Taming neural excitations
A theoretical study of short- and long-range effects on neural excitation pulses might one day lead to controlling harmful signals such as those in strokes
2014-12-03
(Press-News.org) What do lasers, neural networks, and spreading epidemics have in common? They share a most basic feature whereby an initial pulse can propagate through a medium - be it physical, biological or socio-economic, respectively. The challenge is to gain a better understanding - and eventually control - of such systems, allowing them to be applied, for instance to real neural systems. This is the objective of a new theoretical study published in EPJ B by Clemens Bachmair and Eckehard Schöll from the Berlin University of Technology in Germany. Ultimately, with a better theoretical understanding, scientists aim to control such excitations in networks of neurons to prevent their detrimental effects like in stroke.
Scientists have long sought to find a means of controlling the excitation pulses in what are referred to as excitable media - either to suppress or to accelerate them. Or even to generate completely new spatio-temporal patterns that alter the impact of the pulses on their surroundings.
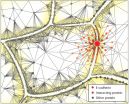
This time, the German team has performed the first systematic theoretical analysis of the influence of a specific kind of spatial interaction on the propagation of excitation pulses. Specifically, they focused on a kind of interaction that is attractive for small distances and repulsive for large distances. This characteristic mirrors interacting neurons in the cortex. Indeed, they combined excitatory coupling of neighbouring cells with long-range interactions of distant cells inhibiting the electric pulse propagation, previously demonstrated by neuroscientists.
In this study, the authors found, for the first time, that such non-local couplings can produce a rich variety of spatio-temporal patterns. These include acceleration, deceleration, and suppression of propagating pulses, and multiple pulses and blinking traveling waves. They also showed that the response all depends on the type of parameters in the short- and long-range coupling.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Bachmair, C. and Schöll, E. (2014). Nonlocal control of pulse propagation in excitable media. European Physical Journal B. DOI 10.1140/epjb/e2014-50339-2
For more information visit: http://www.epj.org
The full-text article is available to journalists on request.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-03
New research from the University of Adelaide has helped to shed light on the complexities of child sleep, and could lead to improved diagnosis of children with sleep-related breathing problems.
For his PhD in the University's School of Medical Sciences, Scott Coussens has been investigating how to accurately measure the level of sleep disturbance being experienced by children, to show whether or not they require treatment.
"Quality sleep is extremely important for children, especially at critical times of development. It can impact on the health of the brain and plays ...
2014-12-03
New Rochelle, NY, December 3, 2014--Are adolescents who view pornography or music videos more likely to engage in sexting, in which they share sexually explicit content via text, photo, or video using cell phones, email, or social networking sites? A study of the media consumption and sexting behavior of more than 300 teens is published in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking website.
In "The Associations ...
2014-12-03
Plastic waste is one of today's major environmental concerns. Most types of plastic do not biodegrade but break up into ever smaller pieces while remaining a polymer. Also, most types are made from oil, a rapidly dwindling resource. But there are promising alternatives, and one of them is polylactic acid (PLA): it is biodegradable and made from renewable resources. Manufacturers use PLA for disposable cups, bags and other sorts of packaging. The demand for PLA is constantly rising and has been estimated to reach about one megaton per year by 2020.
The research groups ...
2014-12-03
Planets orbiting close to low-mass stars -- easily the most common stars in the universe -- are prime targets in the search for extraterrestrial life.
But new research led by an astronomy graduate student at the University of Washington indicates some such planets may have long since lost their chance at hosting life because of intense heat during their formative years.
Low-mass stars, also called M dwarfs, are smaller than the Sun, and also much less luminous, so their habitable zone tends to be fairly close in. The habitable zone is that swath of space that is just ...
2014-12-03
People in the country's unhappiest communities spend about a quarter of the month so far down in the dumps that it can harm their productivity, according to economists.
"This is a real concern not just in the United States, but across the world," said Stephan Goetz, professor of agricultural economics and regional economics, Penn State, and director of the Northeast Regional Center for Rural Development. "Poor mental health can result in considerable economic costs, including losses of billions of dollars to lower productivity and this doesn't even include the staggering ...
2014-12-03
PHILADELPHIA--Quitting smoking sets off a series of changes in the brain that Penn Medicine researchers say may better identify smokers who will start smoking again--a prediction that goes above and beyond today's clinical or behavioral tools for assessing relapse risk.
Reporting in a new study published this week in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology, James Loughead, PhD, associate professor of Psychiatry, and Caryn Lerman, PhD, a professor of Psychiatry and director of Penn's Center for Interdisciplinary Research on Nicotine Addiction, found that smokers who relapsed ...
2014-12-03
Recent research from the Met Office and the University of East Anglia (UEA) suggests breaking the existing global and UK temperature records is much more likely due to human influence on the climate.
Early Figures Suggest Global Record Possible
The global mean temperature for January to October based on the HadCRUT4 dataset (compiled by the Met Office and UEA's Climatic Research Unit) is 0.57 °C (+/- 0.1) above the long-term (1961-1990) average. This is consistent with the statement from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) today.
With two months of data still ...
2014-12-03
Researchers at the Mechanobiology Institute at the National University of Singapore have comprehensively described the network of proteins involved in cell-cell adhesions, or the cadherin interactome. This work was published in Science Signaling (Guo et al. E-cadherin interactome complexity and robustness resolved by quantitative proteomics, Science Signaling, 02 Dec 2014, Vol 7, Issue 354).
Unlocking the complexity of cell adhesion
Many biological processes depend on the ability of cells to stick to one another. The formation of multicellular organisms and precise ...
2014-12-03
Plastic is well-known for sticking around in the environment for years without breaking down, contributing significantly to litter and landfills. But scientists have now discovered that bacteria from the guts of a worm known to munch on food packaging can degrade polyethylene, the most common plastic. Reported in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, the finding could lead to new ways to help get rid of the otherwise persistent waste, the scientists say.
Jun Yang and colleagues point out that the global plastics industry churns out about 140 million tons ...
2014-12-03
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the few cancers in which a continued increase in incidence has been observed over recent years. Globally, there are approximately 750,000 new cases of liver cancer reported each year. Importantly, population-based studies show that HCC ranks as the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Also, a large proportion of HCC patients display symptoms of intrahepatic metastases or postsurgical recurrence, with a five-year survival rate of around only 30-40%.
Among the various pathogenic factors, HBV infection accounts ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Taming neural excitations
A theoretical study of short- and long-range effects on neural excitation pulses might one day lead to controlling harmful signals such as those in strokes