(Press-News.org) MAYWOOD, Il. - Medical schools have an ethical obligation to change admission policies in order to accept applications from undocumented immigrants known as Dreamers, according to an article in the December, 2014 issue of the journal Academic Medicine.
Not allowing Dreamers to apply to medical school "represents a kind of unjustified discrimination and violates the basic ethical principle of the equality of human beings," write co-authors Mark G. Kuczewski, PhD and Linda Brubaker, MD, MS of Loyola University Chicago Stritch of Medicine. Academic Medicine is the journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
In 2012, Loyola became the first medical school in the United States to amend its admissions policies to include qualified students who have received Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) status and are legally recognized as U.S. residents. In August, 2014, Loyola welcomed seven Dreamers to the class of 2018.
The students are known as Dreamers after a proposed federal law called the DREAM Act (Development, Relief and Education of Alien Minors). Although the DREAM Act has yet to become law, the DACA program makes medical training, licensure and medical practice feasible, Drs. Kuczewski and Brubaker write.
The authors write that three main ethical principles and policy considerations support Dreamers' eligibility:
"First, a belief in equality, perhaps the fundamental value in contemporary democratic society, means that these potential applicants must be considered - just like others - on their merits. Second, the medical profession's duty of beneficence, the obligation to help patients, means that medical schools cannot turn away a significant pool of diverse talent in developing the physician workforce. Third, and related to beneficence, the value of social justice requires that medical schools seek to produce a physician workforce that better serves those communities that have been traditionally underserved, such as ethnic minorities and recent immigrants."
Social justice means enabling the participation of all - Dreamers, recent immigrants, minorities, U.S. citizens - in the life and opportunities of the community to the extent possible. "Enabling qualified Dreamers to become physicians is therefore an ethical obligation of the medical education community."
To be eligible for DACA status, an applicant must be between the ages of 16 and 31; must have arrived in the United States before age 16; have resided continuously in the U.S. for at least five years; be currently enrolled in school, have completed high school or earned a GED; have no serious criminal involvement; and be able to prove he or she was in the U.S. on June 15, 2012.
The DACA program was created by the Obama administration and is subject to change by a future president, Drs. Kuczewski and Brubaker write. "Our duty to serve the communities our institutions serve requires that we steward the resources available including the talent of Dreamers. It is time to make the dream a reality."
INFORMATION:
Dr. Kuczewski is the Fr. Michael I. English Professor of Medical Ethics, director of the Neiswanger Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy and chair of the Department of Medical Education of Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine.
Dr. Brubaker is dean and chief diversity officer and professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine.
Their article is titled "Medical Education for 'Dreamers': Barriers and Opportunities for Undocumented Immigrants." Here is a link to the article:
http://journals.lww.com/academicmedicine/Fulltext/2014/12000/Medical_Education_for__Dreamers____Barriers_and.13.aspx
Taking inspiration from nature, researchers have created a versatile model to predict how stalagmite-like structures form in nuclear processing plants - as well as how lime scale builds up in kettles.
"It's a wonderful example of how complex mathematical models can have everyday applications," said Dr Duncan Borman, from the School of Civil Engineering at the University of Leeds, a co-author of the study.
The main aim of the research, which is published in print today in the journal Computers & Chemical Engineering, is to reduce the number of potentially harmful manual ...
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Penn State University in the United States have successfully discovered one of modern human's ancient lineages through the sequencing of genes.
World-renowned geneticist from NTU, Professor Stephan Christoph Schuster, who led an international research team from Singapore, United States and Brazil, said this is the first time that the history of mankind populations has been analysed and matched to Earth's climatic conditions over the last 200,000 years.
Their breakthrough findings are published today ...
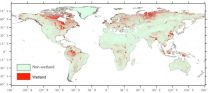
Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth. Yet with increasing urbanization and agricultural expansion, wetlands around the globe are in danger. Better mapping of wetlands worldwide will help in their protection.
But compiling globe-spanning maps of wetlands is impeded by the dramatic diversity and evolving dynamics of wetlands, and by myriad difficulties in doing field work.
To develop a better model, Gong Peng and other scientists at the State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing incorporated hydrologic, ...
A natural substance present in red wine, resveratrol, inhibits the formation of inflammatory factors that trigger cardiovascular diseases. This has been established by a research team at the Department of Pharmacology of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz (JGU) working in collaboration with researchers of the Friedrich Schiller University in Jena and the University of Vienna. Their results have recently been published in the scientific journal Nucleic Acids Research.
Despite the fact that they eat more fatty foods, the French tend ...
When you go to bed, and how long you sleep at a time, might actually make it difficult for you to stop worrying. So say Jacob Nota and Meredith Coles of Binghamton University in the US, who found that people who sleep for shorter periods of time and go to bed very late at night are often overwhelmed with more negative thoughts than those who keep more regular sleeping hours. The findings appear in Springer's journal Cognitive Therapy and Research.
People are said to have repetitive negative thinking when they have bothersome pessimistic thoughts that seem to repeat in ...
This news release is available in German.
In quantum optics, generating entangled and spatially separated photon pairs (e.g. for quantum cryptography) is already a reality. So far, it has, however, not been possible to demonstrate an analogous generation and spatial separation of entangled electron pairs in solids. Physicists from Leibniz University Hannover and from the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) have now taken a decisive step in this direction. They have demonstrated for the first time the on-demand emission of electron pairs from a semiconductor ...
Some patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have changes in the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene, which can drive the development of their cancer. A drug recently developed by Pfizer, crizotinib, targets ALK and is currently given to patients with ALK positive lung cancer when their cancer has worsened after initial chemotherapy. Now doctors have investigated the use of crizotinib in patients with ALK positive lung cancer who have not yet received any chemotherapy treatment.
Dr Fiona Blackhall, a senior lecturer in The University of Manchester's Institute ...
New York | Heidelberg, 4 December 2014 Studying the motion of electrons in a disordered environment is no simple task. Often, understanding such effects requires a quantum simulator designed to expose them in a different physical setup. This was precisely the approach adopted by Denis Makarov and Leonid Kon'kov from the Victor I. Il'ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute in Vladivostok in a new study published in EPJ B. They relied on a simulator of electronic motion subjected to noise stemming from a flux of sound waves.
Their findings could lead to semi-conductor devices ...
A new, innovative "dashboard" from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) won't help you drive your car, but it will help enable reproducible research in biology.
In a recent paper in the journal Nature Communications,* an international multi-laboratory team demonstrates a new software tool, the "erccdashboard," to evaluate the performance of experimental methods used to study gene expression. The analysis tool is designed for use with RNA spike-in controls developed by the NIST-hosted External RNA Controls Consortium (ERCC**). These ERCC controls are ...
Scientists from the Institute of Zoology with the Chinese Academy of Sciences have devoted years of their careers to study the astounding diversity hidden in the depths of the Xishuangbanna tropical rain forests. In a recent paper published in the open access journal ZooKeys Prof. Shuqiang Li and his team reveal 30 new spider species, which constitutes a minor share of what is yet to be found in this biodiversity hotspot.
Xishuangbanna is situated in the southern part of Yunnan with the Lancang (Mekong) River flowing through it. The region is well-known for its rich biodiversity ...