(Press-News.org) A University of Texas at Dallas professor applied robot control theory to enable powered prosthetics to dynamically respond to the wearer's environment and help amputees walk.
In research available online and in an upcoming print issue of IEEE Transactions on Robotics, wearers of the robotic leg could walk on a moving treadmill almost as fast as an able-bodied person.
"We borrowed from robot control theory to create a simple, effective new way to analyze the human gait cycle," said Dr. Robert Gregg, a faculty member in the Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science and lead author of the paper. "Our approach resulted in a method for controlling powered prostheses for amputees to help them move in a more stable, natural way than current prostheses."
Humanoid robots can walk, run, jump and climb stairs autonomously, but modern prosthetics limit similar actions in humans. While prosthetics have been made lighter and more flexible, they fail to mimic the power generated from human muscles in able-bodied individuals. Powered prostheses, or robotic legs, have motors to generate force, but lack the intelligence to stably respond to disturbances or changing terrain.
Control engineers view the human gait cycle through the lens of time -- the interval at which each movement in the walking cycle needs to occur. Gregg, an assistant professor of bioengineering and mechanical engineering, proposed a new way to view and study the process of human walking: measuring a single variable that represents the motion of the body. In this study, that variable was the center of pressure on the foot, which moves from heel to toe through the gait cycle.
"The gait cycle is a complicated phenomenon with lots of joints and muscles working together," Gregg said. "We used advanced mathematical theorems to simplify the entire gait cycle down to one variable. If you measure that variable, you know exactly where you are in the gait cycle and exactly what you should be doing."
Gregg first tested his theory on computer models, and then with three above-knee amputee participants at the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago, an affiliate of Northwestern University. He implemented his algorithms with sensors measuring the center of pressure on a powered prosthesis. Inputted with only the user's height, weight and dimension of the residual thigh into his algorithm, the prosthesis was configured for each subject in about 15 minutes. Subjects then walked on the ground and on a treadmill moving at increasing speeds.
"We did not tell the prosthesis that the treadmill speed was increasing. The prosthesis responded naturally just as the biological leg would do," Gregg said.
The participants were able to move at speeds of more than 1 meter per second; the typical walking speed of fully able-bodied people is about 1.3 meters per second, Gregg said. The participants also reported exerting less energy than with their traditional prostheses.
Gregg said current powered prosthetic devices require a team of physical rehabilitation specialists spending significant amounts of time tuning hundreds of knobs and training each powered leg to the individual wearer.
"Our approach unified multiple modes of operation into one and resulted in technology that could help people in the future," he said. "That and the feedback from participants were very rewarding."
Gregg said the next step in the research will be to compare results of experiments with robotic legs using both the time paradigm and center of pressure paradigm.
INFORMATION:
Researchers from the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago, Northwestern University and the University of New Brunswick were also involved in the study.
The work was funded by the United States Army Medical Research Acquisition Activity, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund and the National Institutes of Health through the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. END
New Rochelle, NY, December 4, 2014--Recommendations by physician groups to avoid bedsharing among mothers and their babies are intended to reduce sleep-related infant deaths. But evidence suggests that the risks of bedsharing have been over-emphasized, advice never to bedshare is unrealistic, and avoiding bedsharing may interfere with breastfeeding, according to an article in Breastfeeding Medicine, the official journal of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Breastfeeding Medicine website ...
New genetic research reveals that a small group of hunger-gatherers now living in Southern Africa once was so large that it comprised the majority of living humans during most of the past 150,000 years. Only during the last 22,000 years have the other African ethnicities, including the ones giving rise to Europeans and Asians, become vastly most numerous. Now the Khoisan (who sometimes call themselves Bushmen) number about 100,000 individuals, while the rest of humanity numbers 7 billion. Their lives and ways have remained unaltered for hundreds of generations, with only ...
SEATTLE--Pragmatic clinical trials--real-life tests done in real-world settings--are increasingly important for answering pressing questions about how best to deliver health care. But these pragmatic trials require close collaboration between two professional groups who often have contrasting styles. One group is researchers, who follow structure like classical musicians. The other is and health care providers and administrators, who may need to improvise like jazz musicians. How in the world can such disparate players make beautiful music together?
"The key is not just ...
MAYWOOD, Il. - Medical schools have an ethical obligation to change admission policies in order to accept applications from undocumented immigrants known as Dreamers, according to an article in the December, 2014 issue of the journal Academic Medicine.
Not allowing Dreamers to apply to medical school "represents a kind of unjustified discrimination and violates the basic ethical principle of the equality of human beings," write co-authors Mark G. Kuczewski, PhD and Linda Brubaker, MD, MS of Loyola University Chicago Stritch of Medicine. Academic Medicine is the journal ...
Taking inspiration from nature, researchers have created a versatile model to predict how stalagmite-like structures form in nuclear processing plants - as well as how lime scale builds up in kettles.
"It's a wonderful example of how complex mathematical models can have everyday applications," said Dr Duncan Borman, from the School of Civil Engineering at the University of Leeds, a co-author of the study.
The main aim of the research, which is published in print today in the journal Computers & Chemical Engineering, is to reduce the number of potentially harmful manual ...
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Penn State University in the United States have successfully discovered one of modern human's ancient lineages through the sequencing of genes.
World-renowned geneticist from NTU, Professor Stephan Christoph Schuster, who led an international research team from Singapore, United States and Brazil, said this is the first time that the history of mankind populations has been analysed and matched to Earth's climatic conditions over the last 200,000 years.
Their breakthrough findings are published today ...
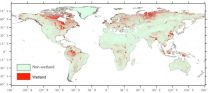
Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth. Yet with increasing urbanization and agricultural expansion, wetlands around the globe are in danger. Better mapping of wetlands worldwide will help in their protection.
But compiling globe-spanning maps of wetlands is impeded by the dramatic diversity and evolving dynamics of wetlands, and by myriad difficulties in doing field work.
To develop a better model, Gong Peng and other scientists at the State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing incorporated hydrologic, ...
A natural substance present in red wine, resveratrol, inhibits the formation of inflammatory factors that trigger cardiovascular diseases. This has been established by a research team at the Department of Pharmacology of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz (JGU) working in collaboration with researchers of the Friedrich Schiller University in Jena and the University of Vienna. Their results have recently been published in the scientific journal Nucleic Acids Research.
Despite the fact that they eat more fatty foods, the French tend ...
When you go to bed, and how long you sleep at a time, might actually make it difficult for you to stop worrying. So say Jacob Nota and Meredith Coles of Binghamton University in the US, who found that people who sleep for shorter periods of time and go to bed very late at night are often overwhelmed with more negative thoughts than those who keep more regular sleeping hours. The findings appear in Springer's journal Cognitive Therapy and Research.
People are said to have repetitive negative thinking when they have bothersome pessimistic thoughts that seem to repeat in ...
This news release is available in German.
In quantum optics, generating entangled and spatially separated photon pairs (e.g. for quantum cryptography) is already a reality. So far, it has, however, not been possible to demonstrate an analogous generation and spatial separation of entangled electron pairs in solids. Physicists from Leibniz University Hannover and from the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) have now taken a decisive step in this direction. They have demonstrated for the first time the on-demand emission of electron pairs from a semiconductor ...