(Press-News.org) Bethesda, MD (Dec. 2, 2014) -- Women with celiac disease present with fertility problems no more often than women in the general population, according to a new study in Gastroenterology1, the official journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Despite inconsistent findings from small studies, concern has been raised that celiac disease may cause infertility," said lead study author Nafeesa N. Dhalwani, PhD, from the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom. "Celiac patients should rest assured; our findings indicate that women with celiac disease do not report fertility problems more often than women without celiac disease."
Researchers conducted a large population-based cohort study, analyzing more than 2 million women of childbearing age in the United Kingdom, to compare the rates of new clinically recorded fertility problems in groups of women with and without celiac disease. The findings show women with celiac disease do not have a greater likelihood of fertility problems, either before or after diagnosis of celiac disease.
However, rates of infertility were 41 percent higher among women diagnosed with celiac disease when they were 25-29 years old, compared to women in the same age group without the disease. Dr. Dhalwani provides guidance on these findings: "It is important to recognize that this represented only a very small increase in the number of women consulting with fertility problems -- if we followed women between ages 25-29 years over a one-year period, presentation with fertility problems would occur in one of every 100 women without celiac disease, but in 1.5 of every 100 women with celiac disease. The fact that this increase was not seen in women of the same age with undiagnosed celiac disease indicates that it is unlikely to represent a biological impact of the condition on fertility. It may instead be related to heightened concern that may prompt earlier consultation if women experience delays in conception. This does, however, warrant further assessment."
While undiagnosed celiac disease is likely to be an underlying cause of unexplained infertility for some women, these findings indicate that most women with celiac disease, either undiagnosed or diagnosed, do not have a substantially greater likelihood of clinically recorded fertility problems than women without celiac. Therefore, screening when women initially present with fertility problems may not identify a significant number of women with celiac disease, beyond the general population prevalence.
Previous studies associating infertility with celiac disease included small numbers of women attending infertility specialist services and subsequently screened for celiac disease, so they may not be representative of the general population. This is the largest study to assess the association between celiac disease and fertility problems to date with data on more than 2 million women over a period of 20 years.
Celiac disease affects about 1 percent of the population in North America and Western Europe, with women constituting about 60 to 70 percent of the clinically diagnosed population. Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition which can result in intestinal malabsorption and prevents the body from collecting nutrients as food passes through the small intestine. The primary treatment for celiac disease is the strict following of a gluten-free diet. Learn more about celiac disease in the AGA patient brochure.
INFORMATION:
1Dhalwani, Nafeesa N., et al., Women With Celiac Disease Present With Fertility Problems No More Often Than
Women In The General Population, Gastroenterology, Volume 147(6): 1267-1274.e1. http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(14)01036-1/abstract
About the AGA Institute
The American Gastroenterological Association is the trusted voice of the GI community. Founded in 1897, the AGA has grown to include more than 16,000 members from around the globe who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programs of the organization. http://www.gastro.org.
About Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology, the official journal of the AGA Institute, is the most prominent scientific journal in the specialty and is in the top 1 percent of indexed medical journals internationally. The journal publishes clinical and basic science studies of all aspects of the digestive system, including the liver and pancreas, as well as nutrition. The journal is abstracted and indexed in Biological Abstracts, Current Awareness in Biological Sciences, Chemical Abstracts, Current Contents, Excerpta Medica, Index Medicus, Nutrition Abstracts and Science Citation Index. For more information, visit http://www.gastrojournal.org.
Like AGA and Gastroenterology on Facebook.
Join AGA on LinkedIn.
Follow us on Twitter @AmerGastroAssn.
Check out our videos on YouTube.
A research team from Kiel University (CAU) and Goethe University Frankfurt has jointly created a synthetic surface on which the adhesion of E. coli bacteria can be controlled. The layer, which is only approximately four nanometres thick, imitates the saccharide coating (glycocalyx) of cells onto which the bacteria adhere such as during an infection. This docking process can be switched on and off using light. This means that the scientists have now made an important step towards understanding the relationship between sugar (carbohydrates) and bacterial infections. Their ...
