University of Illinois researchers develop inexpensive hydrolysable polymer
2014-12-02
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have figured out how to reverse the characteristics of a key bonding material--polyurea--providing an inexpensive alternative for a broad number of applications, such as drug delivery, tissue engineering, and packaging.
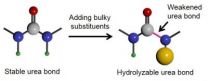
"Polymers with transient stability in aqueous solution, also known as hydrolysable polymers, have been applied in many biomedical applications, such as in the design of drug delivery systems, scaffolds for tissue regeneration, surgical sutures, and transient medical devices and implants," explained Jianjun Cheng, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at Illinois. "Polyurea materials are widely used in our daily life as coating, painting, and adhesive materials. The highly inert urea bond makes the inexpensive polymer extremely stable, a property that is suitable for some long-lasting applications."
Through some inventive chemistry, Cheng and his colleagues have developed a class of "hindered urea bond-containing polymeric materials" or "poly(hindered urea)s" (PHUs)--cheap polymers that can be designed to degrade over a specified time period, making them potentially useful in biomedical and agricultural applications.
"While conventional polyurea are very stable against hydrolysis, PHUs can be completely hydrolyzed within a few days," Cheng added. "Since 'hindrance' is the cause of the bond destabilization, the hydrolysis kinetics of PHUs can be easily tuned as needed for a specific application. They can potentially be environmentally friendly green and sustainable materials as well."
"Polyurea usually contain ester and other hydrolysable bonds, such as anhydride, acetal, ketal, or imine, in their backbone structures," said Hanze Ying, a graduate student in Cheng's research group and first author of the paper published in the Journal of American Chemical Society. "In this study, we demonstrated the potential of PHUs for the design of water degradable polymeric materials that can be easily synthesized by mixing multifunctional bulky amines and isocyanates, expanding the family of hydrolysable polymers."
"Hydrolysable polymers have also been applied in the design of controlled release systems in agriculture and food industries and used as degradable, environmentally friendly plastics and packaging materials," Cheng said. "These applications usually require short functioning time, complete degradation and clearance of materials after their use."
According to the researchers, the new PHUs potentially have great advantages over many other hydrolyzable polymers. PHUs can be made with inexpensive chemical precursors in ambient conditions via simple and clean chemistry with no catalyst or by-products, making it possible for end-users to control the copolymer recipe for specific use without the need of complicated synthesis apparatus.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-02
Some of the most elaborately decorated instruments in history were produced in 18th century Naples. The materials for varnishes and decorations used by individual mandolin masters, honed for wealthy clients in the ancient city's labyrinthine artisan quarter, have been kept secret for over 200 years. Details are disclosed for the first time by Tommaso Rovetta from the Università degli Studi di Pavia and colleagues at the Laboratorio Arvedi Research Group in Springer's journal Applied Physics A - Materials Science & Processing.
Italian conservation scientists studied ...
2014-12-02
Philadelphia, PA, December 2, 2014 - Few classes of drugs have had such a transformative effect on the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) as have statins, prescribed to reduce total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. However, some clinicians have ongoing concerns regarding the potential for lens opacities (cataracts) as a result of statin use. In an article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, researchers report increased risk for cataracts in patients treated with statins. An accompanying editorial discusses the history of statins and positions ...
2014-12-02
SALT LAKE CITY, Utah, Dec. 2, 2014 - Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ: MYGN) today announced that clinical data from three studies with Prolaris in prostate cancer patients will be highlighted at the 2014 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Annual Meeting being held tomorrow in Rockville, Md. The new data show that the Prolaris test could save the healthcare system $6 billion over 10 years and that physicians are using the test appropriately to personalize treatment options for their patients.
"Improving patient care is our highest priority, and we strive to prevent the ...
2014-12-02
With the help of citizen scientists, a team of astronomers has found an important new example of a very rare type of galaxy that may yield valuable insight on how galaxies developed in the early Universe. The new discovery technique promises to give astronomers many more examples of this important and mysterious type of galaxy.
The galaxy they studied, named J1649+2635, nearly 800 million light-years from Earth, is a spiral galaxy, like our own Milky Way, but with prominent "jets" of subatomic particles propelled outward from its core at nearly the speed of light. The ...
2014-12-02
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Today's atmosphere likely bears little trace of its primordial self: Geochemical evidence suggests that Earth's atmosphere may have been completely obliterated at least twice since its formation more than 4 billion years ago. However, it's unclear what interplanetary forces could have driven such a dramatic loss.
Now researchers at MIT, Hebrew University, and Caltech have landed on a likely scenario: A relentless blitz of small space rocks, or planetesimals, may have bombarded Earth around the time the moon was formed, kicking up clouds of gas with enough ...
2014-12-02
This news release is available in French. Montreal, December 2, 2014 -- "Selfish" may be the adjective most often attached to millennials. But new research from Concordia University shows that the young men and women who make up the millennial generation aren't so self-centred when it comes to supporting charities -- as long as marketers use the right tactics for each gender.
The forthcoming study in The Journal of Nonprofit & Public Sector Marketing confirms stereotypes and reveals an important paradox. When asked to support charitable causes, millennials -- those ...
2014-12-02
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers from the Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University Center for Aging Research report that waking intensive care unit patients and having them breathe on their own decreased both sedation levels and coma prevalence. The Wake Up and Breathe program also showed a trend toward reduced delirium in a critically ill population.
Participants in the study, which is published in the December 2014 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Critical Care Medicine, were 702 Eskenazi Health ICU patients 18 and older. Results were achieved without a change ...
2014-12-02
International research led by the University of Leicester published in Nature Communications reveals:
Analysis of all the available evidence confirms identity of King Richard III to the point of 99.999% (at its most conservative).
Analysis of the mitochondrial DNA shows a match between Richard III and modern female-line relatives, Michael Ibsen and Wendy Duldig.
The male line of descent is broken at one or more points in the line between Richard III and living male-line relatives descended from Henry Somerset, 5th Duke of Beaufort.
King Richard was almost certainly ...
2014-12-02
RIVERSIDE, Calif. - First developed in China in about the year A.D. 150, paper has many uses, the most common being for writing and printing upon. Indeed, the development and spread of civilization owes much to paper's use as writing material.
According to some surveys, 90 percent of all information in businesses today is retained on paper, even though the bulk of this printed paper is discarded after just one-time use.
Such waste of paper (and ink cartridges)--not to mention the accompanying environmental problems such as deforestation and chemical pollution to air, ...
2014-12-02
Health is high on the agenda in many countries with efforts to get more people exercising in order to reduce the problems associated with obesity, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Unfortunately, risk assessment is inadequate in terms of sports facilities and many fitness programs rely on the participants taking out insurance and signing legal waivers rather than their being taught safe practices and given a safe environment in which to exercise.
Writing in the International Journal of Business Continuity and Risk Management, Betul Sekendiz, School ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] University of Illinois researchers develop inexpensive hydrolysable polymer



