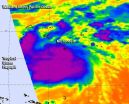
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Hagupit was just a low pressure area on Nov. 30, but warm waters and good atmospheric conditions allowed the storm to develop rapidly. By Dec. 1 the low pressure area strengthened into a tropical storm when NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Radiometer known as the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Hagupit in the western Pacific Ocean on Dec. 1 at 00:05 UTC (7:05 p.m. EST, Nov. 30). The picture showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation and fragmented bands of thunderstorms spiraling into the center from the western quadrant.
Hagupit developed from low pressure area System 95W. On Nov. 30, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) was monitoring System 95W when it was a couple of hundred miles south of the island of Chuuk. Chuuk is an island and one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia, located in the western North Pacific Ocean.
By Dec. 1 at 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST), the low pressure area had been designated as a tropical depression and was renamed Tropical Depression 22W. Six hours later, the storm had quickly intensified into Tropical Storm Hagupit as maximum sustained winds strengthened near 40 knots (46 mph/73 kph). At that time Hagupit was centered about 140 nautical miles south-southwest of Chuuk and was moving toward the west-northwest at 15 knots (17.2 mph/27.7 kph).
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated infrared satellite imagery on Dec. 1 confirmed the low-level circulation center was consolidating and fragmented bands of thunderstorms were wrapping into the low-level center. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on the storm on Dec. 1 at 02:59 UTC (Nov. 30 at 9:59 p.m. EST). The AIRS data showed strong thunderstorms with cloud top temperatures exceeding -63F/-53C around the center, which indicated the storms were high in the troposphere and capable of generating heavy rainfall.
The forecast from JTWC calls for slow intensification of the tropical storm over the next day. Thereafter, the storm is expected to intensify rapidly because of improved upper-level atmospheric conditions and warm sea surface temperatures. The JTWC is forecasting Hagupit as a typhoon as its center passes just to the north of the island of Yap on Dec. 3 while continuing to move in a west-northwesterly direction.
There are several warnings and watches now in effect for Tropical Storm Hagupit. A tropical storm warning is in effect for Satawal in Yap state. A typhoon watch is in effect in Faraulep, Woleai, Fais and Ulithi in Yap state, and a tropical storm watch is in force in Puluwat in Chuuk state.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
If we believe a negative trait we possess is linked to a related positive characteristic, we will be more productive in that domain, New York University researchers have found. Their study, which appears in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, establishes a novel "silver lining theory": negative attributes can produce positive results.
"People know that a weakness can be also be a strength, but these results show that if we actually believe it, we can use these beliefs to our advantage," says Alexandra Wesnousky, an NYU doctoral candidate and the study's lead ...
This news release is available in German. Jülich, 27 November 2014 - The resolution of scanning tunnelling microscopes can be improved dramatically by attaching small molecules or atoms to their tip. The resulting images were the first to show the geometric structure of molecules and have generated a lot of interest among scientists over the last few years. Scientists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic in Prague have now used computer simulations to gain deeper insights into the physics of these new imaging techniques. ...
This news release is available in German.
Genome engineering with the RNA-guided CRISPR-Cas9 system in animals and plants is changing biology. It is easier to use and more efficient than other genetic engineering tools, thus it is already being applied in laboratories all over the world just a few years after its discovery. This rapid adoption and the history of the system are the core topics of a review published in the renowned journal Science. The review was written by the discoverers of the system Prof. Emmanuelle Charpentier, who works at the Helmholtz Centre ...
Teenage boys are perhaps more known for playing computer games but girls are better at making them, a University of Sussex study has found.
Researchers in the University's Informatics department asked pupils at a secondary school to design and program their own computer game using a new visual programming language that shows pupils the computer programs they have written in plain English.
Dr Kate Howland and Dr Judith Good found that the girls in the classroom wrote more complex programs in their games than the boys and also learnt more about coding compared to the ...
"We have not seen an ice free period in the Arctic Ocean for 2,6 million years. However, we may see it in our lifetime." says marine geologist Jochen Knies. In an international collaborative project, Knies has studied the historic emergence of the ice in the Arctic Ocean. The results are published in Nature Communications.
The extent of sea ice cover in Arctic was much less than it is today between four and five million years ago. The maximum winter extent did not reaching its current location until around 2.6 million years ago. This new knowledge can now be used to ...
This news release is available in German. FRANKFURT The chances of patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukaemia (Ph+) being cured has greatly increased in recent years. Nevertheless, a high percentage of patients have developed resistance to available medication. But now, haematologists from Frankfurt, working with a Russian pharmaceutical company, have developed a new active substance that effectively combats the most aggressive forms of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukaemia, both in vitro and in vivo. They have reported this in the current edition ...
Tropical Depression 21W crossed the Philippines and moved into the South China Sea where warm waters helped strengthen the storm into Tropical Storm Sinlaku. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the storm and captured an image that showed it appeared elongated.
Despite the strengthening of Tropical Depression 21W into a tropical storm on Nov. 28, it appeared elongated from southwest to northeast on visible imagery taken by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard Aqua. The MODIS image also showed that the strongest thunderstorms ...
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone 02S after it formed in the Southern Indian Ocean on Nov. 28. An image from Terra showed that the new tropical storm is close to Mauritius and Reunion Islands.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of newborn Tropical Cyclone 02S northeast of the islands of Mauritius and Reunion. The MODIS image showed that thunderstorms were mostly west of the low-level center of circulation and bands of thunderstorms were wrapping into the center. ...
This news release is available in German. Humans don't like being alone, and their genes are no different. Together we are stronger, and the two versions of a gene - one from each parent - need each other. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin have analysed the genetic makeup of several hundred people and decoded the genetic information on the two sets of chromosomes separately. In this relatively small group alone they found millions of different gene forms. The results also show that genetic mutations do not occur randomly in the ...
Two physicists from the University of Warwick have taken to the kitchen to explain the complexity surrounding what they say is one of the last big mysteries in polymer physics.
As a way of demonstrating the complicated shapes that ring-shaped polymers can adopt, the researchers have created a brand new type of ring-shaped pasta, dubbed "anelloni" (anello being the Italian word for "ring"), which they've exclusively unveiled in this month's Physics World.
With just 2 eggs and 200 g of plain flour, Davide Michieletto and Matthew S Turner have created large loops of pasta ...