(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - Chemists and engineers at Oregon State University have discovered a fascinating new way to take some of the atmospheric carbon dioxide that's causing the greenhouse effect and use it to make an advanced, high-value material for use in energy storage products.
This innovation in nanotechnology won't soak up enough carbon to solve global warming, researchers say. However, it will provide an environmentally friendly, low-cost way to make nanoporous graphene for use in "supercapacitors" - devices that can store energy and release it rapidly.
Such devices are used in everything from heavy industry to consumer electronics.
The findings were just published in Nano Energy by scientists from the OSU College of Science, OSU College of Engineering, Argonne National Laboratory, the University of South Florida and the National Energy Technology Laboratory in Albany, Ore. The work was supported by OSU.
In the chemical reaction that was developed, the end result is nanoporous graphene, a form of carbon that's ordered in its atomic and crystalline structure. It has an enormous specific surface area of about 1,900 square meters per gram of material. Because of that, it has an electrical conductivity at least 10 times higher than the activated carbon now used to make commercial supercapacitors.
"There are other ways to fabricate nanoporous graphene, but this approach is faster, has little environmental impact and costs less," said Xiulei (David) Ji, an OSU assistant professor of chemistry in the OSU College of Science and lead author on the study. "The product exhibits high surface area, great conductivity and, most importantly, it has a fairly high density that is comparable to the commercial activated carbons.
"And the carbon source is carbon dioxide, which is a sustainable resource, to say the least," Ji said. "This methodology uses abundant carbon dioxide while making energy storage products of significant value."
Because the materials involved are inexpensive and the fabrication is simple, this approach has the potential to be scaled up for production at commercial levels, Ji said.
The chemical reaction outlined in this study involved a mixture of magnesium and zinc metals, a combination discovered for the first time. These are heated to a high temperature in the presence of a flow of carbon dioxide to produce a controlled "metallothermic" reaction. The reaction converted the elements into their metal oxides and nanoporous graphene, a pure form of carbon that's remarkably strong and can efficiently conduct heat and electricity. The metal oxides could later be recycled back into their metallic forms to make an industrial process more efficient.
By comparison, other methods to make nanoporous graphene often use corrosive and toxic chemicals, in systems that would be challenging to use at large commercial levels.
"Most commercial carbon supercapacitors now use activated carbon as electrodes, but their electrical conductivity is very low," Ji said. "We want fast energy storage and release that will deliver more power, and for that purpose the more conductive nanoporous graphene will work much better. This solves a major problem in creating more powerful supercapacitors."
A supercapacitor is a type of energy storage device, but it can be recharged much faster than a battery and has a great deal more power. They are mostly used in any type of device where rapid power storage and short, but powerful energy release is needed.
They are being used in consumer electronics, and have applications in heavy industry, with the ability to power anything from a crane to a forklift. A supercapacitor can capture energy that might otherwise be wasted, such as in braking operations. And their energy storage abilities may help "smooth out" the power flow from alternative energy systems, such as wind energy.
They can power a defibrillator, open the emergency slides on an aircraft and greatly improve the efficiency of hybrid electric automobiles. Nanoporous carbon materials can also adsorb gas pollutants, work as environmental filters, or be used in water treatment. The uses are expanding constantly and have been constrained mostly by their cost.
INFORMATION:
New research in mice suggests that restricting access to food to 8-12 hours rather than allowing constant access to food may help prevent and even reverse obesity and type 2 diabetes. The results of two studies publishing online December 2 in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism suggest that this time-restricted eating affects the balance of bacteria found in the gut. Researchers also found the occasional "cheat days" on weekends did not undo the benefits of time-restricted eating in mice.
Previously, investigators led by Dr. Satchidananda Panda of the Salk Institute ...
VIDEO:
This video gives another case against the midnight snack.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA-These days, with the abundance of artificial light, TV, tablets and smartphones, adults and children alike are burning the midnight oil. What they are not burning is calories: with later bedtimes comes the tendency to eat.
A new study by researchers at the Salk Institute cautions against an extended period of snacking, suggesting instead that confining caloric consumption ...
Researchers from Weill Cornell Medical College and the Gladstone Institutes have found a way to prevent noise-induced hearing loss in a mouse using a simple chemical compound that is a precursor to vitamin B3. This discovery has important implications not only for preventing hearing loss, but also potentially for treating some aging-related conditions that are linked to the same protein.
Published today in Cell Metabolism, the researchers used the chemical nicotinamide riboside (NR) to protect the nerves that innervate the cochlea. The cochlea transmits sound information ...
The aging process affects everything from cardiovascular function to memory to sexuality. Most worrisome for many, however, is the potential loss of eyesight due to retinal degeneration.
New progress towards a prosthetic retina could help alleviate conditions that result from problems with this vital part of the eye. An encouraging new study published in Nano Letters describes a revolutionary novel device, tested on animal-derived retinal models, that has the potential to treat a number of eye diseases. The proof-of-concept artificial retina was developed by an international ...
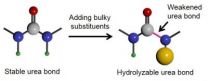
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have figured out how to reverse the characteristics of a key bonding material--polyurea--providing an inexpensive alternative for a broad number of applications, such as drug delivery, tissue engineering, and packaging.
"Polymers with transient stability in aqueous solution, also known as hydrolysable polymers, have been applied in many biomedical applications, such as in the design of drug delivery systems, scaffolds for tissue regeneration, surgical sutures, and transient medical devices and implants," ...
Some of the most elaborately decorated instruments in history were produced in 18th century Naples. The materials for varnishes and decorations used by individual mandolin masters, honed for wealthy clients in the ancient city's labyrinthine artisan quarter, have been kept secret for over 200 years. Details are disclosed for the first time by Tommaso Rovetta from the Università degli Studi di Pavia and colleagues at the Laboratorio Arvedi Research Group in Springer's journal Applied Physics A - Materials Science & Processing.
Italian conservation scientists studied ...
Philadelphia, PA, December 2, 2014 - Few classes of drugs have had such a transformative effect on the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) as have statins, prescribed to reduce total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. However, some clinicians have ongoing concerns regarding the potential for lens opacities (cataracts) as a result of statin use. In an article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, researchers report increased risk for cataracts in patients treated with statins. An accompanying editorial discusses the history of statins and positions ...
SALT LAKE CITY, Utah, Dec. 2, 2014 - Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ: MYGN) today announced that clinical data from three studies with Prolaris in prostate cancer patients will be highlighted at the 2014 Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Annual Meeting being held tomorrow in Rockville, Md. The new data show that the Prolaris test could save the healthcare system $6 billion over 10 years and that physicians are using the test appropriately to personalize treatment options for their patients.
"Improving patient care is our highest priority, and we strive to prevent the ...
With the help of citizen scientists, a team of astronomers has found an important new example of a very rare type of galaxy that may yield valuable insight on how galaxies developed in the early Universe. The new discovery technique promises to give astronomers many more examples of this important and mysterious type of galaxy.
The galaxy they studied, named J1649+2635, nearly 800 million light-years from Earth, is a spiral galaxy, like our own Milky Way, but with prominent "jets" of subatomic particles propelled outward from its core at nearly the speed of light. The ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Today's atmosphere likely bears little trace of its primordial self: Geochemical evidence suggests that Earth's atmosphere may have been completely obliterated at least twice since its formation more than 4 billion years ago. However, it's unclear what interplanetary forces could have driven such a dramatic loss.
Now researchers at MIT, Hebrew University, and Caltech have landed on a likely scenario: A relentless blitz of small space rocks, or planetesimals, may have bombarded Earth around the time the moon was formed, kicking up clouds of gas with enough ...