are P. Murali Doraiswamy, M.D., and Kingshuk R. Choudhury, Ph.D.
Note: Copies of RSNA 2014 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press14 beginning Monday, Dec. 1.
RSNA is an association of more than 54,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on MRI and PET, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
CHICAGO - Some high school football players exhibit measurable brain changes after a single season of play even in the absence of concussion, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"This study adds to the growing body of evidence that a season of play in a contact sport can affect the brain in the absence of clinical findings," said Christopher T. Whitlow, M.D., Ph.D., M.H.A., associate professor of radiology at Wake Forest School of Medicine and radiologist at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center ...
(PHILADELPHIA) - Although prostate cancer can be successfully treated in many men, when the disease metastasizes to the bone, it is eventually lethal. In a study published online December 1st in the journal Cancer Research, researchers show that the receptor CCR5 best known for its role in HIV therapy, may also be involved in driving the spread of prostate cancer to the bone.
"Because this work shows we can dramatically reduce metastasis in pre-clinical models, and because the drug is already FDA approved for HIV treatment- we may be able to test soon whether this drug ...
'Tis the season for toys. Children are writing lists full of them, and parents are standing in lines (or tapping on computers) trying to find them. Playing with toys this season or any other is an important way for children to develop, learn, and explore. But anyone planning to buy new toys, or anyone with toys already at home, should know that many toys pose an injury risk to children.
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers in the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital have found that an estimated 3,278,073 children were treated in ...
A breast cancer vaccine developed at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis is safe in patients with metastatic breast cancer, results of an early clinical trial indicate. Preliminary evidence also suggests that the vaccine primed the patients' immune systems to attack tumor cells and helped slow the cancer's progression.
The study appears Dec. 1 in Clinical Cancer Research.
The new vaccine causes the body's immune system to home in on a protein called mammaglobin-A, found almost exclusively in breast tissue. The protein's role in healthy tissue is unclear, ...
Nearly 55 percent of U.S. infants are placed to sleep with bedding that increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome, or SIDS, despite recommendations against the practice, report researchers at the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and other institutions.
Soft objects and loose bedding--such as thick blankets, quilts, and pillows--can obstruct an infant's airway and pose a suffocation risk, according to the NIH's Safe to Sleep campaign. Soft bedding has also been shown to increase the risk of SIDS Infants should be ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY'S HAAS SCHOOL OF BUSINESS -People may associate political correctness with conformity but new research finds it also correlates with creativity in work settings. Imposing a norm that sets clear expectations of how women and men should interact with each other into a work environment unexpectedly encourages creativity among mixed-sex work groups by reducing uncertainty in relationships.
The study highlights a paradoxical consequence of the political correctness (PC) norm. While PC behavior is generally thought to threaten the free expression ...
Behavioural and drug interventions aiming to prevent people with prediabetes progressing to full blown type 2 diabetes are equally effective for both sexes at preventing progression and reducing weight, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis. The research is by Dr Anna Glechner, Danube University Krems, Austria, and Dr Jürgen Harreiter, Medical University of Vienna, Austria, and colleagues.
Prediabetes is a general term that refers to an intermediate stage between normal blood glucose control (normoglycaemia) and type 2 diabetes (high blood glucose ...
Using a patient's own rib cartilage (autologous) for rhinoplasty appears to be associated with low rates of overall long-term complications and problems at the rib site where the cartilage is removed, according to a report published online by JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery.
Autologous rib cartilage is the preferred source of graft material for rhinoplasty because of its strength and ample volume. However, using rib cartilage for dorsal augmentation to build up the bridge of the nose has been criticized for its tendency to warp and issues at the cartilage donor site, such ...
The five-year survival rate for advanced-stage laryngeal cancer was higher than national levels in a small study at a single academic center performing a high rate of surgical therapy, including a total laryngectomy (removal of the voice box), to treat the disease, despite a national trend toward organ preservation, according to a report published online by JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery.
The larynx is a common site of head and neck cancer with more than 10,000 cases annually. Over the past two decades, treatment for advanced-stage laryngeal cancer has shifted ...
The way that tetanus neurotoxin enters nerve cells has been discovered by UCL scientists, who showed that this process can be blocked, offering a potential therapeutic intervention for tetanus. This newly-discovered pathway could be exploited to deliver therapies to the nervous system, opening up a whole new way to treat neurological disorders such as motor neuron disease and peripheral neuropathies.
The research in mice, published in Science and funded by the Medical Research Council, shows that proteins called nidogens that coat cell surfaces are key to tetanus neurotoxin ...