A poisonous cure
2014-12-04
(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. - Take two poisonous mushrooms, and call me in the morning. While no doctor would ever write this prescription, toxic fungi may hold the secrets to tackling deadly diseases.
A team of Michigan State University scientists has discovered an enzyme that is the key to the lethal potency of poisonous mushrooms. The results, published in the current issue of the journal Chemistry and Biology, reveal the enzyme's ability to create the mushroom's molecules that harbor missile-like proficiency in attacking and annihilating a single vulnerable target in the human liver.
The team revealed how the enzyme contributes to the manufacture of chemical compounds known as cyclic peptides, a favorite type of molecule that pharmaceutical companies use to create new drugs. These findings could lead to single-minded medicines with zero side effects, said Jonathan Walton, professor of plant biology and co-lead author.
"Mushrooms are prolific chemical factories, yet only a few of their peptides are poisonous," he said. "These toxins survive the high temperatures of cooking and the acids of digestion, and yet they're readily absorbed by the bloodstream and go directly to their intended target. These are the exact qualities needed for an effective medicine."
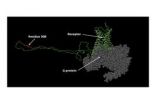
Walton published the paper with fellow MSU scientists Hong Luo, Sung-Yong Hong, R. Michael Sgambelluri and Evan Angelos. Working with the mushroom species Amanita, Walton and his teammates disassembled one of its poisonous peptides, which can be compared to a laser-guided missile with a nuclear warhead.
By removing the molecular equivalent of the deadly warhead, they now have a sturdy, precise delivery system that can supply medicine - rather than poison - to a single target. By taking a laser, rather than a shotgun approach, scientists could develop medicines capable of curing disease without the patient suffering any side effects.
The enzyme the team discovered is called POPB, and it converts toxins from their initial linear shape into cyclic peptides, fortress-like molecular circles comprising eight amino acids.
Harnessing the distinct properties of POPB will allow scientist to create billions of variant molecules, which can be tested against many different medical targets such as pathogenic bacteria and cancer.
"We've found some variables that are key," said Walton, an AgBioResearch scientist. "By making more variants, we can add or replace molecules that may or may not work. To date we've created a library of a hundred or so, and we eventually plan to create millions."
The challenge of the next stage of research, though, is testing the variants against diseases such as cancer. The bottleneck lies in the screening process. While Walton's team has discovered a missile capable of carrying a million different potential medicines, as of yet the payload that will be effective remains a mystery.
INFORMATION:
Xuan Li, at the Kunming University of Science and Technology (China), also contributed to the paper.
Walton's research is funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 150 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-04
Some National Football League (NFL) players have been seeking out unproven stem cell therapies to help accelerate recoveries from injuries, according to a new paper from Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy. While most players seem to receive treatment within the United States, several have traveled abroad for therapies unavailable domestically and may be unaware of the risks involved, the paper found.
The paper is published in the 2014 World Stem Cell Report, which is a special supplement to the journal Stem Cells and Development and is the official publication ...
2014-12-04
Today's smartphones are designed to entertain and are increasingly marketed to young adults as leisure devices. Not surprisingly, research suggests that young adults most often use their phones for entertainment purposes rather than for school or work.
With this in mind, three Kent State University researchers, Andrew Lepp, Ph.D., Jacob Barkley, Ph.D. and Jian Li, Ph.D., and a Kent State graduate student, Saba Salehi-Esfahani, surveyed a random sample of 454 college students to examine how different types of cell phone users experience daily leisure.
The trio from ...
2014-12-04
Boston, MA - A study published this week in Genetics in Medicine is the first to explore new parents' attitudes toward newborn genomic testing. The findings suggest that if newborn genomic testing becomes available, there would be robust interest among new parents, regardless of their demographic background.
The study, led by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) and Boston Children's Hospital, found that the majority of parents surveyed were interested in newborn genomic testing.
As next-generation whole-exome and genome sequencing is integrated into clinical ...
2014-12-04
TORONTO, Dec. 4, 2014 - Results from an ongoing survey conducted by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) show that 2.2 per cent of adults --or over 230,000 people in Ontario, Canada -- seriously contemplated suicide in the last year. The 2013 edition of the CAMH Monitor, released today, included questions about suicidal ideation for the first time in the survey's history.
"Suicide is a major public health issue, and these data confirm that large numbers of Ontario adults report having suicidal thoughts," said Dr. Hayley Hamilton, CAMH scientist and co-principal ...
2014-12-04
Insecticides aimed at controlling early-season crop pests, such as soil-dwelling grubs and maggots, can increase slug populations, thus reducing crop yields, according to researchers at Penn State and the University of South Florida.
"Neonicotinoids are the most widely used insecticides in the world," said Margaret Douglas, graduate student in entomology, Penn State. "Seed applications of neonicotinoids are often viewed as cheap insurance against pest problems, but our results suggest that they can sometimes worsen pest problems and should be used with care."
According ...
2014-12-04
GAINESVILLE, Fla. -- It's no secret that low-birth-weight babies face significantly greater risks for certain health problems early on, such as respiratory distress or infection. Now, a new study from researchers at the University of Florida and Northwestern University shows that lower weights at birth also have an adverse effect on children's performance in school, which is likely due to the early health struggles small babies often face.
Using a unique set of data that matched birth and school records from 1.6 million children born in Florida between 1992 and 2002, ...
2014-12-04
Nalmefene (trade name Selincro) has been approved since February 2013 for people with alcohol dependence who currently drink a lot of alcohol, but who do not have physical withdrawal symptoms and who do not require immediate detoxification. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether the drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy in this patient group.
According to the findings, such an added benefit is not proven: In its dossier, the drug manufacturer only presented data for ...
2014-12-04
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine reveals the role of a receptor protein derived from a gene that has been linked to human growth. Co-author Stefano Costanzi, Ph.D., an assistant professor of biochemistry at American University, developed the three-dimensional computer model of the receptor that appears in the study.
"As the study reveals the receptor's role in growth, it may ultimately lead to the development of drugs to treat those affected with conditions that alter growth, such as gigantism or dwarfism," Costanzi said. "The construction of the ...
2014-12-04
The intermittent light emitted by pulsars, the most precise timekeepers in the universe, allows scientists to verify Einstein's theory of relativity, especially when these objects are paired up with another neutron star or white dwarf that interferes with their gravity. However, this theory could be analysed much more effectively if a pulsar with a black hole were found, except in two particular cases, according to researchers from Spain and India.
Pulsars are very dense neutron stars that are the size of a city (their radius approaches ten kilometres), which, like lighthouses ...
2014-12-04
A University of Texas at Dallas professor applied robot control theory to enable powered prosthetics to dynamically respond to the wearer's environment and help amputees walk.
In research available online and in an upcoming print issue of IEEE Transactions on Robotics, wearers of the robotic leg could walk on a moving treadmill almost as fast as an able-bodied person.
"We borrowed from robot control theory to create a simple, effective new way to analyze the human gait cycle," said Dr. Robert Gregg, a faculty member in the Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A poisonous cure