This news release is available in German.
The FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51) is an established risk factor for stress-related psychiatric disorders such as major depression. Drug discovery for FKBP51 has been hampered by the inability to pharmacologically differentiate against the very similar functional counterplayer FKBP52. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry in Munich have now developed the first potent and highly selective inhibitor of FKBP51. The so-called SAFit-ligand inhibits FKBP51 enhancing growth of neuronal cell cultures and improving ...
Molecular clocks -- based on changes in genetic material -- indicate much younger ages for a wide variety of plants found as fossils in southern Argentina than do the solid, geologic dates of those fossils, according to geoscientists who surveyed recent paleobotanical discoveries in Patagonia.
The finding suggests serious biases in molecular clocks, which are heavily used to date many kinds of living things. It also directly refutes a widely-held idea about how most Southern Hemisphere plant and animal groups attained their current distributions.
Geologists date fossils ...
A team of scientists has revealed how certain harmful bacteria drill into our cells to kill them. Their study shows how bacterial 'nanodrills' assemble themselves on the outer surfaces of our cells, and includes the first movie of how they then punch holes in the cells' outer membranes. The research, published today in the journal eLife, supports the development of new drugs that target this mechanism, which is implicated in serious diseases. The team brings together researchers from UCL, Birkbeck, University of London, the University of Leicester, and Monash University ...
In the city that never sleeps, it's easy to overlook the insects underfoot. But that doesn't mean they're not working hard. A new study from North Carolina State University shows that insects and other arthropods play a significant role in disposing of garbage on the streets of Manhattan.
"We calculate that the arthropods on medians down the Broadway/West St. corridor alone could consume more than 2,100 pounds of discarded junk food, the equivalent of 60,000 hot dogs, every year - assuming they take a break in the winter," says Dr. Elsa Youngsteadt, a research associate ...
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (December 2, 2014) - If you are one of the millions of Americans who experiences a severe allergic reaction to food, latex or an insect sting, you should know the first line of defense in combating the reaction is epinephrine. Unfortunately, not all medical personnel know how important epinephrine is in bringing an allergic reaction under control.
According to new guidelines published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), the fast administration ...
AUSTIN, Texas -- Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have identified a network of genes that appear to work together in determining alcohol dependence. The findings, which could lead to future treatments and therapies for alcoholics and possibly help doctors screen for alcoholism, are being published this week in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
By comparing patterns of genetic code from the brain tissue of alcoholics and nonalcoholics, the researchers discovered a particular set of genes co-expressed together in the individuals who had consumed the most ...
CHICAGO - According to a new long-term study, diabetic patients with even mild coronary artery disease face the same relative risk for a heart attack or other major adverse heart events as diabetics with serious single-vessel obstructive disease. Results of the study were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Researchers at the University of British Columbia and St. Paul's Hospital in Vancouver analyzed data from the Coronary CT Angiography Evaluation For Clinical Outcomes: An International Multicenter (CONFIRM) Registry, ...
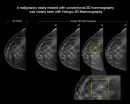
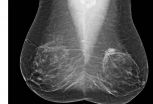
CHICAGO - A major new study being presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) has found that digital breast tomosynthesis, also known as 3-D mammography, has the potential to significantly increase the cancer detection rate in mammography screening of women with dense breasts.
Breasts are considered dense if they have a lot of fibrous or glandular tissue but not much fatty tissue. Research has shown that dense breasts are more likely to develop cancer, a problem compounded by the fact that cancer in dense breasts can be difficult ...
CHICAGO - A study of breast cancers detected with screening mammography found that strong family history and dense breast tissue were commonly absent in women between the ages of 40 and 49 diagnosed with breast cancer. Results of the study were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"Screening recommendations for this age group continue to be debated," said Bonnie N. Joe, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor in residence and chief of women's imaging at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). "Recent publications ...