Researchers recreate stem cells from deceased patients to study present-day illnesses
Cedars-Sinai team remakes brain and gut stem cells in a dish to test potential therapies for debilitating and fatal diseases
2014-12-02
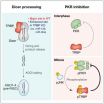
(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES (Dec. 1, 2014) - Research scientists have developed a novel method to re-create brain and intestinal stem cells from patients who died decades ago, using DNA from stored blood samples to study the potential causes of debilitating illnesses such as inflammatory bowel disease.
The lab research, published in the journal STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, could yield new therapies for people who suffer from aggressive motor-neuron and gut-related conditions that proved fatal to the deceased patients who long-ago volunteered their blood samples.
"The potential implications of this research are vast," said Dhruv Sareen, PhD, the study's lead author, and assistant professor and director of the David and Janet Polak Foundation Stem Cell Core Laboratory in the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute.
By using a deceased patient's stored blood samples, Sareen and his colleagues found that they can develop stem cells known as iPSCs in a petri dish - essentially reanimating diseased cells from patients long after they have died.
This approach allows researchers to connect the dots between a deceased patient's symptoms, genetic information contained in DNA and the behavior of stem cells in the lab. This, in turn, enables investigators to study the biological mechanisms behind diseases and potentially design new therapies.
The technique also allows physicians to replace invasive biopsy procedures typically required of living patients to create iPSC cells.
"These novel developments allow us to create new lines of stem cells from literally millions of patient samples stored in large repositories," said Clive Svendsen, PhD, director of the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute. "Some of these deceased patients were diagnosed with rare and important diseases."
The Cedars-Sinai research represents a step forward in the quest to advance personalized and precise medical treatments for patients battling many types of diseases. Crohn's disease is among the first to be studied this way in the lab.
"Our researchers can now make an entire gut in the petri dish from deceased patients with a specific type of Crohn's disease caused by a rare mutation," said Robert Barrett, PhD, first author of the study and a scientist in the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel and Immunobiology Research Institute at the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute. "This development will allow us to better understand how these mutations affect the gut."
INFORMATION:
Investigators at the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute collaborate with patients, clinicians and scientists to gain a better understanding of how diseases occur, with the ultimate goal of translating novel stem cell therapies for clinical use with patients. The Institute already has pioneered research breakthroughs, including new stem cell models for Huntington's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease.
Additional investigators on the current stem cell study include Loren Ornelas, Nicole Yeager, Berhan Mandefro, Anais Sahabian, Lindsay Lenaeus and Stephan R. Targan, MD. All researchers are part of the Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute.
Citation: STEM CELLS Translational Medicine. 2014 October: "Reliable Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells From Human Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-02
Philadelphia, PA, December 1, 2014 - "Triple-negative" breast cancer (TNBC) occurs in patients whose cells do not express receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and/or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (ER/PR/HER2). Because of the absence of these predictive biomarkers, treatment assignment can be difficult. Now, researchers report that high levels of the microRNA miR-21 in the tumor microenvironment, but not in the tumor epithelia (cancer cells), are associated with worse clinical outcomes for patients with TNBC, thus identifying a possible ...
2014-12-02
Research at the University of Adelaide has discovered cancer cells may be particularly susceptible to metabolic stress - opening the way for new targeted therapy that won't harm normal cells.
The researchers showed that chromosomal instability - which is a hallmark of rapidly dividing cancer cells - makes them stressed and vulnerable to mild metabolic disruption. Metabolism is the normal process by which the body turns food into energy.
"A common problem in treating cancers is that they don't respond to chemotherapy, or they respond for a while, but then come back," ...
2014-12-02
The research team of the Center for RNA Research at IBS has succeeded in revealing that the dsRNAs and Protein Kinase R (PKR) regulate division of mammalian cells.
This finding will provide important clues to understanding the process of tumor formation and the mechanism for suppressing cancer since the abnormal cell division marks the early events of cancer development.
For the first time, the IBS research team has found that during mitosis, the cellular dsRNAs activate PKR, an enzyme previously known as a trigger of immune response during virus infection. Activated ...
2014-12-02
Inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis may result from abnormal activation of cell death pathways previously believed to suppress inflammation, a surprise finding that could help to develop new ways of treating these diseases.
Mr James Rickard, Associate Professor John Silke and colleagues from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute made the discovery while investigating how cell death pathways are linked to inflammatory disease development. The study was published today in the journal eLife.
Infected cells, cancerous cells, or those that are simply unnecessary to ...
2014-12-02
Vitamin D deficiency is not just harmful to physical health--it also might impact mental health, according to a team of researchers that has found a link between seasonal affective disorder, or SAD, and a lack of sunlight.
"Rather than being one of many factors, vitamin D could have a regulative role in the development of SAD," said Alan Stewart of the University of Georgia College of Education.
An international research partnership between UGA, the University of Pittsburgh and the Queensland University of Technology in Australia reported the finding in the November ...
2014-12-02
URBANA, Ill. - A 12-year University of Illinois study shows that, although the use of cover crops does not improve crop yields, the practice does increase the amount of sequestered soil organic carbon using three different soil management systems.
U of I soil scientist Ken Olson evaluated plots that were subjected to no-till, chisel plow and moldboard plow treatments with and without hairy vetch and cereal rye cover crops.
"By 2012, we found that the soil tillage plots that had cover-crop treatments had more soil organic carbon stock than those without cover crops ...
2014-12-02
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Most patients with triple-negative breast cancer should undergo genetic testing for mutations in known breast cancer predisposition genes, including BRCA1 and BRCA2, a Mayo Clinic-led study has found. The findings come from the largest analysis to date of genetic mutations in this aggressive form of breast cancer. The results of the research appear in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"Clinicians need to think hard about screening all their triple-negative patients for mutations because there is a lot of value in learning that information, both in ...
2014-12-02
Researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have identified what they believe to be the cells responsible for fibrosis, the buildup of scar tissue. Fibrotic diseases, such as chronic kidney disease and failure, lung disease, heart failure and cirrhosis of the liver, are estimated to be responsible for up to 45 percent of deaths in the developed world.
The findings are published online in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
"Previous research indicated that myofibroblasts are the cells responsible for fibrosis," said Benjamin Humphreys, MD, PhD, senior author of ...
2014-12-02
New research from North Carolina State University and the University of Minnesota shows that the majority of consumers will accept the presence of nanotechnology or genetic modification (GM) technology in foods - but only if the technology enhances the nutrition or improves the safety of the food.
"In general, people are willing to pay more to avoid GM or nanotech in foods, and people were more averse to GM tech than to nanotech," says Dr. Jennifer Kuzma, senior author of a paper on the research and co-director of the Genetic Engineering in Society Center at NC State. ...
2014-12-02
Bethesda, MD (Dec. 2, 2014) -- Women with celiac disease present with fertility problems no more often than women in the general population, according to a new study in Gastroenterology1, the official journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Despite inconsistent findings from small studies, concern has been raised that celiac disease may cause infertility," said lead study author Nafeesa N. Dhalwani, PhD, from the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom. "Celiac patients should rest assured; our findings indicate that women with celiac disease do not ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers recreate stem cells from deceased patients to study present-day illnesses
Cedars-Sinai team remakes brain and gut stem cells in a dish to test potential therapies for debilitating and fatal diseases